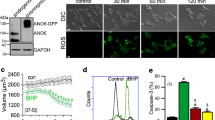
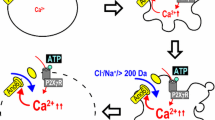
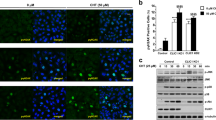
Abstract
A remarkable feature of apoptosis is the initial massive cell shrinkage, which requires opening of ion channels to allow release of K+, Cl−, and organic osmolytes to drive osmotic water movement and cell shrinkage. This article focuses on the role of the Cl− channels LRRC8, TMEM16/anoctamin, and cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) in cellular apoptosis. LRRC8A-E has been identified as a volume-regulated anion channel expressed in many cell types. It was shown to be required for regulatory and apoptotic volume decrease (RVD, AVD) in cultured cell lines. Its presence also determines sensitivity towards cytostatic drugs such as cisplatin. Recent data point to a molecular and functional relationship of LRRC8A and anoctamins (ANOs). ANO6, 9, and 10 (TMEM16F, J, and K) augment apoptotic Cl− currents and AVD, but it remains unclear whether these anoctamins operate as Cl− channels or as regulators of other apoptotic Cl− channels, such as LRRC8. CFTR has been known for its proapoptotic effects for some time, and this effect may be based on glutathione release from the cell and increase in cytosolic reactive oxygen species (ROS). Although we find that CFTR is activated by cell swelling, it is possible that CFTR serves RVD/AVD through accumulation of ROS and activation of independent membrane channels such as ANO6. Thus activation of ANO6 will support cell shrinkage and induce additional apoptotic events, such as membrane phospholipid scrambling.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almaca J, Tian Y, AlDehni F, Ousingsawat J, Kongsuphol P, Rock JR, Harfe BD, Schreiber R, Kunzelmann K (2009) TMEM16 proteins produce volume regulated chloride currents that are reduced in mice lacking TMEM16A. J Biol Chem 284:28571–28578
Barriere H, Poujeol C, Tauc M, Blasi JM, Counillon L, Poujeol P (2001) CFTR modulates programmed cell death by decreasing intracellular pH in Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts. Am J Physiol 281:C810–C824
Barriere H, Belfodil R, Rubera I, Tauc M, Poujeol C, Bidet M, Poujeol P (2003) CFTR null mutation altered cAMP-sensitive and swelling-activated Cl− currents in primary cultures of mouse nephron. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 284:F796–F811
Billet A, Hanrahan JW (2013) The secret life of CFTR as a calcium-activated chloride channel. J Physiol 591:5273–5278
Braunstein GM, Roman RM, Clancy JP, Kudlow BA, Taylor AL, Shylonsky VG, Jovov B, Peter K, Jilling T, Ismailov II et al (2001) Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator facilitates ATP release by stimulating a separate ATP release channel for autocrine control of cell volume regulation. J Biol Chem 276:6621–6630
Burg ED, Remillard CV, Yuan JX (2006) K+ channels in apoptosis. J Membr Biol 209:3–20
Gawenis LR, Franklin CL, Simpson JE, Palmer BA, Walker NM, Wiggins TM, Clarke LL (2003) cAMP inhibition of murine intestinal Na/H exchange requires CFTR-mediated cell shrinkage of villus epithelium. Gastroenterology 125:1148–1163
Gottlieb RA, Dosanjh A (1996) Mutant cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator inhibits acidification and apoptosis in C127 cells: possible relevance to cystic fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:3587–3591
Grassme H, Jendrossek V, Riehle A, von Kurthy G, Berger J, Schwarz H, Weller M, Kolesnick R, Gulbins E (2003) Host defense against Pseudomonas aeruginosa requires ceramide-rich membrane rafts. Nat Med 9:322–330
Grubb S, Poulsen KA, Juul CA, Kyed T, Klausen TK, Larsen EH, Hoffmann EK (2013) TMEM16F (anoctamin 6), an anion channel of delayed Ca2+ activation. J Gen Physiol 141:585–600
Gulbins E, Jekle A, Ferlinz K, Grassme H, Lang F (2000) Physiology of apoptosis. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 279:F605–F615
Hammer C, Wanitchakool P, Sirianant L, Papiol S, Monnheimer M, Faria D, Ousingsawat J, Schramek N, Schmitt C, Margos G et al (2015) A coding variant of ANO10, affecting volume regulation of macrophages, is associated with Borrelia seropositivity. Mol Med 21:26–37
Hudson VM (2001) Rethinking cystic fibrosis pathology: the critical role of abnormal reduced glutathione (GSH) transport caused by CFTR mutation. Free Radic Biol Med 30:1440–1461
Ise T, Shimizu T, Lee EL, Inoue H, Kohno K, Okada Y (2005) Roles of volume-sensitive Cl− channel in cisplatin-induced apoptosis in human epidermoid cancer cells. J Membr Biol 205:139–145
Jentsch TJ (2016) VRACs and other ion channels and transporters in the regulation of cell volume and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 17:293–307
Jentsch TJ, Lutter D, Planells-Cases R, Ullrich F, Voss FK (2015) VRAC: molecular identification as LRRC8 heteromers with differential functions. Pflugers Arch 468:385–393
Jungas T, Motta I, Duffieux F, Fanen P, Stoven V, Ojcius DM (2002) Glutathione levels and BAX activation during apoptosis due to oxidative stress in cells expressing wild-type and mutant cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. J Biol Chem 277:27912–27918
Juul CA, Grubb S, Poulsen KA, Kyed T, Hashem N, Lambert IH, Larsen EH, Hoffmann EK (2014) Anoctamin 6 differs from VRAC and VSOAC but is involved in apoptosis and supports volume regulation in the presence of Ca. Pflugers Arch 466:1899–1910
Klausen TK, Bergdahl A, Hougaard C, Christophersen P, Pedersen SF, Hoffmann EK (2007) Cell cycle-dependent activity of the volume- and Ca2+-activated anion currents in Ehrlich Lettre ascites cells. J Cell Physiol 210:831–842
Kmit A, van Kruchten R, Ousingsawat J, Mattheij NJ, Senden-Gijsbers B, Heemskerk JW, Bevers EM, Kunzelmann K (2013) Calcium-activated and apoptotic phospholipid scrambling induced by Ano6 can occur independently of Ano6 ion currents. Cell Death Dis 25(4):e611
Kondratskyi A, Kondratska K, Skryma R, Prevarskaya N (2015) Ion channels in the regulation of apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1848:2532–2546
König J, Schreiber R, Mall M, Kunzelmann K (2002) No evidence for inhibition of ENaC through CFTR mediated release of ATP. Biochim Biophys Acta 1565:17–28
Kunzelmann K, Nilius B, Owsianik G, Schreiber R, Ousingsawat J, Sirianant L, Wanitchakool P, Bevers EM, Heemskerk JW (2014) Molecular functions of anoctamin 6 (TMEM16F): a chloride channel, cation channel or phospholipid scramblase? Pflügers Arch 466:407–414
Kunzelmann K, Cabrita I, Wanitchakool P, Ousingsawat J, Sirianant L, Benedetto R, Schreiber R (2016) Modulating Ca2+ signals: a common theme for TMEM16, Ist2, and TMC. Pflügers Arch 468:475–490
Lang F, Hoffmann EK (2012) Role of ion transport in control of apoptotic cell death. Compr Physiol 2:2037–2061
Lang F, Foller M, Lang K, Lang P, Ritter M, Vereninov A, Szabo I, Huber SM, Gulbins E (2007) Cell volume regulatory ion channels in cell proliferation and cell death. Methods Enzymol 428:209–225
Lee EL, Shimizu T, Ise T, Numata T, Kohno K, Okada Y (2007) Impaired activity of volume-sensitive Cl− channel is involved in cisplatin resistance of cancer cells. J Cell Physiol 211:513–521
L’hoste S, Chargui A, Belfodil R, Corcelle E, Duranton C, Rubera I, Poujeol C, Mograbi B, Tauc M, Poujeol P (2010) CFTR mediates apoptotic volume decrease and cell death by controlling glutathione efflux and ROS production in cultured mice proximal tubules. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 298:F435–F453
L’hoste S, Chargui A, Belfodil R, Duranton C, Rubera I, Mograbi B, Poujeol C, Tauc M, Poujeol P (2009) CFTR mediates cadmium-induced apoptosis through modulation of ROS level in mouse proximal tubule cells. Free Radic Biol Med 46:1017–1031
Linsdell P, Hanrahan JW (1998) Glutathione permeability of CFTR. Am J Physiol 275:C323–C326
Maeno E, Ishizaki Y, Kanaseki T, Hazama A, Okada Y (2000) Normotonic cell shrinkage because of disordered volume regulation is an early prerequisite to apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:9487–9492
Maisonneuve P, Marshall BC, Knapp EA, Lowenfels AB (2013) Cancer risk in cystic fibrosis: a 20-year nationwide study from the United States. J Natl Cancer Inst 105:122–129
Martins JR, Faria D, Kongsuphol P, Reisch B, Schreiber R, Kunzelmann K (2011) Anoctamin 6 is an essential component of the outwardly rectifying chloride channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:18168–18172
Milenkovic A, Brandl C, Milenkovic VM, Jendrike T, Sirianant L, Wanitchakool P, Zimmermann S, Reif CM, Horling F, Schrewe H et al (2015) Bestrophin1 is the volume-regulated anion channel in mouse sperm and human retinal pigment epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:E2630–E2639
Namkung W, Finkbeiner WE, Verkman AS (2010) CFTR-adenylyl cyclase I association is responsible for UTP activation of CFTR in well-differentiated primary human bronchial cell cultures. Mol Biol Cell 21:2639–2648
Namkung W, Phuan PW, Verkman AS (2011) TMEM16A inhibitors reveal TMEM16A as a minor component of CaCC conductance in airway and intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 286:2365–2374
Nilius B (2004) Is the volume-regulated anion channel VRAC a “water-permeable” channel? Neurochem Res 29:3–8
Noe J, Petrusca D, Rush N, Deng P, VanDemark M, Berdyshev E, Gu Y, Smith P, Schweitzer K, Pilewsky J et al (2009) CFTR regulation of intracellular pH and ceramides is required for lung endothelial cell apoptosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 41:314–323
Okada Y, Shimizu T, Maeno E, Tanabe S, Wang X, Takahashi N (2006) Volume-sensitive chloride channels involved in apoptotic volume decrease and cell death. J Membr Biol 209:21–29
Okiyoneda T, Barriere H, Bagdany M, Rabeh WM, Du K, Hohfeld J, Young JC, Lukacs GL (2010) Peripheral protein quality control removes unfolded CFTR from the plasma membrane. Science 329:805–810
Ousingsawat J, Wanitchakool P, Kmit A, Romao AM, Jantarajit W, Schreiber S, Kunzelmann K (2015) Anoctamin 6 mediates effects essential for innate immunity downstream of P2X7-receptors in macrophages. Nat Commun 6:6245
Pedersen SF, Klausen TK, Nilius B (2015) The identification of VRAC (volume regulated anion channel): an amazing Odyssey. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 213:868–881
Planells-Cases R, Lutter D, Guyader C, Gerhards NM, Ullrich F, Elger DA, Kucukosmanoglu A, Xu G, Voss FK, Reincke SM et al (2015) Subunit composition of VRAC channels determines substrate specificity and cellular resistance to Pt-based anti-cancer drugs. EMBO J 34:2993–3008
Poulsen KA, Andersen EC, Hansen CF, Klausen TK, Hougaard C, Lambert IH, Hoffmann EK (2010) Deregulation of apoptotic volume decrease and ionic movements in multidrug-resistant tumor cells: role of chloride channels. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 298:C14–C25
Qiu Z, Dubin AE, Mathur J, Tu B, Reddy K, Miraglia LJ, Reinhardt J, Orth AP, Patapoutian A (2014) SWELL1, a plasma membrane protein, is an essential component of volume-regulated anion channel. Cell 157:447–458
Rottner M, Tual-Chalot S, Mostefai HA, Andriantsitohaina R, Freyssinet JM, Martinez MC (2011) Increased oxidative stress induces apoptosis in human cystic fibrosis cells. PLoS One 6:e24880
Rubera I, Duranton C, Melis N, Cougnon M, Mograbi B, Tauc M (2013) Role of CFTR in oxidative stress and suicidal death of renal cells during cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Cell Death Dis 4:e817
Schreiber R, Faria D, Skryabin BV, Rock JR, Kunzelmann K (2014) Anoctamins support calcium-dependent chloride secretion by facilitating calcium signaling in adult mouse intestine. Pflügers Arch 467:1203–1213
Shen MR, Droogmans G, Eggermont J, Voets T, Ellory JC, Nilius B (2000) Differential expression of volume-regulated anion channels during cell cycle progression of human cervical cancer cells. J Physiol 529(Pt 2):385–394
Shimizu T, Iehara T, Sato K, Fujii T, Sakai H, Okada Y (2013) TMEM16F is a component of a Ca2+-activated Cl− channel but not a volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying Cl− channel. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 304:C748–C759
Sirianant L, Ousingsawat J, Wanitchakool P, Schreiber R, Kunzelmann K (2015) Cellular volume regulation by anoctamin 6:Ca2+, phospholipase A2, osmosensing. Pflügers Arch 468:335–349
Sirianant L, Wanitchakool P, Ousingsawat J, Benedetto R, Zormpa A, Cabrita I, Schreiber R, Kunzelmann K (2016) Non-essential contribution of LRRC8A to volume regulation. Pflügers Arch 468:805–816
Sorensen BH, Thorsteinsdottir UA, Lambert IH (2014) Acquired cisplatin resistance in humane ovarian cancer A2780 cells correlates with shift in taurine homeostasis and ability to volume regulate. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 307:C1071–C1080
Suzuki J, Umeda M, Sims PJ, Nagata S (2010) Calcium-dependent phospholipid scrambling by TMEM16F. Nature 468:834–838
Syeda R, Qiu Z, Dubin AE, Murthy SE, Florendo MN, Mason DE, Mathur J, Cahalan SM, Peters EC, Montal M et al (2016) LRRC8 proteins form volume-regulated anion channels that sense ionic strength. Cell 164:499–511
Szabo I, Lepple-Wienhues A, Kaba KN, Zoratti M, Gulbins E, Lang F (1998) Tyrosine kinase-dependent activation of a chloride channel in CD95-induced apoptosis in T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6169–6174
Tait SW, Oberst A, Quarato G, Milasta S, Haller M, Wang R, Karvela M, Ichim G, Yatim N, Albert ML et al (2013) Widespread mitochondrial depletion via mitophagy does not compromise necroptosis. Cell Rep 5:878–885
Tian Y, Schreiber R, Kunzelmann K (2012) Anoctamins are a family of Ca2+ activated Cl− channels. J Cell Sci 125:4991–4998
Uramoto H, Okada T, Okada Y (2012) Protective role of cardiac CFTR activation upon early reperfusion against myocardial infarction. Cell Physiol Biochem 30:1023–1038
Valverde MA, O’Briens JA, Sepulveda FV, Ratcliff RA, Evans MJ, Colledge WH (1995) Impaired cell volume regulation in intestinal crypt epithelia of cystic fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 92:9038–9041
Vitzthum C, Clauss WG, Fronius M (2015) Mechanosensitive activation of CFTR by increased cell volume and hydrostatic pressure but not shear stress. Biochim Biophys Acta 1848:2942–2951
Voets T, Droogmans G, Raskin G, Eggermont J, Nilius B (1999) Reduced intracellular ionic strength as the initial trigger for activation of endothelial volume-regulated anion channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:5298–5303
Voss FK, Ullrich F, Munch J, Lazarow K, Lutter D, Mah N, Andrade-Navarro MA, von Kries JP, Stauber T, Jentsch TJ (2014) Identification of LRRC8 heteromers as an essential component of the volume-regulated anion channel VRAC. Science 344:634–638
Wanitchakool P, Wolf L, Koehl G, Sirianant L, Gaumann A, Schreiber R, Duvvuri U, Kunzelmann K (2014) Role of anoctamins in cancer and apoptosis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 369:20130096
Yang H, Kim A, David T, Palmer D, Jin T, Tien J, Huang F, Cheng T, Coughlin SR, Jan YN et al (2012) TMEM16F forms a Ca(2+)-activated cation channel required for lipid scrambling in platelets during blood coagulation. Cell 151:111–122
Yu H, Zeidan YH, Wu BX, Jenkins RW, Flotte TR, Hannun YA, Virella-Lowell I (2009) Defective acid sphingomyelinase pathway with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 41:367–375
Zampighi GA, Kreman M, Boorer KJ, Loo DD, Bezanilla F, Chandy G, Hall JE, Wright EM (1995) A method for determining the unitary functional capacity of cloned channels and transporters expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Membr Biol 148:65–78
Zeuthen T, Belhage B, Zeuthen E (2006) Water transport by Na+-coupled cotransporters of glucose (SGLT1) and of iodide (NIS). The dependence of substrate size studied at high resolution. J Physiol 570:485–499
Zhang WK, Wang D, Duan Y, Loy MM, Chan HC, Huang P (2010) Mechanosensitive gating of CFTR. Nat Cell Biol 12:507–512
Acknowledgments
Supported by DFG SFB699-A7/A12, DFG KU756/12-1, and Volkswagenstiftung AZ 87 499. We thank Dr. Johan Heemskerk and Dr. Eduard Bevers (Department of Cell Biochemistry of Thrombosis and Hemostasis Biochemistry, Cardiovascular Research Institute Maastricht; CARIM), for supplying the B-lymphocyte cell lines. HCT116 control cells and HCT116 cells lacking expression of LRRC8A were generously provided by Dr. F. Voss/Prof. Dr. T. Jentsch (FMP, Berlin). The assistance by Mss. B. Wild, P. Seeberger, and E. Tartler is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue: Ion Channels, Transporters and Cancer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wanitchakool, P., Ousingsawat, J., Sirianant, L. et al. Cl− channels in apoptosis. Eur Biophys J 45, 599–610 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-016-1140-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-016-1140-3