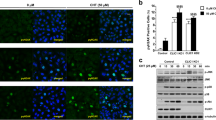
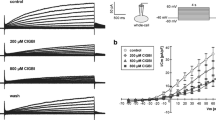
Abstract
The anti-cancer drug cisplatin induces apoptosis by damaging DNA. Since a stilbene-derivative blocker of Cl−/HCO −3 exchangers and Cl− channels, SITS, is known to induce cisplatin resistance in a manner independent of intracellular pH and extracellular HCO −3 , we investigated the relation between cisplatin-induced apoptosis and Cl− channel activity in human adenocarcinoma KB cells. A stilbene derivative, DIDS, reduced cisplatin-induced caspase-3 activation and cell death, which were detected over 18 h after treatment with cisplatin. DIDS was also found to reduce sensitivity of KB cells to 5-day exposure to cisplatin. Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings showed that KB cells functionally express volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying (VSOR) Cl− channels which are activated by osmotic cell swelling and sensitive to DIDS. Pretreatment of the cells with cisplatin for 12 h augmented the magnitude of VSOR Cl− current. Thus, it is concluded that cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in KB cells is associated with augmented activity of a DIDS-sensitive VSOR Cl− channel and that blockade of this channel is, at least in part, responsible for cisplatin resistance induced by a stilbene derivative.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barry M.A., Behnke A., Eastman A. 1990. Activation of programmed cell death (apoptosis) by cisplatin, other anticancer drugs, toxins and hyperthermia. Biochem. Pharmacol. 40:2353–2362
Chu G. 1994. Cellular responses to cisplatin. The roles of DNA binding proteins and DNA repair. J. Biol. Chem. 269:787–790
Cummings B.S., Schnellmann R.G. 2002. Cisplatin-induced renal cell apoptosis: caspase 3-dependent and -independent pathways. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 302:8–17
Deschesnes R.G., Huot J., Valerie K., Landry J. 2001. Involvement of p38 in apoptosis-associated membrane blebbing and nuclear condensation. Mol. Biol. Cell 12:1569–1582
Eastman A. 1990. Activation of programmed cell death by anticancer gents: cisplatin as a model system. Cancer Cells 2:275–280
Fan H.-T., Morishima S., Kida H., Okada Y. 2001. Phloretin differentially inhibits volume-sensitive and cAMP-activated, but not Ca-activated, Cl− channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 133:1096–1106
Fujii R., Mutoh M., Niwa K., Yamada K., Aikou T., Nakagawa M., Kuwano M., Akiyama S. 1994. Active efflux system for cisplatin in cisplatin-resistant human KB cells. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 85:426–433
Jamieson E.R., Lippard S.J. 1999. Structure, recognition, and processing of cisplatin-DNA adducts. Chem. Rev. 99:2467–2498
Kharbanda S., Ren R., Pandey P., Shafman T.D., Feller S.M., Weichselbaum R., Kufe D. 1995. Activation of the c-Abl tyrosine kinase in the stress response to DNA-damaging agents. Nature 376:785–788
Kharbanda S., Yuan Z.M., Weichselbaum R., Kufe D. 1998. Determination of cell fate by c-Abl activation in the response to DNA damage. Oncogene 17:3309–3318
Kharbanda S., Pandey P., Yamauchi T., Kumar S., Kaneki M., Kumar V., Bharti A., Yuan Z.M., Ghanem L., Rana A., Weichselbaum R., Johnson G., Kufe D. 2000. Activation of MEK kinase 1 by the c-Abl protein tyrosine kinase in response to DNA damage. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:4979–4989
Kubo M., Okada Y. 1992. Volume-regulatory Cl− channel currents in cultured human epithelial cells. J. Physiol. 456:351–371
Laurencot C.M., Kennedy K.A. 1995. Influence of pH on the cytotoxicity of cisplatin in EMT6 mouse mammary tumor cells. Oncol Res. 7:371–379
Loehrer P.J., Einhorn L.H. 1984. Drugs five years later. Cisplatin. Ann. Intern. Med. 100:704–713
Maeno E., Ishizaki Y., Kanaseki T., Hazama A., Okada Y. 2000. Normotonic cell shrinkage because of disordered volume regulation is an early prerequisite to apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:9487–9492
Matsuo K., Khono K., Takano H., Sato S., Kiue A., Kuwano M. 1990. Reduction of drug accumulation and DNA topoisomerase II activity in acquired teniposide-resistant human cancer KB cell lines. Cancer Res. 50:5819–5824
Miller S.E., House D.A. 1990. The hydrolysis products of cis-dichlorodiammineplatinum (II). 3. Hydrolysis kinetics at physiological pH. Inorg. Chim. Acta 173:53–60
Okada Y. 1997. Volume expansion-sensing outward-rectifier Cl− channel: fresh start to the molecular identity and volume sensor. Am. J. Physiol. 273:C755–C789
Okada Y., Maeno E., Shimizu T., Dezaki K., Wang J., Morishima S. 2001. Receptor-mediated control of regulatory volume decrease (RVD) and apoptotic volume decrease (AVD). J. Physiol. 532:3–16
Pandey P., Raingeaud J., Kaneki M., Weichselbaum R., Davis R.J., Kufe D., Kharbanda S. 1996. Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase by c-Abl-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 271:23775–23779
Persons D.L., Yazlovitskaya E.M., Cui W., Felling J.C. 1999. Cisplatin-induced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in ovarian carcinoma cells: inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity increases sensitivity to cisplatin. Clin. Cancer Res. 5:1007–1014
Ravi R., Somani S.M., Rybak L.P. 1995. Mechanism of cisplatin ototoxicity: antioxidant system. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 76:386–394
Sanchez-Prieto R., Rojas J.M., Taya Y., Gutkind J.S. 2000. A role for the p38 mitogen-acitvated protein kinase pathway in the transcriptional activation of p53 on genotoxic stress by chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Res. 60:2464–2472
Sanchez-Perez I., Perona R. 1999. Lack of c-Jun activity increases survival to cisplatin. FEBS lett. 453:151–158
Sanchez-Perez I., Martinez-Gomariz M., William S.D., Keyse S.M., Perona R. 2000. CL100/MKP-1 modulates JNK activation and apoptosis in response to cisplatin. Oncogene 19:5142–5152
Shimizu T., Morishima S., Okada Y. 2000. Ca+-sensing receptor-mediated regulation of volume-sensitive Cl− channels inhuman epithelial cells. J. Physiol. 528:457–472
Shimizu T., Numata T., Okada Y. 2004. A role of reactive oxygen species in apoptotic activation of volume-sensitive Cl− channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:6770–6773
Sklar M.D., Prochownik E.V. 1991. Modulation of cis-platinum resistance in Friend erythroleukemia cells by c-myc. Cancer Res. 51:2118–2123
Sorenson C.M., Barry M.A., Eastman A. 1990. Analysis of events associated with cell cycle arrest at G2 phase and cell death induced by cisplatin. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 82:749–755
Thornberry N.A. 1994. Interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme. Methods Enzymol. 244:615–631
Tsuruya K., Tokumoto M., Ninomiya T., Hirakawa M., Masutani K., Taniguchi M., Fukuda K., Kanai H., Hirakata H., Iida M. 2003. Antioxidant ameliorates cisplatin-induced renal tubular cell death through inhibition of death receptor-mediated pathways. Am. J. Physiol. 285:F208–F218
Tsutsumishita Y., Onda T., Okada K., Takeda M., Endou H., Futaki S., Niwa M. 1998. Involvement of H2O2 production in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 242:310–312
Wang X., Martindale J.L., Holbrook N.J. 2000. Requirement for ERK activation in cisplatin-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 275:39435–39443
Worrell R.T., Butt A.G., Cliff W.H., Frizzell R.A. 1989. A volume-sensitive chloride conductance inhuman colonic cell line T84. Am. J. Physiol. 256:C1111–C1119
Yarbrough J.W., Merryman J.I., Barnhill M.A., Hahn K.A. 1999. Inhibitors of intracellular chloride regulation induce cisplatin resistance in canine osteosarcoma cells. In Vivo 13:375–384
Yoshida K., Weichselbaum R., Kharbanda S., Kufe D. 2000. Role for Lyn tyrosine kinase as a regulator of stress-activated protein kinase activity in response to DNA damage. Mol Cell. Biol. 20:5370–5380
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to E. Maeno, H. Liu and T. Numata for discussion, M. Ohara, S. Tanaka and K. Shigemoto for technical assistance, and T. Okayasu for secretarial assistance. This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from MEXT of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ise, T., Shimizu, T., Lee, E. et al. Roles of Volume-sensitive Cl− Channel in Cisplatin-induced Apoptosis in Human Epidermoid Cancer Cells. J Membrane Biol 205, 139–145 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-005-0779-y
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-005-0779-y