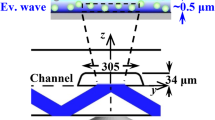
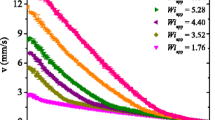
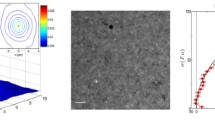
Abstract
“Banded structures” of macroscopic dimensions can be induced by simple shear flow in many different types of soft matter systems. Depending on whether these bands extend along the gradient or vorticity direction, the banding transition is referred to as “gradient banding” or “vorticity banding,” respectively. The main features of gradient banding can be understood on the basis of a relatively simple constitutive equation. This minimal model for gradient banding will be discussed in some detail, and its predictions are shown to explain many of the experimentally observed features. The minimal model assumes a decrease of the shear stress of the homogeneously sheared system with increasing shear rate within a certain shear-rate interval. The possible microscopic origin of the severe shear-thinning behaviour that is necessary for the resulting nonmonotonic flow curves is discussed for a few particular systems. Deviations between experimental observations and predictions by the minimal model are due to obvious simplifications within the scope of the minimal model. The most serious simplifications are the neglect of concentration dependence of the shear stress (or on other degrees of freedom) and of the elastic contributions to the stress, normal stresses, and the possibility of shear-induced phase transitions. The consequences of coupling of stress and concentration will be analyzed in some detail. In contrast to predictions of the minimal model, when coupling to concentration is important, a flow instability can occur that does not require strong shear thinning. Gradient banding is sometimes also observed in glassy- and gel-like systems, as well as in shear-thickening systems. Possible mechanisms that could be at the origin of gradient-band formation in such systems are discussed. Gradient banding can also occur in strongly entangled polymeric systems. Banding in these systems is discussed on the basis of computer simulations. Vorticity banding is less well understood and less extensively investigated experimentally as compared to gradient banding. Possible scenarios that are at the origin of vorticity banding will be discussed. Among other systems, the observed vorticity-banding transition in rod-like colloids is discussed in some detail. It is argued, on the basis of experimental observations for these colloidal systems, that the vorticity-banding instability for such colloidal suspensions is probably related to an elastic instability, reminiscent of the Weissenberg effect in polymeric systems. This mechanism might explain vorticity banding in discontinuously shear-thickening systems and could be at work in other vorticity-banding systems as well. This overview does not include time-dependent phenomena like oscillations and chaotic behaviour.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajdari A (1998) Rheological behavior of a solution of particles aggregating on the containing walls. Phys Rev E 58:6294–6298
Berret J-F (2005) Molecular gels. In: Weiss RG, Terech P (eds) Rheology of wormlike micelles: equilibrium properties and shear banding transition. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 235–275
Berret J-F, Porte G (1999) Metastable versus unstable transients at the onset of a shear-induced phase transition. Phys Rev E 60:4268–4271
Berret J-F, Porte G, Decruppe J-P (1997) Inhomogeneous shear flows of wormlike micelles: a master dynamic phase diagram. Phys Rev E 55:1668–1676
Berret J-F, Roux DC, Lindner P (1998) Structure and rheology of concentrated wormlike micelles at the shear-induced isotropic-to-nematic transition. Eur Phys J B 5:67–77
Berret J-F, Gamez-Corrales R, Lerouge S, Decruppe J-P (2000) Shear thickening transition in surfactant solutions: new experimental features from rheology and flow birefringence. Eur Phys J E 2:343–350
Berret J-F, Gamez-Corrales R, Séréro Y, Molino F, Lindner P (2001) Shear-induced micellar growth in dilute surfactant solutions. Europhys Lett 54:605–611
Berret J-F, Lerouge S, Decruppe J-P (2002) Kinetics of shear-thickening transitions observed in dilute surfactant solutions and investigated by flow birefringence. Langmuir 18:7279–7286
Boltenhage P, Hu YT, Matthys EF, Pine DJ (1997a) Observation of bulk phase separation and coexistence in a sheared micellar solution. Phys Rev Lett 79:2359–2362
Boltenhage P, Hu Y, Matthys EF, Pine DJ (1997b) Inhomogeneous structure formation and shear-thickening in worm-like micellar solutions. Europhys Lett 38:389–394
Bonn D, Meunier J, Greffier O, Al-Kahwaji A, Kellay H (1998) Bistability in non-Newtonian flow: rheology and lyotropic liquid crystals. Phys Rev E 58:2115–2118
Briels WJ, Mulder P, den Otter WK (2004) Simulations of elementary processes in entangled wormlike micelles under tension: a kinetic pathway to Y-junctions and shear induced structures. J Phys Condens Matter 16:S3965–S3974
Britton MM, Callaghan PT (1997a) Nuclear magnetic resonance visualization of anomalous flow in cone-and-plate rheometry. J Rheol 6:1365–1384
Britton MM, Callaghan PT (1997b) Two-phase shear band structures at uniform stress. Phys Rev Lett 78:4930–4933
Britton MM, Callaghan PT (1999) Shear banding instability in wormlike micellar solutions. Eur Phys J B7:237–249
Britton MM, Mair RW, Lambert RK, Callaghan PT (1999) Transition to shear banding in pipe and Couette flow of wormlike micellar solutions. J Rheol 43:897–909
Butler S, Harrowell P (2002) Factors determining crystal-liquid coexistence under shear. Nature 415:1008–1011
Cahn JW, Hilliard JE (1958) Free energy of a nonuniform system. I. Interfacial free energy. J Chem Phys 28:258–267
Cahn JW, Hilliard JE (1959) Free energy of a nonuniform system. III. Nucleation in a two- component incompressible fluid. J Chem Phys 31:688–699
Callaghan PT (1999) Rheo-NMR: nuclear magnetic resonance and the rheology of complex fluids. Rep Prog Phys 62:599–670
Callaghan PT, Gil AM (2000) Rheo-NMR of semidilute polyacrylamide in water. Macro-molecules 33:4116–4124
Cappelaere E, Berret J-F, Decruppe J-P, Cressely R, Lindner P (1997) Rheology, birefringence and small-angle neutron scattering in a charged micellar system: evidence of a shear-induced phase transition. Pys Rev E 56:1869–1878
Cates ME, Candau SJ (2001) Ring-driven shear thickening in wormlike micelles? Europhys Lett 55:887–893
Cates ME, Fielding SM (2006) Rheology of giant micelles. Adv Phys 55:799–879
Cates ME, McLeish TCB, Marrucci G (1993) The rheology of entangled polymers at very high shear rates. Europhys Lett 21:451–456
Chen LB, Zukoski CF, Ackerson BJ, Hanley HJM, Straty GC, Barker J, Glinka CJ (1992) Structural changes and orientational order in a sheared colloidal suspension. Phys Rev Lett 69:688–691
Cloitre M, Borrega R, Monti F, Leibler L (2003) Glassy dynamics and flow properties of soft colloidal particles. Phys Rev Lett 90:068303–1–068303-4
Coussot P, Raynaud JS, Bertrand F, Moucheront P, Guilbaud JP, Huynh HT, Jarny S, Lesueur D (2002) Coexistence of liquid and solid phases in flowing soft-glassy materials. Phys Rev Lett 88:218301–1–218301-4
Decruppe JP, Cappelaere E, Cressely R (1997) Optical and rheological properties of a semi-dilute equimolar solution of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide and potassium bromide. J Phys II France 5:257–270
Decruppe J-P, Lerouge S, Berret J-F (2001) Insight in shear banding under transient flow. Phys Rev E 63:022501–1–022501-4
Dehmoune J, Decruppe J-P, Greffier O, Xu H (2007) Rheometric and rheo-optical investigation on the effect of the aliphatic chain length of the surfactant on the shear thickening of dilute worm-like micellar solutions. Rheol Acta 46:1121–1129
Dhont JKG (1996) Spinodal decomposition of colloids in the initial and intermediate stages. J Chem Phys 105:5112–5125
Dhont JKG (1999) A constitutive relation describing the shear-banding transition. Phys Rev E 60:4534–4544
Dhont JKG, Briels WJ (2002) Stresses in inhomogeneous suspensions. J Chem Phys 117:3992–3999
Dhont JKG, Briels WJ (2003a) Festschrift on the occasion of the 60th birthday of C.G. de Kruif, Viscoelasticity of suspensions of long, rigid rods. Coll Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects 213:131–156
Dhont JKG, Briels WJ (2003b) Inhomogeneous suspensions of rigid rods in flow. J Chem Phys 118:1466–1478
Dhont JKG, Briels WJ (2006) Soft matter. In: Gompper G, Schick M (eds) Chapter 3: Rod-like Brownian particles in shear flow. Wiley–VCH, Weinheim, pp 147–283
Dhont JKG, Lettinga MP, Dogic Z, Lenstra TAJ, Wang H, Rathgeber S, Carletto P, Willner L, Frielinghaus H, Lindner P (2003) Shear-banding and microstructure of colloids in shear flow. Faraday Disscuss 123:157–172
Eiser E, Molino F, Porte G (2000a) Nonhomogeneous textures and banded flow in a soft cubic phase under shear. Pys Rev E 61:6759–6764
Eiser E, Molino F, Porte G, Pithon X (2000b) Flow in micellar cubic crystals. Rheol Acta 39:201–206
El-Kareh AW, Leal LG (1989) Existence of solutions for all Deborah numbers for a non-Newtonian model modified to include diffusion. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 33:257–287
Fielding SM (2007a) Complex dynamics of shear banded flows. Soft Matter 3:1262–1279
Fielding SM (2007b) Vorticity structuring and velocity rolls triggered by gradient shear bands. Phys Rev E 76:016311–1–016311-8
Fielding SM, Olmsted PD (2003a) Early stage kinetics in a unified model of shear-induced demixing and mechanical shear banding instabilities. Phys Rev Lett 22:224501–1–224501-4
Fielding SM, Olmsted PD (2003b) Kinetics of the shear banding instability in startup flows. Phys Rev E 68:036313–036333
Fielding SM, Olmsted PD (2003c) Flow phase diagrams for concentration-coupled shear banding. Eur Phys J E 11:65–83
Fielding SM, Olmsted PD (2004) Spatiotemporal oscillations and rheochaos in a simple model of shear banding. Phys Rev Lett 92:084502–1–084502-4
Fischer E, Callaghan PT (2000) Is a birefringence band a shear band? Europhys Lett 50:803–809
Fischer E, Callaghan PT (2001) Shear banding and the isotropic-to-nematic transition in wormlike micelles. Phys Rev E 64:011501–1–011501-15
Fischer P, Wheeler EK, Fuller GG (2002) Shear-banding structure oriented in the vorticity direction observed for equimolar micellar solution. Rheol Acta 41:35–44
Frank M, Anderson D, Weeks ER, Morris JF (2003) Particle migration in pressure-driven flow of a Brownian suspension. J Fluid Mech 493:363–378
Georgiou GC, Vlassopoulos D (1998) On the stability of the simple shear flow of a Johnson–Segalman fluid. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 75:77–97
Goddard JD (2003) Material instability in complex fluids. Ann Rev Fluid Mech 35:113–133
Goveas JL, Olmsted PD (2001) A minimal model for vorticity and gradient banding in complex fluids. Eur Phys J E 6:79–89
Grady DE (1994) Dissipation in adiabatic shear bands. Mech Mater 17:289–293
Grizzuti N, Maffetone PL (2003) Quiescent and flow-induced transitional behaviour of hydroxypropylcellulose solutions. J Chem Phys 118:5195–5200
Groisman A, Steinberg V (1998) Mechanism of elastic instability in Couette flow of polymer solutions: experiment. Phys Fluids 10:2451–2463
Head DA, Ajdari A, Cates ME (2001) Jamming, hysteresis, and oscillation in scalar models for shear thickening. Phys Rev E 64:061509–1–06509-16
Herle V, Fischer P, Windhab EJ (2005) Stress driven sgear bands and the effect of confinement on their structures—a rheological, flow visualization and rheo-SALS study. Langmuir 21:9051–9057
Holmes CB, Fuchs M, Cates ME (2003) Jamming transitions in a schematic model of suspension rheology. Europhys Lett 63:240
Holmes WM, Callaghan PT, Vlassopoulos D, Roovers J (2004) Shear banding phenomena in ultrasoft colloidal glasses. J Rheol 48:1085–1102
Hu YT, Lips A (2005) Kinetics and mechanism of shear banding in an entangled micellar solution. J Rheol 49:1001–1027
Hu YT, Boltenhagen P, Pine DJ (1998a) Shear thickening in low-concentration solutions of wormlike micelles. I. Direct visualization of transient behavior and phase transitions. J Rheol 42:1185–1208
Hu YT, Boltenhagen P, Pine DJ (1998b) Shear thickening in low-concentration solutions of wormlike micelles. II. Slip, fracture, and stability of the shear-induced phase. J Rheol 42:1209–1226
Hu H, Larson RG, Magda JJ (2002) Measurement of wall-slip-layer rheology in shear-thickening wormy micelle solutions. J Rheol 46:1001–1021
Imhof A, van Blaaderen A, Dhont JKG (1994) Shear melting of colloidal crystals of charged spheres studied with rheology and polarizing microscopy. Langmuir 10:3477–3484
Kang K, Lettinga MP, Dogic Z, Dhont JKG (2006) Vorticity banding in rodlike virus suspensions. Phys Rev E 74:026307–1–026307-12
Kumar S, Larson RG (2000) Shear banding and secondary flow in viscoelastic fluids between a cone and plate. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 95:295–314
Larson RG, Shaqfeh ESG, Muller SJ (1990) A purely elastic instability in Taylor–Couette flow. J Fluid Mech 218:573–600
Lenstra TAJ (2001) Dissertation: colloids near phase transition lines under shear. Utrecht University
Lenstra TAJ, Dhont JKG (2001) Shear-induced displacement of isotropic-nematic spinodals. J Chem Phys 114:10151–10162
Lerouge S, Decruppe JP, Humbert C (1998) Shear banding in a micellar solution under transient flow. Phys Rev Lett 81:5457–5460
Lerouge S, Decruppe J-P, Berret J-P (2000) Correlations between rheological and optical properties of a micellar solution under shear banding flow. Langmuir 16:6464–6474
Lerouge S, Argentina M, Decruppe JP (2006) Interface instability in shear-banding flows. Phys Rev Lett 96:088301–1–088301-4
Liberato MW, Nettesheim F, Wagner NJ (2006) Spatially resolved small-angle neutron scattering in the 1–2 plane: a study of shear-induced phase-separating wormlike micelles. Phys Rev E 73:020504–1–020504-4
Lin-Gibson S, Pathak JA, Grulke EA, Wang H, Hobbie EK (2004) Elastic flow instability in nanotube suspensions. Phys Rev Lett 92:048302–1–048302-4
Lu C-YD, Olmsted PD, Ball RC (2000) Effects of non-local stress on the determination of shear banding flow. Phys Rev Lett 84:642–645
Manneville S, Salmon J-B, Colin A (2004a) A spatio-temporal study of rheo-oscillations in a sheared lamellar phase using ultrasound. Eur Phys J E Soft Matter 13:197–212
Manneville S, Becu L, Colin A (2004b) High-frequency ultrasonic speckle velocimetry in sheared complex fluids. Eur Phys J AP 28:361–373
Manneville S, Colin A, Waton G, Schosseler F (2007) Wall slip, shear banding, and instability in the flow of a triblock copolymer micellar solution. Phys Rev E 75:061502–1–061502-11
Masselon C, Salmon J-P, Colin A (2008) Non-local effects in flows of wormlike micellar solutions. Phys Rev Lett (in press)
Mather PT, Romo-Uribe A, Han CD, Kim SS (1997) Rheo-optical evidence of a flow-induced isotropic-nematic transition in a thermotropic liquid-crystalline polymer. Macromolecules 30:7977–7989
McLeish TCB (1987) Stability of the interface between two dynamic phases in capillary flow in linear polymer melts. J Polym Sci 25:2253–2264
McLeish TCB, Ball RC (1986) A molecular approach to the spurt effect in polymer melt flow. J Polym Sci 24:1735–1745
Michel E, Appell J, Molino F, Kieffer J, Porte G (2001) Unstable flow and nonmonotonic flow curves of transient networks. J Rheol 45:1465–1477
Miller E, Rothstein JP (2007) Transient evolution of shear-banding wormlike micellar solutions. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 143:22–37
Molino F, Appell J, Filali M, Michel E, Porte G, Mora S, Sunyer E (2000) A transient network of telechelic polymers and microspheres: structure and rheology. J Phys Condens Matter 12:A491–A497
Muller SJ, Larson RG, Shaqfeh ESG (1989) A purely elastic transition in Taylor–Couette flow. Rheol Acta 28:499–503
Münch Ch, Hoffmann H, Ibel K, Kalus J, Neubauer G, Schmelzer U, Selbach J (1993) Transient small-angle neutron scattering experiments on micellar solutions with a shear-induced structural transition. J Phys Chem 97:4514–4522
Olmsted PD (1999a) Dynamics and flow-induced separation in polymeric fluids. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 4:95–100
Olmsted PD (1999b) Two-state shear diagrams for complex fluids in shear flow. Europhys Lett 48:339–345
Olmsted PD, Goldbart PM (1992) Isotropic-nematic transition in shear flow: state selection, coexistence, phase transitions, and critical behaviour. Phys Rev A 46:4966–4993
Olmsted PD, Lu C-YD (1997) Coexistence and phase separation in sheared complex fluids. Phys Rev E 56:R55–R58
Olmsted PD, Lu C-YD (1999a) Phase coexistence of complex fluids in shear flow. Faraday Discuss 112:183–194
Olmsted PD, Lu C-YD (1999b) Phase separation of rigid-rod suspensions in shear flow. Phys Rev E 60:4397–4415
Olmsted PD, Radulescu O, Lu C-YD (2000) Johnson–Segalman model with a diffusion term in cylindrical Couette flow. J Rheol 44:257–275
Pakdel P, McKinley GH (1996) Elastic instability and curved streamlines. Phys Rev Lett 77:2459–2462
Palberg T, Würth M (1996) Multiphase coexistence and non-linear rheology of colloidal dispersions as observed in an optical model capillary viscosimeter. J Phys I (France) 6:237–244
Picard G, Ajdari A, Bocquet L, Lequeux F (2002) A simple model for heterogeneous flows of yield stress fluids. Phys Rev E 66:051501–1–051501-12
Pignon F, Magnin A, Piau J-M (1996) Thixotropic colloidal suspensions and flow curves with minimum: identification of flow regimes and rheometric consequences. J Rheol 40:573–587
Porte G, Berret J-F, Harden JL (1997) Inhomogeneous flows of complex fluids: mechanical instability versus non-equilibrium phase transition. J Phys II France 7:459–472
Preis T, Biehl R, Palberg T (1998) Phase transitions in colloidal dispersions flowing through a cylindrical capillary. Prog Colloid Polym Sci 110:129–133
Pujolle-Robic C, Olmsted PD, Noirez L (2002) Transient and stationary flow behaviour of side chain liquid-crystalline polymers: evidence of a shear-induced isotropic-to-nematic phase transition. Eutophys Lett 59:364–369
Radulescu O, Olmsted PD, Lu C-YD (1999) Shear banding in reaction-diffusion models. Rheol Acta 38:606–613
Radulescu O, Olmsted PD, Decruppe JP, Lerouge S, Berret J-F, Porte G (2003) Time scales in shear banding of wormlike micelles. Europhys Lett 62:230–236
Ramos L, Molino F, Porte G (2000) Shear melting in lyotropic hexagonal phases. Langmuir 16:5846–5848
Rofe CJ, de Vargas L, Perez-González J, Lambert RK, Callaghan PT (1996) Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of apparent slip effects in xanthan solutions. J Rheol 40:1115–1128
Roux D, Nallet F, Diat O (1993) Rheology of lyotropic lamellar phases. Europhys Lett 24:53–58
Salmon J-P, Colin A, Manneville S, Molino F (2003a) Velocity profiles in shear-banding worm-like micelles. Phys Rev Lett 90:228303–1–228303-4
Salmon J-B, Becu L, Manneville S, Colin A (2003b) Towards local rheology of emulsions under Couette flow using dynamic light scattering. Eur Phys J E 10:209–221
Salmon J-B, Manneville S, Colin A (2003c) Shear-banding in a lyotropic lamellar phase. Part 1: Time-averaged velocity profiles. Phys Rev E 68:051503
Salmon J-B, Manneville S, Colin A (2003d) Shear-banding in a lyotropic lamellar phase. Part 2: Temporal fluctuations. Phys Rev E 68:051504
Salmon J-B, Manneville S, Colin A, Pouligny B (2003e) An optical fiber based interferometer to measure velocity profiles in sheared complex fluids. Eur Phys J AP 22:143–154
Schmitt V, Lequeux F, Pousse A, Roux D (1994) Flow behaviour and shear induced transition near an isotropic/nematic transition in equilibrium polymers. Langmuir 10:955–961
Schmitt V, Marques CM, Lequeux F (1995) Shear-induced phase separation of complex fluids: the role of flow-concentration coupling. Phys Rev E 52:4009–4015
Shaqfeh ESG (1996) Purely elastic instabilities in viscometric flows. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 28:129–185
Shaqfeh ESG, Muller SJ, Larson RG (1992) The effects of gap width and dilute solution properties on the viscoelastic Taylor–Couette instability. J Fluid Mech 235:285–317
Sollich P (1998) Rheological constitutive equation for a model of soft glassy materials. Phys Rev E 58:738–759
Sollich P, Lequeux F, Hébraud P, Cates ME (1997) Rheology of soft materials. Phys Rev Lett 78:2020–2023
Spenley NA, Cates ME, McLeish TCB (1993) Nonlinear rheology of wormlike micelles. Phys Rev Lett 71:939–942
Spenley NA, Yuan XF, Cates ME (1996) Nonmonotonic constitutive laws and the formation of shear-banded flows. J Phys II (France) 6:551–571
Stiakakis E, Vlassopoulos D, Loppinet B, Roovers J, Meier G (2002) Kinetic arrest of crowded soft spheres in solvents of varying quality. Phys Rev E 66:051804–1–051804-9
Tao Y-G, den Otter WK, Dhont JKG, Briels WJ (2006) Isotropic-nematic spinodals of rigid, long thin rod-like colloids by event-driven Brownian dynamics simulations. J Chem Phys 124:134906–1–134906-10
Tapadia P, Ravindranath S, Wang S-Q (2006) Banding in entangled polymer fluids under oscillatory shearing. Phys Rev Lett 96:19600–1–19600-4
ten Brinke AJW, Bailey L, Lekkerkerker HNW, Maitland GC (2007) Rheology modification in mixed shape colloidal dispersions. Part I: Pure components. Soft Matter 3:1145–1162
van den Noort A, Briels WJ (2008) Coarse-grained simulations of elongational viscosities, super-position rheology and shear banding in model core-shell systems. Macromol Theory Simul 16:742–754
van den Noort A, Briels WJ (2007) Brownian dynamics simulations of concentration coupled shear banding. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech (in press) DOI 10.1016/j.jnnfm.2007.11.001
van den Noort A, den Otter WK, Briels WJ (2007) Coarse graining of slow variables in dynamics simulations of soft matter. Europhys Lett 80:28003-1–28003-5
van der Gucht J, Lemmers M, Knoben W, Besseling NAM, Lettinga MP (2006) Multiple shear-banding transitions in a supramolecular polymer solution. Phys Rev Lett 97:108301–1–108301-4
Varnik F, Bocquet L, Barrat J-L, Berthier L (2003) Shear localization in a model glass. Phys Rev Lett 90:095702–1–095702-4
Vasquez PA, Cook LP, McKinley GH (2007) A network scission model for wormlike micellar solutions I. Model formulation and viscometric flow predictions. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 144:122–139
Vermant J (2003) Large-scale structures in sheared colloidal dispersions. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 6:489–495
Vermant J, Raynaud L, Mewis J, Ernst B, Fuller GG (1999) Large-scale bundle ordering in sterically stabilized latices. J Coll Int Sci 211:221–229
Vlassopoulos D, Hatzikiriakos (1995) A generalized Giesekus constitutive model with retarda- tion time and its association to the spurt effect. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 57:119–136
Vlassopoulos D, Pakula T, Fytas G (1997) Ordering and viscoelastic relaxation in multiarm star polymer melts. Europhys Lett 39:617–622
Vlassopoulos D, Fytas G, Pakula T, Roovers J (2001) Multiarm star polymer dynamics. J Phys Condens Matter 13:R855–R876
von Hünerbein S, Würth M, Palberg T (1996) Microscopic mechanisms of non-linear rheology of crystalline colloidal suspensions. Prog Colloid Polym Sci 100:241–245
Wang S-Q, Ravindranath S, Wang Y, Boukany P (2007) New theoretical considerations in polymer rheology: elastic breakdown of chain entanglement network. J Chem Phys 127:064903–1–064903-14
Wilkins GMH, Olmsted PD (2006) Vorticity banding during the lamellar-to-onion transition in a lyotropic surfactant solution in shear flow. Eur Phys J E 21:133–143
Yesilata B, Clasen C, McKinley GH (2006) Nonlinear shear and extensional flow dynamics of wormlike surfactant solutions. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 133:73–90
Yuan X-F (1999) Dynamics of a mechanical interface in shear-banded flow. Europhys Lett 46:542–548
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhont, J.K.G., Briels, W.J. Gradient and vorticity banding. Rheol Acta 47, 257–281 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-007-0245-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-007-0245-0