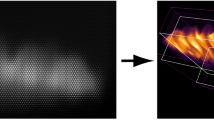
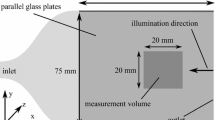
Abstract
This review paper addresses the integration of advanced visualization techniques into the analysis of volumetric vector fields obtained by experimental measurement techniques such as holographic PIV, tomographic PIV, 3D PTV or defocusing PIV. The paper follows the idea of the pipeline process for flow visualization focusing on experimental data generation and advanced visualization techniques. The paper tries to help the experimentalist navigating the landscape of recently developed volumetric measurement techniques and advanced visualization techniques. The processing steps and related difficulties are illustrated with the transitional backward facing step flow experiment at Re h = 4,440. The paper shows the usage of flow visualization for quantitative volumetric PIV data analysis.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agüi JC, Jimenez J (1987) On the performance of particle tracking. J Fluid Mech 185:447–468
Akenine-Möller T, Haines E, Hoffman N (2008) Real-time rendering, 3rd edn. A.K. Peters Ltd
Arroyo MP, Hinsch KD (2008) Recent developments of PIV towards 3D measurements. Top App Phys 112:127–154
Asimov D (1993) Notes on the topology of vector fields and flows. NASA Ames Research Center Report RNR-93-003
Atkinson CH, Soria J (2007) Algebraic reconstruction techniques for tomographic particle image velocimetry. 16th Australasian fluid mechanics conference
Atkinson CH, Soria J (2009) An efficient simultaneous reconstruction technique for tomographic particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids
Awatsuji Y, Fujii A, Kubota T, Matoba O (2006) Parallel three-step phase-shifting digital holography. Appl Opt 45:2995–3002
Baek SJ, Lee SJ (1996) A new two-frame particle tracking algorithm using match probability. Exp Fluids 23:261–304
Barnhardt DH, Hampp N, Halliwell NA, Coupland JM (2002) Digital holographic velocimetry with bacteriorhodopsin (BR) for real-time recording and numeric reconstruction. 11th International symposium on application of laser techniques to fluid mechanics
Battke H, Stalling D, Hege HC (1996) Fast line integral convolution for arbitrary surfaces in 3D. Vis Math
Berkooz G, Holmes P, Lumley JL (1993) The proper orthogonal decomposition in the analysis of turbulent flows. Annu RevFluid Mech 25:539–575
Biswas G, Breuer M, Durst F (2004) Backward-facing step flows for various expansion ratios at low and moderate Reynolds numbers. Trans ASME 126:362–374
Biwole PH, Yan W, Zhang Y, Roux1 J-J (2009) A complete 3D particle tracking algorithm and its applications to the indoor airflow study. Meas Sci Technol 20:115403
Blundell B, Schwarz A (2000) Volumetric three dimensional display systems. Wiley, New York
Boring E, Pang A (1996) Directional flow visualization of vector fields. IEEE Visualization’96, 389–392
Bouhoubeiny E, Druault P (2009) Note on the POD-based time interpolation from successive PIV images. CR Mecanique 337:776–780
Brill M, Hagen H, Djatschin W, Klimenko SV (1994) Streamball techniques for flow visualization. In: Proceedings of IEEE visualization 94, Oct 17–21, Washington, DC, pp 225–231
Brücker C (1996) 3-D scanning-particle-image-velocimetry: technique and application to a spherical cap wake flow. Appl Sci Res 56:157–179
Brunton SL, Rowley CW (2010) Fast computation of finite-time Lyapunov exponent fields for unsteady flows. CHAOS 20:017503
Buraga-Lefevre C, Coetemllec S, Lebrun D, Özkul C (2000) Application of wavelet transform to hologram analysis: three-dimensional location of particles. Opt Lasers Eng 33:409–421
Burger K, Schneider J, Kondratieva P, Kruger J, Westermann R(2007) Interactive visual exploration of instationary 3D-flows. Eurographics/IEEE VGTC Symposium on Visualization (EuroVis)
Buxton W, Fitzmaurice GW (1998) HMD’s, caves, and chameleon: a human-centric analysis of interaction in virtual space. Comput Graph 32(4):64–68
Chabral B, Leedom LC (1993) Imaging vector fields using line integral convolution. Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ’93, 263–270
Chakraborty O, Balchandar S, Adrian RJ (2005) On the relationships between local vortex identification schemes. J Fluid Mech 535:189–214
Champagnat F, Plyer A, Le Besnerais G, Leclaire B, Le Sant Y (2009) How to calculate dense PIV vector fields at video rate. 8th International symposium on particle image velocimetry, PIV09, Melbourne, Victoria (Australia), August 25–28
Chaves H, Uhlemann Ch, Brücker Ch (2010) Dynamic focussing for wide-field light-sheet scanning. In: Proceedings of 15th international symposium on application of laser techniques to fluid mechanics, Lisbon
Chong MS, Perry AE, Cantwell BJ (1990) A general classification of three-dimensional flow fields. Phys Fluids A2:765–777
Coetemllec S, Lebrun D, Özkul C (2002) Application of the two-dimensional fractional-order fourier transformation to particle field digital holography. J Opt Soc Am A 19:1537–1546
Cossairt OS, Napoli J, Hill SL, Dorval RK, Favalora GE (2007) Occlusion-capable multiview volumetric three-dimensional display. Appl Opt 46(8):1244–1250
Crawfis R, Max N, Becker B, Cabral B (1993) Volume rendering of 3D scalar and vector fields at LLNL. Proceedings, Supercomputing’93, 570–576
Cucitore R, Quadrio M, Baron A (1999) On the effectiveness and limitations of local criteria for the identification of a vortex. Eur J Mech B Fluids 18:261–282
de Kat R, van Oudheusden BW (2010) Instantaneous planar pressure from PIV: analytic and experimental test-cases. In: Proceedings of 15th international symposium on applications of laser techniques to fluid mechanics, Lisbon
de Leeuw W, van Liere R (1998) Comparing LIC and spot noise. In: Proceedings of the conference on Visualization ’98, pp 359–365
Dodgson NA (2005) Autostereoscopic 3D displays. Computer 38(8):31–36
Druault P, Guibert Ph (2004) Use of turbulent flow statistical properties for correcting erroneous velocity vectors in PIV. CR Mecanique 332(9):731–736
Druault P, Guibert P, Alizon F (2005) Use of proper orthogonal decomposition for time interpolation from PIV data. EIF 39:1009–1023
Durault Ph, Guibert Ph, Alizon F (2005) Use of proper orthogonal decomposition for time interpolation from PIV data. Exp Fluids 39:1009–1023
Ebert D, Musgrave K, Peachey P, Perlin K, Worley S (1998) Texturing and modeling: a procedural approach, 3rd edn. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco
Elsinga GE (2008) Tomographic particle image velocimetry. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Aerospace Engineering, Delft University of Technology
Elsinga GE, Scarano F, Wieneke B, van Oudheusden BW (2006) Tomographic particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids 41:933–947
Engel K, Hadwiger M, Kniss J, Rezk-Salama C, Weiskopf D (2006) Real-time volume graphics. A.K. Peters Ltd
Fuchs R, Peikert R, Hauser H, Sadlo F, Muigg P (2008) Parallel vectors criteria for unsteady flow vortices. VisComput Gr, IEEE 14/3
Garcia D (2010) A fast all-in-one method for automated post-processing of PIV data. Exp Fluids. doi:10.1007/s00348-010-0985-y
Garth C, Tricoche X, Scheuermann G (2004) Tracking of vector field singularities in unstructured 3D time-dependent data sets. Proceedings of IEEE Visualization 2004, 329–336
Garth C, Gerhardt F, Tricoche X, Hagen H (2007) Efficient computation and visualization of coherent structures in fluid flow application. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph (Proc. IEEE Visualization), 13(6):1464–1471
Green MA, Rowley CW, Haller G (2007) Detection of lagrangian coherent structures in 3D turbulence. J Fluid Mech 572:111–120
Gunes H, Rist U (2007) Spatial resolution enhancement/smoothing of stereo-particle-image-velocimetry data using proper-orthogonal-decomposition-based and Kriging interpolation methods. Phys Fluids 19
Gunes H, Sirisup S, Karniadakis GE (2006) Gappy data: to Krig or not to Krig. J Chem Phys 212
Haber RB, McNabb DA (1990) Visualization idioms: a conceptual model for scientific visualization systems. Vis Sci Comput, 75–93
Haimes R, Kenwright D (1999) On the velocity gradient tensor and fluid feature extraction. AIAA 14th computational fluid dynamics conference, pp 3288–3297
Hain R, Kahler CJ, Tropea C (2007) Comparison of CCD, CMOS and intensified cameras. Exp Fluids 42:403–411
Hain R, Kähler CJ, Radespiel R (2009) Principles of a volumetric velocity measurement technique based on optical aberrations. Notes on numerical fluid mechanics and multidisciplinary design, vol 106. Springer, pp 1–10
Hairer E, Norsett SP, Wanner G (1993) Solving ordinary differential equations I. Springer, Berlin
Halle M (1997) Autostereoscopic displays and computer graphics. Comput Graph ACM SIGGRAPH 31(2):58–62
Haller G (2001) Distinguished material surfaces and coherent structures in three-dimensional fluid flows. Phys D 149:248–277
Haller G (2002) Lagrangian coherent structures from approximate velocity data. Phys Fluids 14(6):1851–1861
Haller G (2005) An objective definition of a vortex. J Fluid Mech 525:1–26
Hege H-C, Stalling D (1998) Fast LIC with piecewise polynomial filter kernels. Math Vis Algorithm Appl, 295–314
Helman J, Hesselink L (1989) Representation and display of vector field topology in fluid flow data sets. Computer 22(8):27–36
Helman JL, Hesselink L (1990) Surface representations of two- and three-dimensional fluid flow topology. IEEE Comput Soc Press, 6–13
Helman J, Hesselink L (1991) Visualizing vector field topology in fluid flows. IEEE Comput Graph Appl 11:36–46
Herman GT, Lent A (1976) Iterative reconstruction algorithms. Computers in Biology and Medicine 6, Pergamon Press, pp 273–294
Hesselink L, Post F, van Wijk JJ (1994) Research issues in vector and tensor field visualization. IEEE Comput Graph Appl 14(2)
Hoyer K, Holzner M, Lüthi B, Guala M, Liberzon A, Kinzelbach W (2005) 3D scanning particle tracking velocimetry. Exp Fluids 29:145–153
Hultquist JPM (1992) Constructing stream surfaces in steady 3D vector fields. In: Proceedings of IEEE visualization 92, Oct 19–23, Boston, Massachusetts, pp 171–178
Hunt JCR, Wray AA, Moin P (1988) Eddies, streams, and convergence zones in turbulent flows. Cent Turbul Res Rep CTR-288:193–208
In den Haak M, Spoelder HJW, Groen FCA (1992) Matching of images by using automatically selected regions of interest. Computer Science in the Netherlands’92, 33–39
Interrante V, Grosch C (1997) Strategies for effectively visualizing 3D flow with volume LIC. Proceedings of visualization’97, pp 421–424
Ishikawa M, Murai Y, Wada A, Iguchi M, Okamoto K, Yamamoto F (2000) A novel algorithm for particle tracking velocimetry using the velocity gradient tensor. Exp Fluids 29:519–531
Jeong J, Hussain F (1995) On the identification of a vortex. J Fluid Mech 173:303–356
Jiang M, Machiraju R, Thompson D (2005) Detection and visualization of vortices. The Visualization Handbook, pp 295–309
Kalivas DS, Sawchuk AA (1991) A region matching motion estimation algorithm. Comput Vis Graph image process Image underst 54(2):275–288
Kenwright DN (1998) Automatic detection of open and closed separation and attachment lines. Proceedings of Visualization’98, pp 151–158
Kenwright DN, Mallinson GD (1992) A 3-D streamline tracking algorithm using dual stream functions. In: Proceedings of IEEE visualization 92, Oct 19–23, Boston, pp 62–68
Kenwright DN, Henze C, Levit C (1999) Feature extraction of separation and attachment lines. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 5/2:135–144
Kitzhofer J (2011) Volumetric measurements of the transitional backward facing step flow. Dissertation, TU Freiberg, Germany (submitted)
Kitzhofer J, Brücker C (2010) Tomographic particle tracking velocimetry using telecentric imaging. Exp Fluids. doi: 10.1007/s00348-010-0879-z
Kitzhofer J, Westfeld P, Pust O, Nonn T, Maas HG, Brücker C (2010) Calculation of 3D deformation and rotation rate tensor from volumetric particle data via 3D least squares matching. In: Proceedings of the 15th international symposium on applications of laser techniques to fluid mechanics, 5–8 July 2010, Lisbon (Submitted to special issue)
Klassen RV, Harrington SJ (1991) Shadowed hedgehogs: a technique for visualizing 2D slices of 3D vector fields. IEEE Visualization’91, 148–153
Kolár V (2007) Vortex identification: new requirements and limitations. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 28:638–652
Krishnan H, Garth C, Joy K (2009) Time and streak surfaces for flow visualization in large time-varying data sets. Proceedings of IEEE Visualization ’09, pp 1267–1274
Lane DA (1993) Visualization of time-dependent flow fields. In: Proceedings of IEEE visualization 93, Oct 25–29, San Jose, California, pp 32–38
Lane DA (1994) UFAT—a particle tracer for time-dependent flow fields. In: Proceedings of IEEE visualization 94, Oct 17–21, Washington, DC, pp 257–264
Laramee RS, Gearth C, Schneider J, Hauser H (2006) Texture advection on streamsurfaces: a novel hybrid visualization applied to CFD results. EuroVis2006, Eurographics Association, pp 155–162
Laurentini A (1994) How many 2D silhouettes does it take to reconstruct a 3D object? Comput Vis Image Underst 67(1):81–87
Li M, Kudo H, Hu J, Johnson RH (2004) Improved iterative algorithm for sparse object reconstruction and its performance evaluation with micro-ct data. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 51:659–666
Li G-S, Tricoche X, Weiskopf D, Hansen CD (2008) Flow charts: visualization of vector fields on arbitrary surfaces. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 14(5):1–14
Liang DF, Jiang CB, Li YL (2003) Cellular neural network to detect spurious vectors in PIV data. Exp Fluids 34:52–62
Lobutova E, Resagk C, Rank R, Müller D, Putze T, Maas H-G (2007) Investigation of large-scale flow structures in Rayleigh-Bernard convection using 3D particle tracking velocimetry. Symposium Lasermethoden in der Strömungsmesstechnik, Rostock
Loffelmann H, Mroz L, Groller E, Purgathofer W (1997) Stream arrows: enhancing the use of stream surfaces for the visualization of dynamical systems. Vis Comput 13(8):359–369
Löffelmann H, Mroz L, Gröller E (1997) Hierarchical streamarrows fort he visualization of dynamical systems. 8th EUROGRAPHICS workshop on visualization in scientific computing, pp 155–163
Lu W, Yin F (2004) Adaptive algebraic reconstruction technique. Med Phys 31:3222–3230
Lu J, Fugal JP, Nordsiek H, Saw EW, Shaw RA, Yang W (2008) Lagrangian particle tracking in three dimensions via single-camera in-line digital holography. New J Phys 10:24
Lumley JL (1967) The structure of inhomogeneous turbulent flows. In: Yaglom AM, Tatarsky VI (eds) Proceedings of Atmospheric turbulence and radio wave propagation. Nauka, Moscow, pp 166–178
Lüthi B, Tsinoba A, Kinzelbach W (2005) Lagrangian measurement of vorticity dynamics in turbulent flow. J Fluid Mech 528:87–118
Maas HG (1992) Digitale photogrammetrie in der dreidimensionalen Strömungsmesstechnik. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zürich
Maas HG, Stefanidis A, Grün A (1994) From pixels to voxels—tracking volume elements in sequences of 3-d digital images. Int Arch Photogramm Remote Sens 30(3/2)
Maas HG, Westfeld P, Putze T., Botkjaer N, Kitzhofer J, Brücker C (2009) Photogrammetric techniques in multi-camera tomographic PIV. In: Proceedings of the 8th international symposium on particle image velocimetry, Melbourne
Malik NA, Dracos T (1995) Interpolation schemes for three-dimensional velocity fields from scattered data using Taylor expansions. J Comput Phys 119:231–243
Malik N, Dracos T, Papantoniou D (1993) Particle tracking in three dimensional turbulent flows—part II: particle tracking. Exp Fluids 15:279–294
Malkiel E, Sheng J, Katz J, Strickler JR (2003) The three-dimensional flow field generated by a feeding calanoid copepod measured using digital holography. J Exp Bio 206:3657–3666
Mattausch O, Theußl T, Hauser H, Gröller E (2003) Strategies for interactive exploration of 3D flow using evenly-spaced illuminated streamlines. In: Proceedings of the 19th spring conference on computer graphics, pp 213–222
McLoughlin T, Laramee RS, Peikert R, Post FH, Chen M (2009) Over two decades of integration-based, geometric flow visualization. Eurographics 2009 STAR report
McLoughlin T, Laramee RS, Peikert R, Post FH, Chen M (2010) Over two decades of integration-based, geometric flow visualization. Computer graphics (in print)
Meng H, Hussain F (1995) In-line recording and off-axis viewing technique for holographic particle velocimetry. Appl Opt 34:1827–1840
Morris SC (2010) Shear-layer instabilities: particle image velocimetry measurements and implications for acoustics. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 2011.43
Mullin JA, Dahm WJA (2006) Dual-plane stereo particle image velocimetry measurements of velocity gradient tensor fields in turbulent shear flow II. Experimental results. Phys Fluids 18:035102
Nie JH, Armaly BF (2003) Reattachment of three-dimensional flow adjacent to backward-facing step. Trans ASME 125:422–428
NozickV, Saito H (2007) Multiple view computation for multi-stereoscopic display. In: IEEE Pacific-rim symposium on image amd video technology (PSIVT 2007), vol 4872, pp 399–412
Okamoto K, Hassan YA, Schmidl WD (1995) New tracking algorithm for particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids 19:342–347
Ouelette NT, Xu H, Bodenschatz E (2006) A quantitative study of three-dimensional Lagrangian particle tracking algorithms. Exp Fluids 40:301–313
Pagendarm H-G, Walter B (1994) Feature detection from vector quantities in a numerically simulated hypersonic flow field in combination with experimental flow visualization. IEEE Comput Soc Press, 117–123
Palero V, Arroyo MP, Soria J (2001) Digital in-line holographic PIV for 3D particulate flow diagnostics. In: Proceedings of 4th international symposium on particle image velocimetry, Göttingen
Pan G, Meng H (2003) Digital holography of particle fields: reconstruction by use of complex amplitude. Appl Opt 42:827–833
Peikert R, Rozh M (1999) The “Parallel Vectors” operator—a vector field visualization primitive. Proceedings of IEEE Visualization ’99, pp 263–270
Peikert R, Sadlo F (2009) A robust stream surface method for the visualization of vector field singularities. Comput Graph Geom 11(2):2–13
Pereira F, Gharib M (2002) Defocusing digital particle image velocimetry and the three-dimensional characterization of two-phase flows. Meas Sci Technol 13:683–694
Perry A, Chong M (1994) Topology of flow patterns in vortex motions and turbulence. Appl Sci Res 53:357–374
Pobitzer A, Peikert R, Fuchs R, Schindler B, Kuhn A, Theisel H, Matkovic K, Hauser H (2010) On the way towards topology based visualization of unsteady flow—the state of the art. In: Proceedings of EuroGraphics 2010 state of the art reports
Post F, van Walsum T (1995) Iconic techniques for feature visualization. IEEE Visualization’95, 288–295
Post FH, Vrolijk B, Hauser H, Laramee RS, Doleisch H (2002) Feature Extraction and Visualization of Flow Fields. Eurographics 2002 STAR
Post FH, Vrolijk B, Hauser H, Laramee RS, Doleisch H (2003) The state of the art in flow visualization. Feature extraction and tracking. Comput Graph Forum 22(4):775–792
Pothos S, Troolin D, Lai W, Menon R (2009) V3 V—volumetric three-component velocimetry for 3D flow measurements—main principle, theory and applications. Revista Termotehnica 2/2009
Pu Y, Meng H (2005) Four-dimensional dynamic flow measurement by holographic particle image velocimetry. Appl Opt 44:7697–7708
Pun CS, Susanto A, Dabiri D (2007) Mode-ratio bootstrapping method for PIV outlier correction. Meas Sci Technol 18:3511–3522
Putze T (2008) Geometrische und stochastische Modelle zur Optimierung der Leistungsfähigkeit des 3D PTV. Ph.D. Thesis, Fakultät Forst-, Geo- und Hydro-wissenschaften, Dresden University of Technology
Raffel M, Gharib M, Ronneberger O, Kompenhans J (1995) Feasibility study of three-dimensional PIV by correlating images of particles within parallel light sheet planes. Exp Fluids 19:69–77
Raffel M, Westerweel J, Willert C, Gharib M, Kompenhans J (1996) Analytical and experimental investigations of dual-plane particle image velocimetry. Opt Eng 35:2067–2074
Raffel M, Willert C, Wereley S, Kompenhans J (2007) Post-processing of PIV data in particle image velocimetry. A practical guide. Springer, Berlin, pp 177–208
Reinders F, Post FH, Spoelder HJW (2001) Visualization of time-dependent data using feature tracking and event detection. Vis Comput 17(1):55–71
Robinson O, Rockwell D (1993) Construction of three-dimensional images of flow structure via particle tracking techniques. Exp Fluids 14:257–270
Sadlo F, Peikert R (2007) Efficient visualization of lagrangian coherent structures by filtered AMR ridge extraction. Trans Vis Comput Graph 13(6):1456–1463
Sadlo F, Weiskopf D (2010) Time-dependent 2-D vector field topology: An approach inspired by lagrangian coherent structures. Comput Graph Forum 29:88–100
Sahner J, Weinkauf T, Teuber N, Hege HC (2007) Vortex and strain skeletons in eulerian and lagrangian frames. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 13(5)
Samtaney R, Silver D, Zabusky N, Cao J (1994) Visualizing features and tracking their evolution. IEEC 27(7):20–27
Sanna A, Montrucchio B, Montuschi P (2000) A survey on visualization of vector fields by texture-based methods. Recent Res Dev Pattern Recognit 1(1):13–27
Scarano F, Moore P (2010) An advection model to increase the time-resolution of PIV time-series. In: Proceedings of 15th international symposium on applications of laser technoques to fluid mechanics, Lisbon
Scarano F, Poelma C (2009) Three-dimensional vorticity patterns of cylinder wakes. Exp Fluids 47:69–83
Scarano F, Riethmuller ML (2000) Advances in iterative multigrid PIV image processing. Exp Fluids 29:S51–S60
Schafhitzel T, Tejada E, Weiskopf D, Ertl T (2007) Point-based stream surfaces and path surfaces. Proceedings of graphics interface 2007, pp 289–296
Schafhitzel T, Baysal K, Vaaraniemi M, Rist U, Weiskopf D (2010) Visualizing the evolution and interaction of vortices and shear layers in time-dependent 3D flow. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph (To appear)
Schiwietz T, Westermann R (2004) GPU-PIV, VMV
Schnars U, Juptner WP (1994) Direct recording of holograms by a CCD target and numerical reconstruction. Appl Opt 33:179–181
Schnars U, Jüptner PO (2002) Digital recording and numerical reconstruction of holograms. Meas Sci Technol 13:85–101
Schreer O (2005) Stereoanalyse und Bildsynthese. Springer, Berlin
Schröder A, Geisler R, Staack K, Elsinga GE, Scarano F, Wieneke B, Henning A, Poelma C, Westerweel J (2011) Eulerian and Lagrangian views of a turbulent boundary layer flow using time-resolved tomographic PIV. Exp Fluids 50:1071–1091
Schroeder WJ, Volpe CR, Lorensen WE (1991) The stream polygon: a technique for 3D vector field visualization. In: Proceedings of IEEE visualization 91, Oct 22–25, San Diego, pp 126–132
Shadden S, Lekien F, Marsden J (2005) Definition and properties of Lagrangian coherent structures from finite-time Lyapunov exponents in two-dimensional aperiodic flows. Phys D Nonlinear Phenom 212:271–304
Shen H-W, Kao DL (1997) UFLIC: a line integral convolution algorithm for visualizing unsteady flows. Proceedings visualization’97, pp 317–322
Shepard D (1968) A two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly-spaced data. In: Proceedings of the 1968 ACM national conference, pp 517–524
Sirovich L (1987) Turbulence and the dynamics of coherent structures. Part I: coherent structures. Q Appl Math XLV:561–571
Soria J, Atkinson C (2008) Towards 3C–3D digital holographic fluid velocity vector field measurement—tomographic digital holographic PIV. Meas Sci Technol 19:12
Strawn RC, Kenwright DN, Ahmad J (1999) Computer visualization of vortex wake systems. AIAA J 37(4):511–512
Stuer H, Blaser S (2000) Interpolation of scattered 3D PTV data to a regular grid. Flow Turbul Combust 64:215–232
Surana A, Grunberg O, Haller G (2006) Exact theory of three-dimensional flow separation. Part1. Steady separation. J Fluid Mech 564:57–103
Surana A, Jacobs G, Grunberg O, Haller G (2008) Exact theory of three-dimensional fixed unsteady separation. Phys Fluids 20(1–22)
Telea A, van Wijk J (2003) 3D IBFV: hardware-accelerated 3D flow visualization. IEEE visualization ’03
Theisel H, Seidel HP (2003) Feature flow fields. In: Proceedings of joint eurographics—IEEE TCVG symposium on visualization (VisSym’03)
Theisel H, Weinkauf T, Hege HC, Seidel HP(2003) Saddle connectors—an approach to visualizing the topological skeleton of complex 3D vector fields. In: Proceedings of IEEE visualization 2003, Seattle
Theisel H, Sahner J, Weinkauf T, Hege H-C, Seidel HP (2005) Extraction of parallel vector surfaces in 3D time-dependent fields and applications to vortex core line tracking. Proceedings of IEEE visualization 2005
Trolinger JD, Belz RA, Farmer WM (1969) Holographic techniques for the study of dynamic particle fields. Appl Opt 8:957–961
Ueng S-K, Sikorski C, Ma K-L (1996) Efficient streamline, streamribbon, and streamtube constructions on unstructured grids. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 2(2):100–110
Upson C, Faulhaber T, Kamins D, Laidlaw D, Schlegel D, Vroom J, Gurwitz R, van Dam A (1998) The application visualization system: a computational environment for scientific visualization. IEEE Comput Graph Appl 9(4):30–42
van Walsum T, Post FH, Silver D, Post FJ (1996) Feature extraction and iconic visualization. IEEE TVCG 2(2):111–119
van Wijk JJ (1991) Spot noise texture synthesis for data visualization. Comput Graph 91:309–318
Venugopal V, Patterson C, Shinpaugh K (2009) Accelerating particle image velocimetry using hybrid architectures. Symposium on application accelerators in high performance computing
Wegenkittl R, Gröller E (1997) Fast oriented line integral convolution for vector field visualization. Proceedings of visualization’97, 309–316
Weinkauf T, Theisel H (2010) Streak lines as tangent curves of a derived vector field. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph16(6) (Vis 2010 Best Paper Award)
Westerweel J, Scarano F (2005) Universal outlier detection for PIV data. Exp Fluids 39:1096–1100
Willert CE, Gharib M (1992) Three-dimensional particle imaging with a single camera. Exp Fluids 12:353–358
Willert C, Stasicki B, Klinner J, Moessner S (2010) Pulsed operation of high-power light emitting diodes for imaging flow velocimetry. Meas Sci Technol 21:11
Willneff J (2003) A spatio-temporal matching algorithm for 3D particle tracking velocimetry. ETH Zürich—Dissertation Nr. 15276
Wu JZ, Gu JW, Wu JM (1987) Steady three-dimensional fluid particle separation from arbitrary smooth surface and formation of free vortex layers. AIAA Paper 87-2348
Xu H (2008) Tracking Lagrangian trajectories in position-velocity space. Meas Sci Technol 19:10
Yamamoto F, Uemura T, Iguchi M, Ohta J, Wada A, Mori K (1993) §DPTV based on binary image correlations method and its applications to a mixing flow with a bubbling jet. In: Brebbia CA, Carlomagno GM (eds) Computational methods and experimental measurements, vol 6. Springer, Berlin, pp 229–246
Zhou J, Adrian RJ, Balachandar S, Kendall TM (1999) Mechanism for generating coherent packets of hairpin vortices in channel flow. J Fluid Mech 387:353–396
Zhu Y, Zhen T (2009) 3D multi-view autostereoscopic display and its key technologie. apcip, Asia-pacific conference on information processing, 2009, vol 2, pp 31–35
Zöckler M, Stalling D, Hege H (1996) Parallel line integral convolution.In: Proceedings first eurographics workshop on parallel graphic and visualization, pp 249–256
Acknowledgments
The authors are not aware of any biases that might be perceived as affecting the objectivity of the review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitzhofer, J., Nonn, T. & Brücker, C. Generation and visualization of volumetric PIV data fields. Exp Fluids 51, 1471–1492 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-011-1176-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-011-1176-1