Abstract
Purpose
Hindbrain herniation (HH) is frequently found in syndromic craniosynostosis. It may cause impairment of the respiratory centres and manifest as sleep-disordered breathing. Our aim was to quantify sleep apnoea caused by HH in children with syndromic craniosynostosis.
Methods
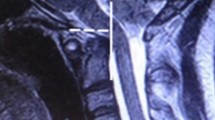
Seventy-one children with syndromic and complex craniosynostosis (aged 0–18 years) underwent prospective magnetic resonance imaging and a sleep study. The position of the cerebellar tonsils and respiratory parameters were evaluated and analysed. None of the included patients had undergone previous foramen magnum decompression.
Results
HH was present in 35 % of the patients and was more frequent in children with Crouzon syndrome (63 %) than in other types of craniosynostosis (p = .018). There was a positive association between the position of the cerebellar tonsils and papilledema (p = .002). Sleep studies of children with craniosynostosis and HH were not different from those without HH. Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome was not more prevalent in children with HH compared to those without HH (p = .12). A cluster analysis using indices of apnoea revealed that three new clusters between which age was significantly different (p = .025).
Conclusion
Sleep apnoea in syndromic craniosynostosis is not caused by HH. Rather, our evidence suggests that sleep-disordered breathing in craniosynostosis may be caused by brain stem immaturity in young children or upper airway obstruction. Therefore, as long as the child remains asymptomatic, our preferred management of HH is to be conservative and provide regular neurosurgical follow-up.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bejjani GK (2001) Definition of the adult Chiari malformation: a brief historical overview. Neurosurg Focus 11:E1
Bokinsky GE, Hudson LD, Weil JV (1973) Impaired peripheral chemosensitivity and acute respiratory failure in Arnold–Chiari malformation and syringomyelia. N Engl J Med 288:947–948
Botelho RV, Bittencourt LR, Rotta JM, Tufik S (2003) A prospective controlled study of sleep respiratory events in patients with craniovertebral junction malformation. J Neurosurg 99:1004–1009
Botelho RV, Bittencourt LR, Rotta JM, Tufik S (2010) The effects of posterior fossa decompressive surgery in adult patients with Chiari malformation and sleep apnea. J Neurosurg 112:800–807
Chern JJ, Gordon AJ, Mortazavi MM, Tubbs RS, Oakes WJ (2011) Pediatric Chiari malformation type 0: a 12-year institutional experience. J Neurosurg 8:1–5
Cinalli G, Renier D, Sebag G, Sainte-Rose C, Arnaud E, Pierre-Kahn A (1995) Chronic tonsillar herniation in Crouzon’s and Apert’s syndromes: the role of premature synostosis of the lambdoid suture. J Neurosurg 83:575–582
Cinalli G, Chumas P, Arnaud E, Sainte-Rose C, Renier D (1998) Occipital remodeling and suboccipital decompression in severe craniosynostosis associated with tonsillar herniation. Neurosurgery 42:66–71, discussion 71–63
Cinalli G, Sainte-Rose C, Kollar EM, Zerah M, Brunelle F, Chumas P, Arnaud E, Marchac D, Pierre-Kahn A, Renier D (1998) Hydrocephalus and craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg 88:209–214
Cinalli G, Spennato P, Sainte-Rose C, Arnaud E, Aliberti F, Brunelle F, Cianciulli E, Renier D (2005) Chiari malformation in craniosynostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 21:889–901
Dauvilliers Y, Stal V, Abril B, Coubes P, Bobin S, Touchon J, Escourrou P, Parker F, Bourgin P (2007) Chiari malformation and sleep related breathing disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:1344–1348
Frim DM, Jones D, Goumnerova L (1990) Development of symptomatic Chiari malformation in a child with craniofacial dysmorphism. Pediatr Neurosurg 16:228–231
Gonsalez SL, Thompson D, Hayward R, Lane R (1998) Breathing patterns in children with craniofacial dysostosis and hindbrain herniation. Eur Respir J 11:866–872
Guilleminault C (1987) Sleep and its disorders in children. Raven, New York
Guilleminault C, Pelayo R, Clerk A, Leger D, Bocian RC (1995) Home nasal continuous positive airway pressure in infants with sleep-disordered breathing. J Pediatr 127:905–912
Guilleminault C, Lee JH, Chan A (2005) Pediatric obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 159:775–785
Hayward R, Gonsalez S (2005) How low can you go? Intracranial pressure, cerebral perfusion pressure, and respiratory obstruction in children with complex craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg 102:16–22
Henriques-Filho PS, Pratesi R (2008) Sleep apnea and REM sleep behavior disorder in patients with Chiari malformations. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 66:344–349
Iber C, Ancoli-Israel S, Chesson AL, Quan SF (2007) The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules, terminology, and technical specifications. American Academy of Sleep Medicine, Westchester
Juranek J, Salman MS (2010) Anomalous development of brain structure and function in spina bifida myelomeningocele. Dev Disabil Res Rev 16:23–30
Kirsch WM, Duncan BR, Black FO, Stears JC (1968) Laryngeal palsy in association with myelomeningocele, hydrocephalus, and the Arnold–Chiari malformation. J Neurosurg 28:207–214
Lowe LH, Booth TN, Joglar JM, Rollins NK (2000) Midface anomalies in children. Radiographics 20:907–922, quiz 1106–1107, 1112
Noudel R, Jovenin N, Eap C, Scherpereel B, Pierot L, Rousseaux P (2009) Incidence of basioccipital hypoplasia in Chiari malformation type I: comparative morphometric study of the posterior cranial fossa. Clinical article. J Neurosurg 111:1046–1052
Petersen MC, Wolraich M, Sherbondy A, Wagener J (1995) Abnormalities in control of ventilation in newborn infants with myelomeningocele. J Pediatr 126:1011–1015
Sandberg DI, Navarro R, Blanch J, Ragheb J (2007) Anomalous venous drainage preventing safe posterior fossa decompression in patients with Chiari malformation type I and multisutural craniosynostosis. Report of two cases and review of the literature. J Neurosurg 106:490–494
Sgouros S, Kountouri M, Natarajan K (2007) Skull base growth in children with Chiari malformation type I. J Neurosurg 107:188–192
Sieben RL, Hamida MB, Shulman K (1971) Multiple cranial nerve deficits associated with the Arnold–Chiari malformation. Neurology 21:673–681
Strahle J, Muraszko KM, Kapurch J, Bapuraj JR, Garton HJ, Maher CO (2011) Chiari malformation type I and syrinx in children undergoing magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg 8:205–213
Tubbs RS, Lyerly MJ, Loukas M, Shoja MM, Oakes WJ (2007) The pediatric Chiari I malformation: a review. Childs Nerv Syst 23:1239–1250
Venes JL (1988) Arnold–Chiari malformation in an infant with Kleeblattschadel: an acquired malformation? Neurosurgery 23:360–362
Ward SL, Marcus CL (1996) Obstructive sleep apnea in infants and young children. J Clin Neurophysiol 13:198–207
Waters KA, Forbes P, Morielli A, Hum C, O’Gorman AM, Vernet O, Davis GM, Tewfik TL, Ducharme FM, Brouillette RT (1998) Sleep-disordered breathing in children with myelomeningocele. J Pediatr 132:672–681
Disclosure
CD has received a research grant from Carolien Bijl Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Driessen, C., Joosten, K.F.M., Florisson, J.M.G. et al. Sleep apnoea in syndromic craniosynostosis occurs independent of hindbrain herniation. Childs Nerv Syst 29, 289–296 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1922-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1922-6