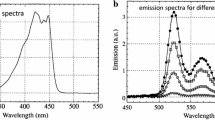
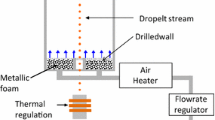
Abstract
In the present study, a molecular tagging technique is introduced to achieve simultaneous measurements of droplet size, flying velocity and transient temperature of in-flight liquid droplets in a spray flow. For the molecular tagging measurements, a pulsed laser is used to “tag” phosphorescent 1-BrNp·Mβ-CD·ROH triplex molecules premixed within liquid droplets. After the same laser excitation pulse, long-lived laser-induced phosphorescence is imaged at two successive times within the phosphorescence lifetime of the tagged phosphorescent triplex molecules. While the sizes of the droplets are determined quantitatively based on the acquired droplet images with a precalibrated scale ratio between the image plane and the object plane, the displacement vectors of the in-flight droplets between the two image acquisitions are used to estimate the flying velocities of the droplets. The simultaneous measurements of the transient temperatures of the in-flight droplets are achieved by taking advantage of the temperature dependence of phosphorescence lifetime, which is estimated from the intensity ratio of the acquired phosphorescence image pair of the inflight droplets. The feasibility and implementation of the molecular tagging technique are demonstrated by conducting simultaneous measurements of droplet size, flying velocity and transient temperature of micro-sized water droplets exhausted from a piezoelectric droplet generator into ambient air at different test conditions in order to characterize the dynamic and thermodynamic behaviors of the micro-sized in-flight droplets. The unsteady heat transfer process between the in-flight droplets and the ambient air is also analyzed theoretically by using a lumped capacitance method to predict the temperature changes of the in-flight water droplets along their flight trajectories. The measured temperature data are compared with the theoretical analysis results quantitatively, and the discrepancies between measurement results and the theoretical predictions are found to be within 0.80 °C.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castanet G, Lavieille P, Lemoine F et al (2002) Energetic budget on an evaporating monodisperse droplet stream using combined optical methods. Int J Heat Mass Transf 45:5053–5067. doi:10.1016/S0017-9310(02)00204-1
Coppeta J, Rogers C (1998) Dual emission laser induced fluorescence for direct planar scalar behavior measurements. Exp Fluids 25:1–15. doi:10.1007/s003480050202
Ferraudi GJ (1988) Elements of inorganic photochemistry. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Gendrich C, Koochesfahani M, Nocera D (1997) Molecular tagging velocimetry and other novel applications of a new phosphorescent supramolecule. Exp Fluids 23:361–372
González JE, Black WZ (1997) Study of droplet sprays prior to impact on a heated horizontal surface. J Heat Transf 119:279. doi:10.1115/1.2824221
Hall DD, Mudawar I (1995) Experimental and numerical study of quenching complex-shaped metallic alloys with multiple, overlapping sprays. Int J Heat Mass Transf 38:1201–1216. doi:10.1016/0017-9310(94)00244-P
Hartmann W, Gray M, Ponce A (1996) Substrate induced phosphorescence from cyclodextrin·lumophore host-guest complexes. Inorg Chim Acta 234:239–248
Hopkins RJ, Symes R, Sayer RM, Reid JP (2003) Determination of the size and composition of multicomponent ethanol/water droplets by cavity-enhanced Raman scattering. Chem Phys Lett 380:665–672. doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2003.09.048
Hu H, Huang D (2009) Simultaneous measurements of droplet size and transient temperature within surface water droplets. AIAA J 47:813–820
Hu H, Jin Z (2010) An icing physics study by using lifetime-based molecular tagging thermometry technique. Int J Multiph Flow 36:672–681
Hu H, Koochesfahani M (2003) A novel technique for quantitative temperature mapping in liquid by measuring the lifetime of laser induced phosphorescence. J Vis 6:143–153
Hu H, Koochesfahani MM (2006) Molecular tagging velocimetry and thermometry and its application to the wake of a heated circular cylinder. Meas Sci Technol 17:1269–1281. doi:10.1088/0957-0233/17/6/S06
Hu H, Koochesfahani MM (2011) Thermal effects on the wake of a heated circular cylinder operating in mixed convection regime. J Fluid Mech 685:235–270. doi:10.1017/jfm.2011.313
Hu H, Saga T, Kobayashi T, Okamoto T, Taniguchi N (1998) Evaluation of cross correlation method by using PIV standard images. J Vis 1(1):87–94
Hu H, Koochesfahani M, Lum C (2006) Molecular tagging thermometry with adjustable temperature sensitivity. Exp Fluids 40:753–763
Hu H, Jin Z, Koochesfahani M, Nocera D (2010) Experimental investigations of micro-scale flow and heat transfer phenomena by using molecular tagging techniques. Meas Sci Technol 21:085401 (14 pp)
Incropera F, DeWitt D (1996) Introduction to heat transfer. Wiley, New York
Kim HJ, Kihm KD, Allen JS (2003) Examination of ratiometric laser induced fluorescence thermometry for microscale spatial measurement resolution. Int J Heat Mass Transf 46:3967–3974. doi:10.1016/S0017-9310(03)00243-6
Lavieille P, Lemoine F, Lavergne G, Lebouché M (2001) Evaporating and combusting droplet temperature measurements using two-color laser-induced fluorescence. Exp Fluids 31:45–55. doi:10.1007/s003480000257
Lemoine F, Castanet G (2013) Temperature and chemical composition of droplets by optical measurement techniques: a state-of-the-art review. Exp Fluids 54(7):1572
Mochizuki T, Nozaki T, Mori YH, Kaji N (1999) Heat transfer to liquid drops passing through an immiscible liquid medium between tilted parallel-plate electrodes. Int J Heat Mass Transf 42:3113–3129. doi:10.1016/S0017-9310(98)00381-0
Müller T, Grünefeld G, Beushausen V (2000) High-precision measurement of the temperature of methanol and ethanol droplets using spontaneous Raman scattering. Appl Phys B 70(1):155–158
Nozaki T, Mochizuki T, Kaji N, Mori YH (1995) Application of liquid-crystal thermometry to drop temperature measurements. Exp Fluids 18:137–144. doi:10.1007/BF00230257
Omrane A, Juhlin G, Ossler F, Aldén M (2004a) Temperature measurements of single droplets by use of laser-induced phosphorescence. Appl Opt 43:3523–3529
Omrane A, Santesson S, Alden M, Nilsson S (2004b) Laser techniques in acoustically levitated micro droplets. Lab Chip 4:287–291. doi:10.1039/b402440k
Ramamurthy V, Schanze KS (1998) Organic and inorganic photochemistry. Mol Supramol Photochem viii:355
Richards CD, Richards RF, Boltzman S (1998) Transient temperature measurements in a convectively cooled droplet. Exp Fluids 25(5):392–400
Saga T, Kobayashi T, Segawa S, Hu H (2001) Development and evaluation of an improved correlation based PTV method. J Vis 4:29–37. doi:10.1007/BF03182453
Salazar VM, González JE, Rivera LA (2004) Measurement of temperatures on in-flight water droplets by laser induced fluorescence thermometry. J Heat Transf 126:279. doi:10.1115/1.1667527
Schulz C, Sick V (2005) Tracer-LIF diagnostics: quantitative measurement of fuel concentration, temperature and fuel/air ratio in practical combustion systems. Prog Energy Combust Sci 31:75–121. doi:10.1016/j.pecs.2004.08.002
Schweiger G (1990) Raman scattering on single aerosol particles and on flowing aerosols: a review. J Aerosol Sci 21:483–509. doi:10.1016/0021-8502(90)90126-I
Tuckermann R, Bauerecker S, Cammenga HK (2005) IR-thermography of evaporating acoustically levitated drops. Int J Thermophys 26:1583–1594. doi:10.1007/s10765-005-8105-6
Van Beeck JP, Riethmuller ML (1995) Nonintrusive measurements of temperature and size of single falling raindrops. Appl Opt 34:1633–1639. doi:10.1364/AO.34.001633
Van Beeck JP, Giannoulis D, Zimmer L, Riethmuller ML (1999) Global rainbow thermometry for droplet-temperature measurement. Opt Lett 24:1696–1698. doi:10.1364/OL.24.001696
Vetrano MR, Gauthier S, van Beeck J et al (2005) Characterization of a non-isothermal water spray by global rainbow thermometry. Exp Fluids 40:15–22. doi:10.1007/s00348-005-0042-4
Whitaker S (1972) Forced convection heat transfer correlations for flow in pipes, past flat plates, single cylinders, single spheres, and for flow in packed beds and tube bundles. AIChE J 18:361–371. doi:10.1002/aic.690180219
Wilms J, Gréhan G, Lavergne G (2008) Global rainbow refractometry with a selective imaging method. Part Part Syst Charact 25:39–48. doi:10.1002/ppsc.200700006
Wulsten E, Lee G (2008) Surface temperature of acoustically levitated water microdroplets measured using infra-red thermography. Chem Eng Sci 63:5420–5424. doi:10.1016/j.ces.2008.07.020
Zhang Y, Zhang G, Xu M, Wang J (2013) Droplet temperature measurement based on 2-color laser-induced exciplex fluorescence. Exp Fluids 54:1583. doi:10.1007/s00348-013-1583-6
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank Dr. M.M. Koochesfahani of Michigan State University for the technical help pertinent to the present study. The funding support from National Science Foundation program under award numbers of CBET-1064196 and CBET-1435590 and Iowa Regents Innovation Fund (RIF) program is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Chen, F. & Hu, H. Simultaneous measurements of droplet size, flying velocity and transient temperature of in-flight droplets by using a molecular tagging technique. Exp Fluids 56, 194 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-015-2063-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-015-2063-y