Abstract
Key message
Sixteen major QTLs regulating maize kernel traits were mapped in multiple environments and one of them, qKW - 9.2 , was restricted to 630 Kb, harboring 28 putative gene models.
Abstract
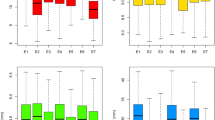
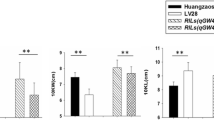
To elucidate the genetic basis of kernel traits, a quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis was conducted in a maize recombinant inbred line population derived from a cross between two diverse parents Zheng58 and SK, evaluated across eight environments. Construction of a high-density linkage map was based on 13,703 single-nucleotide polymorphism markers, covering 1860.9 cM of the whole genome. In total, 18, 26, 23, and 19 QTLs for kernel length, width, thickness, and 100-kernel weight, respectively, were detected on the basis of a single-environment analysis, and each QTL explained 3.2–23.7 % of the phenotypic variance. Sixteen major QTLs, which could explain greater than 10 % of the phenotypic variation, were mapped in multiple environments, implying that kernel traits might be controlled by many minor and multiple major QTLs. The major QTL qKW-9.2 with physical confidence interval of 1.68 Mbp, affecting kernel width, was then selected for fine mapping using heterogeneous inbred families. At final, the location of the underlying gene was narrowed down to 630 Kb, harboring 28 putative candidate-gene models. This information will enhance molecular breeding for kernel traits and simultaneously assist the gene cloning underlying this QTL, helping to reveal the genetic basis of kernel development in maize.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso-Blanco C, Koornneef M (2000) Naturally occurring variation in Arabidopsis: an underexploited resource for plant genetics. Trends Plant Sci 5:22–29
Austin D, Lee M (1996) Comparative mapping in F2:3 and F6:7 generations of quantitative trait loci for grain yield and yield components in maize. Theor Appl Genet 92:817–826
Bai X, Luo L, Yan W, Kovi MR, Zhan W, Xing Y (2010) Genetic dissection of rice grain shape using a recombinant inbred line population derived from two contrasting parents and fine mapping a pleiotropic quantitative trait locus qGL7. BMC Genet 11:16
Bao J (2014) Genes and QTLs for rice grain quality improvement. In: Yan WG, Bao JS (ed) Rice-germplasm genetics and improvement, chap 9. InTech, pp 239–278
Blummel M, Grings E, Erenstein O (2013) Potential for dual-purpose maize varieties to meet changing maize demands: synthesis. Field Crop Res 153:107–112
Borrás L, Gambín BL (2010) Trait dissection of maize kernel weight: towards integrating hierarchical scales using a plant growth approach. Field Crop Res 118:1–12
Brown TA, Jones MK, Powell W, Allaby RG (2009) The complex origins of domesticated crops in the Fertile Crescent. Trends Ecol Evol 24:103–109
Coles ND (2009) The genetic architecture of maize photoperiod sensitivity revealed by recombinant inbred line, backcross, and heterogeneous inbred family populations. Ph.D. thesis, Department of Crop Science, North Carolina State University, Raleigh. http://www.lib.ncsu.edu/resolver/1840.16/4750
Doerge RW, Churchill GA (1996) Permutation tests for multiple loci affecting a quantitative character. Genetics 142:285–294
Fan C, Xing Y, Mao H, Lu T, Han B, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q (2006) GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet 112:1164–1171
Guo J, Su G, Zhang J, Wang G (2008) Genetic analysis and QTL mapping of maize yield and associate agronomic traits under semi-arid land condition. Afr J Biotechnol 7:12
Gupta PK, Rustgi S, Kumar N (2006) Genetic and molecular basis of grain size and grain number and its relevance to grain productivity in higher plants. Genome 49:565–571
Hong Y, Chen L, Du LP, Su Z, Wang J, Ye X, Qi L, Zhang Z (2014) Transcript suppression of TaGW2 increased grain width and weight in bread wheat. Funct Integr Genomics 14:341–349
Hu Z, He H, Zhang S, Sun F, Xin X, Wang W, Qian X, Yang J, Luo X (2012) A Kelch motif-containing serine/threonine protein phosphatase determines the large grain QTL trait in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 54:979–990
Huang R, Jiang L, Zheng J, Wang T, Wang H, Huang Y, Hong Z (2013) Genetic bases of rice grain shape: so many genes, so little known. Trends Plant Sci 18:218–226
Lai J, Li R, Xu X, Jin W, Xu M, Zhao H, Xiang Z, Song W, Ying K, Zhang M (2010) Genome-wide patterns of genetic variation among elite maize inbred lines. Nat Genet 42:1027–1030
Li Y, Wang Y, Shi Y, Song Y, Wand T, Li Y (2009) Correlation analysis and QTL mapping for traits of kernel structure and yield components in maize. Sci Agric Sin 42:408–418
Li M, Guo X, Zhang M, Wang X, Zhang G, Tian Y, Wang Z (2010a) Mapping QTLs for grain yield and yield components under high and low phosphorus treatments in maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Sci 178:454–462
Li Q, Li L, Yang X, Warburton ML, Bai G, Dai J, Li J, Yan J (2010b) Relationship, evolutionary fate and function of two maize co-orthologs of rice GW2 associated with kernel size and weight. BMC Plant Biol 10:143
Li Q, Yang X, Bai G, Warburton ML, Mahuku G, Gore M, Dai J, Li J, Yan J (2010c) Cloning and characterization of a putative GS3 ortholog involved in maize kernel development. Theor Appl Genet 120:753–763
Li Y, Fan C, Xing Y, Jiang Y, Luo L, Sun L, Shao D, Xu C, Li X, Xiao J (2011) Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat Genet 43:1266–1269
Lid SE, Gruis D, Jung R, Lorentzen JA, Ananiev E, Chamberlin M, Niu X, Meeley R, Nichols S, Olsen OA (2002) The defective kernel 1 (dek1) gene required for aleurone cell development in the endosperm of maize grains encodes a membrane protein of the calpain gene superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:5460–5465
Liu XH, Zheng P, Tan ZB, Li Z, He C (2010) Quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping for 100-kernel weight of maize (Zea mays L.) under different nitrogen regimes. Afr J Biotechnol 49:8283–8289
Liu Z, Ji H, Cui Z, Wu X, Duan L, Feng X, Tang J (2011) QTL detected for grain-filling rate in maize using a RIL population. Mol Breed 27:25–36
Liu Y, Wang L, Sun C, Zhang Z, Zheng Y, Qiu F (2014) Genetic analysis and major QTL detection for maize kernel size and weight in multi-environments. Theor Appl Genet 127:1019–1037
Liu J, Deng M, Guo H, Raihan S, Luo J, Xu Y, Dong X, Yan J (2015) Maize orthologs of rice GS5 and their trans-regulator are associated with kernel development. J Integr Plant Biol. doi:10.1111/jipb.12421
Mackay TF, Stone EA, Ayroles JF (2009) The genetics of quantitative traits: challenges and prospects. Nat Rev Genet 10:565–577
Maitz M, Santandrea G, Zhang Z, Lal S, Hannah LC, Salamini F, Thompson RD (2000) rgf1, a mutation reducing grain filling in maize through effects on basal endosperm and pedicel development. Plant J 23:29–42
Messmer R, Fracheboud Y, Bänziger M, Vargas M, Stamp P, Ribaut JM (2009) Drought stress and tropical maize: QTL-by-environment interactions and stability of QTLs across environments for yield components and secondary traits. Theorl Appl Genet 119:913–930
Monaco MK, Sen TZ, Dharmawardhana PD, Ren L, Schaeffer M, Naithani S, Amarasinghe V, Thomason J, Harper L, Gardiner J, Cannon EK (2013) Maize metabolic network construction and transcriptome analysis. Plant Genome 6:1–12
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Nikolić A, Anđelković V, Dodig D, Mladenović-Drinić S, Kravić N, Ignjatović-Micić D (2013) Identification of QTL-s for drought tolerance in maize, II: yield and yield components. Genetika 45:341–350
Pan Q, Li L, Yang X, Tong H, Xu S, Li Z, Li W, Muehlbauer GJ, Li J, Yan J (2015) Genome wide recombination dynamics are associated with phenotypic variation in maize. New Phytol. doi:10.1111/nph.13810
Paterson AH, De Verna JW, Lanini B, Tanksley SD (1990) Fine mapping of quantitative trait loci using selected overlapping recombinant chromosomes, in an interspecies cross of tomato. Genetics 124:735–742
Paterson AH, Lin YR, Li Z, Schertz KF, Doebley JF, Pinson SR, Liu SC, Stansel JW, Irvine JE (1995) Convergent domestication of cereal crops by independent mutations at corresponding genetic loci. Science 269:1714–1718
Peng B, Li Y, Wang Y, Liu C, Liu Z, Tan W, Zhang Y, Wang D, Shi Y, Sun B (2011) QTL analysis for yield components and kernel-related traits in maize across multi-environments. Theor Appl Genet 122:1305–1320
Poehlman JM, Sleper DA (1995) Breeding soybean. In: Breeding field crops, 4th edn. Iowa State University Press, Ames, pp 300–318
Pozzi C, Rossini L, Vecchietti A, Salamini F (2004) Gene and genome changes during domestication of cereals. In: Gupta PK, Varshney RK et al (eds) Cereal genomics. Springer, pp 165–198
Prado SA, César G, López M, Senior L, Borrás L (2014) The genetic architecture of maize (Zea mays L.) kernel weight determination. G3 (Bethesda) 4:1611–1621
Qi X, Zhao Y, Jiang L, Cui Y, Wang Y, Liu B (2009) QTL analysis of kernel soluble sugar content in super sweet corn. Afr J Biotechnol 8:6913–6917
Qi P, Lin YS, Song XJ, Shen JB, Huang W, Shan JX, Zhu MZ, Jiang L, Gao JP, Lin HX (2012) The novel quantitative trait locus GL3. 1 controls rice grain size and yield by regulating Cyclin-T1; 3. Cell Res 22:1666–1680
Ramya P, Chaubal A, Kulkarni K, Gupta L, Kadoo N, Dhaliwal H, Chhuneja P, Lagu M, Gupt V (2010) QTL mapping of 1000-kernel weight, kernel length, and kernel width in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Appl Genet 51:421–429
Revilla P, Butrón A, Malvar R, Ordás R (1999) Relationship among kernel weight, early vigor, and growth in maize. Crop Sci 39:654–658
Ross AJ, Hallauer AR, Lee M (2006) Genetic analysis of traits correlated with maize ear length. Maydica 151(2):301
Sanguinetti CJ, Dias Neto E, Simpson AJG (1994) Rapid silver staining and recovery of PCR products separated on polyacrylamide gels. Biotechniques 17:915–919
Shomura A, Izawa T, Ebana K, Ebitani T, Kanegae H, Konishi S, Yano M (2008) Deletion in a gene associated with grain size increased yields during rice domestication. Nat Genet 40:1023–1028
Song XJ, Ashikari M (2008) Toward an optimum return from crop plants. Rice 1:135–143
Song XJ, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu MZ, Lin HX (2007) A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat Genet 39:623–630
SPSS Inc. (1999) SPSS base 10.0 for Windows user’s guide. SPSS Inc., Chicago
Statista (2014) Worldwide production of grain in 2013, by type. http://www.statista.com/statistics/263977/world-grain-production-by-type/. Accessed 20 Aug 2015
Tang J, Yan J, Ma X, Teng W, Wu W, Dai J, Dhillon BS, Melchinger AE, Li J (2010) Dissection of the genetic basis of heterosis in an elite maize hybrid by QTL mapping in an immortalized F2 population. Theor Appl Genet 120:333–340
Tanksley SD (1988) Resolution of quantitative traits into Mendelian factors by using a complete linkage map of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Nature 335:6170
Team RC (2014) A language and environment for statistical computing 2012. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. ISBN 3-900051-07-0
Thévenot C, Simond-Côte E, Reyss A, Manicacci D, Trouverie J, Le Guilloux M, Ginhoux V, Sidicina F, Prioul J-L (2005) QTLs for enzyme activities and soluble carbohydrates involved in starch accumulation during grain filling in maize. J Exp Bot 56:945–958
Tuinstra M, Ejeta G, Goldsbrough P (1997) Heterogeneous inbred family (HIF) analysis: a method for developing near-isogenic lines that differ at quantitative trait loci. Theor Appl Genet 95:1005–1011
Wan X, Weng J, Zhai H, Wang J, Lei C, Liu X, Guo T, Jiang L, Su N, Wan J (2008) Quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis for rice grain width and fine mapping of an identified QTL allele gw-5 in a recombination hotspot region on chromosome 5. Genetics 179:2239–2252
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB (2010) Windows QTL cartographer 2.5. Department of statistics. North Carolina State University, Raleigh. http://www.statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm
Wang S, Wu K, Yuan Q, Liu X, Liu Z, Lin X, Zeng R, Zhu H, Dong G, Qian Q (2012) Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat Genet 44:950–954
Weng J, Gu S, Wan X, Gao H, Guo T, Su N, Lei C, Zhang X, Cheng Z, Guo X (2008) Isolation and initial characterization of GW5, a major QTL associated with rice grain width and weight. Cell Res 18:1199–1209
Xing Y, Zhang Q (2010) Genetic and molecular bases of rice yield. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:421–442
Xu Y (2010) Molecular plant breeding. CAB International, Wallingford
Yan B, Liu R, Li Y, Wang Y, Gao G, Zhang Q, Liu X, Jiang G, He Y (2014) QTL analysis on rice grain appearance quality, as exemplifying the typical events of transgenic or backcrossing breeding. Breed Sci 64:231
Yang X, Gao S, Xu S, Zhang Z, Prasanna BM, Li L, Li J, Yan J (2011) Characterization of a global germplasm collection and its potential utilization for analysis of complex quantitative traits in maize. Mol Breed 28:511–526
Yang W, Guo Z, Huang C, Duan L, Chen G, Jiang N, Fang W, Feng H, Xie W, Lian X, Wang G (2014) Combining high-throughput phenotyping and genome-wide association studies to reveal natural genetic variation in rice. Nat Commun 5:5087
Yu J, Buckler ES (2006) Genetic association mapping and genome organization of maize. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:155–160
Zeng ZB (1994) Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 136:1457–1468
Zhang X, Wang J, Huang J, Lan H, Wang C, Yin C, Wu Y, Tang H, Qian Q, Li J (2012) Rare allele of OsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:21534–21539
Zhang W, Sun P, He Q, Shu F, Wang J, Deng H (2013) Fine mapping of GS2, a dominant gene for big grain rice. Crop J 1:160–165
Zhang Z, Liu Z, Hu Y, Li W, Fu Z, Ding D, Li H, Qiao M, Tang J (2014) QTL analysis of kernel-related traits in maize using an immortalized F2 population. PLoS One 9:e89645
Acknowledgments
We thankfully acknowledge and greatly appreciate Mr. Xiongbing Yan for his admirable field work. This research was supported by the Genetically Modified Organisms Breeding Major Projects (2014ZX0800944B) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31222041).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by N. de Leon.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raihan, M.S., Liu, J., Huang, J. et al. Multi-environment QTL analysis of grain morphology traits and fine mapping of a kernel-width QTL in Zheng58 × SK maize population. Theor Appl Genet 129, 1465–1477 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-016-2717-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-016-2717-z