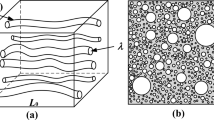
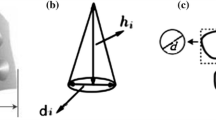
Abstract
A fractal theory employing a box-counting method was used to describe hydrogen gas diffusion into membrane pores in the meso-porosity regime. The diffusion of the gas into the membrane pore network confirmed the existence of fractal structure in the system. Two fractal identities to represent irregularity and roughness of pore surface and tortuosity of the membrane were obtained and analyzed. Their influences on hydrogen permeability were also evaluated. The fractal permeability model that reflects different hydrogen diffusion mechanisms was calculated and compared with that of the state of the art Kozeny–Carman equation.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ao :
-
The unit membrane area, cm2
- C:
-
Kozeny–Carman constant defined by Eq. (29)
- De:
-
Effective diffusivity, cm2 s−1
- dE :
-
Euclid dimension
- Df:
-
Area fractal dimension
- dg :
-
Molecular collision diameter of gas, cm
- Dt:
-
Tortuosity fractal dimension
- F:
-
Gas flow through a single pore, cm3 s−1
- К :
-
Permeability, mol cm cm−2 s−1 Pa−1
- kB :
-
Boltzmann constant, 1.38 × 10−23 J K−1
- Kn :
-
Knudsen number
- L:
-
Length scale, cm
- Lo:
-
Representative length of a straight capillary, cm
- ls :
-
Length of the cell space, cm
- M:
-
Mole molecule weight, g mol−1
- N:
-
Number of pores
- n:
-
Kozeny–Carman constant defined by Eq. (28)
- P:
-
Total pressure, Pa
- P:
-
Partial pressure, Pa
- Q:
-
Total gas flow through a membrane, m3 s−1
- R:
-
Gas constant, 8.314 × 107 g cm2 s−2 mol−1 K−1
- T:
-
Temperature, K
- V:
-
Volume, ml g−1
- x:
-
Pore diameter, cm
- f :
-
Loading factor, mol g−1, defined by Eq. (30)
- r or rp :
-
Membrane pore radius, cm defined by Eq. (30)
- rg :
-
Molecular radius of gas species, cm, defined by Eq. (30)
- Δ:
-
Different
- λ:
-
Mean free path, cm
- μ:
-
Viscosity, Pa s
- ρ:
-
Density, g cm−3
- ε:
-
Porosity
- A:
-
Gas A
- K:
-
Knudsen
- m:
-
Mean
- max:
-
Maximum
- min:
-
Minimum
- mn:
-
Membrane
- P:
-
Poiseulle
- p:
-
Pore
References
Krohn CE, Thompson AH (1986) Fractal sandstone pores: automated measurements using scanning-electron-microscope images. Phys Rev B 33:63
Mandelbrot BB (1982) The fractal geometry of nature. WH Freeman, New York, 23–57, 117–119
Warren TL, Krajcinovic D (1996) Random cantor set models for the elastic–perfectly plastic contact of rough surfaces. Wear 196:1
Borodich FM, Mosolov AB (1992) Fractal roughness in contact problems. J Appl Math 56:681
Majumdar A, Bhushan B (1990) Role of mechanical properties and surface texture in the real area of contact of magnetic rigid disks. J Tribol 112:205
Pitchumani R, Ramakrishnan B (1999) A fractal geometry model for evaluating permeabilities of porous preforms used in liquid composite molding. Int J Heat Mass Transf 42:2219
Yu BM (2001) Comments on a fractal geometry model for evaluating permeabilities of porous preforms used in liquid composite molding. Int J Heat Mass Transf 44:2787
Yu B, Li J (2001) Some fractal characters of porous media. Fractals 9:365
Yu B, Cheng P (2002) A fractal permeability model for bi-dispersed porous media. Int J Heat Mass Transf 45:2983–2993
Yu BM, Lee LJ (2002) A fractal in-plane perme- ability model for fabrics. Polym Compos 23:201
Yu BM, Li JH, Zhang DM (2003) A fractal trans-plane permeability model for textile fabrics. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 30:127
Yu BM, Lee LJ (2000) A simplified in-plane permeability model for textile fabrics. Polym Compos 21:660
Yu BY, Liu W (2004) Fractal analysis of permeabilities for porous media. AIChE J 50:46
Yu BM, Zou MQ, Feng YJ (2005) Permeability of fractal porous media by monte carlo simulations. Int J Heat Mass Transf 48:2787
Meng FG, Zhang HM, Li YS, Zhang XW, Yang FL (2005) Application of fractal permeation model to investigate membrane fouling in membrane bioreactor. J Membr Sci 262:107
He GL, Zhao ZC, Ming PW, Abuliti A, Yin CY (2007) A fractal model for predicting permeability and liquid water relative permeability in the gas diffusion layer (GDL) of PEMFCs. J Power Sources 163:846
Zhang LZ (2008) A fractal model for gas permeation through porous membranes. Int J Heat Mass Transf 51:5288
Wiheeb AD et al (2013) Pore morphological identification of hydrotalcite from nitrogen adsorption. Chaos Soliton Fract 49:7
Cussler EL (2000) Diffusion-mass transfer in fluid systems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Baker RW (2000) Membrane technology and applications. McGraw-Hill, New York
Ahmad AL, Othman MR, Mukhtar H (2004) H2 separation from binary gas mixture using coated alumina-titania membrane by sol-gel technique at high temperature region. Int J Hydrogen Energy 29:817
Acosta JL, Comacho AF (2009) Heat and mass transfer, transport and mechanics. Nova Science Publishers, New York
Othman MR, Kim J (2008) Permeation characteristics of H2, N2 and CO2 in a binary mixture across meso-porous Al2O3 and Pd-Al2O3 asymmetric composites. Micro Meso Mater 112:403
Othman MR, Mukhtar H, Ahmad AL (2001) Permeabilities of gases in porous inorganic membrane. Int Conf Adv Strategic Technol Proc 1:475
Wiheeb AD, Ahmad MA, Murat MN, Kim J, Othman MR (2014) Identification of Molecular Transport Mechanisms in Micro-Porous Hydrotalcite–Silica Membrane Transp Porous Med.104:133
Wiheeb AD, Ahmad MA, Murat MN, Kim J, Othman MR (2014) Predominant Gas transport in microporous hydrotalcite–silica membrane. Transp Porous Med 102:59
Wiheeb AD, Ahmad MA, Murat MN, Kim J, Othman MR (2014) The effect of hydrotalcite content in microporous composite membrane on gas permeability and selectivity. Sep Sci Technol 49:1309
Wiheeb AD, Ahmad MA, Murat MN, Kim J, Othman MR (2014) The declining affinity of microporous hydrotalcite-silica membrane for carbon dioxide. J Porous Med 17:159
Shi Y, Shiao J, Pan M, Yuan R (2006) A fractal permeability model for the gas diffusion layer of PEM fuel cells. J Power Sources 160:277
Othman MR, Helwani Z, Martunus (2010) Simulated fractal permeability for porous membranes. Appl Math Model 34:2452
Othman MR, Martunus, Fernando WJN, Kim J (2010) Fractal rate of adsorption and surface diffusivity of carbon dioxide across mesoporous adsorbents. Adsorpt Sci Technol 27:893
Othman MR, Martunus, Fernando WJN, Kim J (2010) Thermodynamic functions of temperature/pressure induced sorption across micro-porous membranes: Case study of methane and carbon dioxide. Adsorpt Sci Technol 28:179
Othman MR, Tan SC, Bhatia S, Fernando WJN (2011) Separability of hydrogen from hydrogen-carbon dioxide mixture across silica-silicalite-1 film. Fuel Proc Technol 92:428
Martunus, Helwani Z, Wiheeb AD, Kim J, Othman MR (2012) A flow through behavior of gas across meso-porous membranes. Micro Meso Mater 163:115
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2013R1A2A2A01014540).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Helwani, Z., Wiheeb, A.D., Shamsudin, I.K. et al. The effects of fractality on hydrogen permeability across meso-porous membrane. Heat Mass Transfer 51, 751–758 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-014-1445-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-014-1445-7