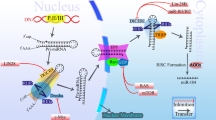
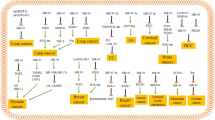
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are 20–22-nucleotide small endogenous non-coding RNAs which regulate gene expression at post-transcriptional level. In the last two decades, identification of almost 2600 miRNAs in human and their potential to be modulated opened a new avenue to target almost all hallmarks of cancer. miRNAs have been classified as tumor suppressors or oncogenes depending on the phenotype they induce, the targets they modulate, and the tissue where they function. miR-200c, an illustrious tumor suppressor, is one of the highly studied miRNAs in terms of development, stemness, proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), therapy resistance, and metastasis. In this review, we first focus on the regulation of miR-200c expression and its role in regulating EMT in a ZEB1/E-cadherin axis-dependent and ZEB1/E-cadherin axis-independent manner. We then describe the role of miR-200c in therapy resistance in terms of multidrug resistance, chemoresistance, targeted therapy resistance, and radiotherapy resistance in various cancer types. We highlight the importance of miR-200c at the intersection of EMT and chemoresistance. Furthermore, we show how miR-200c coordinates several important signaling cascades such as TGF-β signaling, PI3K/Akt signaling, Notch signaling, VEGF signaling, and NF-κB signaling. Finally, we discuss miR-200c as a potential prognostic/diagnostic biomarker in several diseases, but mainly focusing on cancer and its potential application in future therapeutics.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V (1993) The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75:843–854
Vella MC, Choi EY, Lin SY, Reinert K, Slack FJ (2004) The C. elegans microRNA let-7 binds to imperfect let-7 complementary sites from the lin-41 3‵UTR. Genes Dev 18:132–137
Kaufman EJ, Miska EA (2010) The microRNAs of Caenorhabditis elegans. Semin Cell Dev Biol 21:728–737
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2001) Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 294:853–858
Pasquinelli AE, Reinhart BJ, Slack F, Martindale MQ, Kuroda MI, Maller B, Hayward DC, Ball EE, Degnan B, Muller P et al (2000) Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 408:86–89
Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S (2014) miRBase: annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D68–73
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2009) Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 19:92–105
Trang P, Weidhaas JB, Slack FJ (2008) MicroRNAs as potential cancer therapeutics. Oncogene 27(Suppl 2):S52–57
Fasanaro P, Greco S, Ivan M, Capogrossi MC, Martelli F (2010) microRNA: emerging therapeutic targets in acute ischemic diseases. Pharmacol Ther 125:92–104
Hydbring P, Badalian-Very G (2013) Clinical applications of microRNAs. F1000Research 2:136
Li C, Feng Y, Coukos G, Zhang L (2009) Therapeutic microRNA strategies in human cancer. AAPS J 11:747–757
Hurteau GJ, Spivack SD, Brock GJ (2006) Potential mRNA degradation targets of hsa-miR-200c, identified using informatics and qRT-PCR. Cell Cycle 5:1951–1956
Humphries B, Yang C (2015) The microRNA-200 family: small molecules with novel roles in cancer development, progression and therapy. Oncotarget 6:6472–6498
Mutlu M, Saatci Ö, Raza U, Eyüpoglu E, Yurdusev E, Sahin Ö (2015) MIR200C (microRNA 200c). Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol 19:270–285
Burk U, Schubert J, Wellner U, Schmalhofer O, Vincan E, Spaderna S, Brabletz T (2008) A reciprocal repression between ZEB1 and members of the miR-200 family promotes EMT and invasion in cancer cells. EMBO Rep 9:582–589
Browne G, Sayan AE, Tulchinsky E (2010) ZEB proteins link cell motility with cell cycle control and cell survival in cancer. Cell Cycle 9:886–891
Sanchez-Tillo E, Lazaro A, Torrent R, Cuatrecasas M, Vaquero EC, Castells A, Engel P, Postigo A (2010) ZEB1 represses E-cadherin and induces an EMT by recruiting the SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling protein BRG1. Oncogene 29:3490–3500
Mizuguchi Y, Specht S, Lunz JG 3rd, Isse K, Corbitt N, Takizawa T, Demetris AJ (2012) Cooperation of p300 and PCAF in the control of microRNA 200c/141 transcription and epithelial characteristics. PLoS One 7, e32449. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032449
Peng C, Li N, Ng YK, Zhang J, Meier F, Theis FJ, Merkenschlager M, Chen W, Wurst W, Prakash N (2012) A unilateral negative feedback loop between miR-200 microRNAs and Sox2/E2F3 controls neural progenitor cell-cycle exit and differentiation. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 32:13292–13308
Pieraccioli M, Imbastari F, Antonov A, Melino G, Raschella G (2013) Activation of miR200 by c-Myb depends on ZEB1 expression and miR200 promoter methylation. Cell Cycle 12:2309–2320
Knouf EC, Garg K, Arroyo JD, Correa Y, Sarkar D, Parkin RK, Wurz K, O’Briant KC, Godwin AK, Urban ND et al (2012) An integrative genomic approach identifies p73 and p63 as activators of miR-200 microRNA family transcription. Nucleic Acids Res 40:499–510
Wang G, Guo X, Hong W, Liu Q, Wei T, Lu C, Gao L, Ye D, Zhou Y, Chen J et al (2013) Critical regulation of miR-200/ZEB2 pathway in Oct4/Sox2-induced mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition and induced pluripotent stem cell generation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:2858–2863
Vrba L, Jensen TJ, Garbe JC, Heimark RL, Cress AE, Dickinson S, Stampfer MR, Futscher BW (2010) Role for DNA methylation in the regulation of miR-200c and miR-141 expression in normal and cancer cells. PLoS One 5, e8697. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008697
Wiklund ED, Bramsen JB, Hulf T, Dyrskjot L, Ramanathan R, Hansen TB, Villadsen SB, Gao S, Ostenfeld MS, Borre M et al (2011) Coordinated epigenetic repression of the miR-200 family and miR-205 in invasive bladder cancer. Int J Cancer J Int du Cancer 128:1327–1334
Tryndyak VP, Beland FA, Pogribny IP (2010) E-cadherin transcriptional down-regulation by epigenetic and microRNA-200 family alterations is related to mesenchymal and drug-resistant phenotypes in human breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer J Int du Cancer 126:2575–2583
Lamouille S, Xu J, Derynck R (2014) Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:178–196
De Craene B, Berx G (2013) Regulatory networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat Rev Cancer 13:97–110
Peinado H, Olmeda D, Cano A (2007) Snail, Zeb and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer 7:415–428
Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL, Ramaswamy S, Itzykson RA, Come C, Savagner P, Gitelman I, Richardson A, Weinberg RA (2004) Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell 117:927–939
Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E, Peter ME (2008) The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Dev 22:894–907
Li L, Li B, Chen D, Liu L, Huang C, Lu Z, Lun L, Wan X (2015) miR-139 and miR-200c regulate pancreatic cancer endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis. Oncol Rep 34:51–58
Wellner U, Schubert J, Burk UC, Schmalhofer O, Zhu F, Sonntag A, Waldvogel B, Vannier C, Darling D, zur Hausen A et al (2009) The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat Cell Biol 11:1487–1495
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G, Kang Y (2008) The miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem 283:14910–14914
Brabletz S, Brabletz T (2010) The ZEB/miR-200 feedback loop—a motor of cellular plasticity in development and cancer? EMBO Rep 11:670–677
Shimono Y, Zabala M, Cho RW, Lobo N, Dalerba P, Qian D, Diehn M, Liu H, Panula SP, Chiao E et al (2009) Downregulation of miRNA-200c links breast cancer stem cells with normal stem cells. Cell 138:592–603
Bar M, Wyman SK, Fritz BR, Qi J, Garg KS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Bendoraite A, Mitchell PS, Nelson AM et al (2008) MicroRNA discovery and profiling in human embryonic stem cells by deep sequencing of small RNA libraries. Stem Cells 26:2496–2505
Chang CJ, Chao CH, Xia W, Yang JY, Xiong Y, Li CW, Yu WH, Rehman SK, Hsu JL, Lee HH et al (2011) p53 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem cell properties through modulating miRNAs. Nat Cell Biol 13:317–323
Kim T, Veronese A, Pichiorri F, Lee TJ, Jeon YJ, Volinia S, Pineau P, Marchio A, Palatini J, Suh SS et al (2011) p53 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition through microRNAs targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Exp Med 208:875–883
Rajabi H, Alam M, Takahashi H, Kharbanda A, Guha M, Ahmad R, Kufe D (2014) MUC1-C oncoprotein activates the ZEB1/miR-200c regulatory loop and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 33:1680–1689
Jurmeister S, Baumann M, Balwierz A, Keklikoglou I, Ward A, Uhlmann S, Zhang JD, Wiemann S, Sahin O (2012) MicroRNA-200c represses migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by targeting actin-regulatory proteins FHOD1 and PPM1F. Mol Cell Biol 32:633–651
Sigloch FC, Burk UC, Biniossek ML, Brabletz T, Schilling O (2015) miR-200c dampens cancer cell migration via regulation of protein kinase A subunits. Oncotarget 6:23874–23889
Li J, Tan Q, Yan M, Liu L, Lin H, Zhao F, Bao G, Kong H, Ge C, Zhang F et al (2014) miRNA-200c inhibits invasion and metastasis of human non-small cell lung cancer by directly targeting ubiquitin specific peptidase 25. Mol Cancer 13:166
Howe EN, Cochrane DR, Richer JK (2011) Targets of miR-200c mediate suppression of cell motility and anoikis resistance. Breast Cancer Res: BCR 13:R45
Perdigao-Henriques R, Petrocca F, Altschuler G, Thomas MP, Le MT, Tan SM, Hide W, Lieberman J (2015) miR-200 promotes the mesenchymal to epithelial transition by suppressing multiple members of the Zeb2 and Snail1 transcriptional repressor complexes. Oncogene. doi:10.1038/onc.2015.69
Liu M, Casimiro MC, Wang C, Shirley LA, Jiao X, Katiyar S, Ju X, Li Z, Yu Z, Zhou J et al (2009) p21CIP1 attenuates Ras- and c-Myc-dependent breast tumor epithelial mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell-like gene expression in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:19035–19039
Li XL, Hara T, Choi Y, Subramanian M, Francis P, Bilke S, Walker RL, Pineda M, Zhu Y, Yang Y et al (2014) A p21-ZEB1 complex inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the microRNA 183-96-182 cluster. Mol Cell Biol 34:533–550
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y, Goodall GJ (2008) The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol 10:593–601
Hamano R, Miyata H, Yamasaki M, Kurokawa Y, Hara J, Moon JH, Nakajima K, Takiguchi S, Fujiwara Y, Mori M et al (2011) Overexpression of miR-200c induces chemoresistance in esophageal cancers mediated through activation of the Akt signaling pathway. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 17:3029–3038
Madhavan D, Zucknick M, Wallwiener M, Cuk K, Modugno C, Scharpff M, Schott S, Heil J, Turchinovich A, Yang R et al (2012) Circulating miRNAs as surrogate markers for circulating tumor cells and prognostic markers in metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 18:5972–5982
Gottesman MM (2002) Mechanisms of cancer drug resistance. Annu Rev Med 53:615–627
Liu S, Tetzlaff MT, Cui R, Xu X (2012) miR-200c inhibits melanoma progression and drug resistance through down-regulation of BMI-1. Am J Pathol 181:1823–1835
Park IK, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF (2004) Bmi1, stem cells, and senescence regulation. J Clin Invest 113:175–179
Cittelly DM, Dimitrova I, Howe EN, Cochrane DR, Jean A, Spoelstra NS, Post MD, Lu X, Broaddus RR, Spillman MA et al (2012) Restoration of miR-200c to ovarian cancer reduces tumor burden and increases sensitivity to paclitaxel. Mol Cancer Ther 11:2556–2565
Cochrane DR, Spoelstra NS, Howe EN, Nordeen SK, Richer JK (2009) MicroRNA-200c mitigates invasiveness and restores sensitivity to microtubule-targeting chemotherapeutic agents. Mol Cancer Ther 8:1055–1066
Prislei S, Martinelli E, Mariani M, Raspaglio G, Sieber S, Ferrandina G, Shahabi S, Scambia G, Ferlini C (2013) MiR-200c and HuR in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 13:72
Tanaka S, Hosokawa M, Ueda K, Iwakawa S (2015) Effects of decitabine on ınvasion and exosomal expression of miR-200c and miR-141 in oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull 38:1272–1279
Kopp F, Wagner E, Roidl A (2014) The proto-oncogene KRAS is targeted by miR-200c. Oncotarget 5:185–195
Sui H, Cai GX, Pan SF, Deng WL, Wang Y, Chen ZS, Cai SJ, Zhu HR, Li Q (2014) miR-200c attenuates P-gp mediated MDR and metastasis by targeting JNK2/c-Jun signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0167
Kopp F, Oak PS, Wagner E, Roidl A (2012) miR-200c sensitizes breast cancer cells to doxorubicin treatment by decreasing TrkB and Bmi1 expression. PLoS One 7:e50469
Segal RA (2003) Selectivity in neurotrophin signaling: theme and variations. Annu Rev Neurosci 26:299–330
Brodeur GM, Minturn JE, Ho R, Simpson AM, Iyer R, Varela CR, Light JE, Kolla V, Evans AE (2009) Trk receptor expression and inhibition in neuroblastomas. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 15:3244–3250
Ho R, Eggert A, Hishiki T, Minturn JE, Ikegaki N, Foster P, Camoratto AM, Evans AE, Brodeur GM (2002) Resistance to chemotherapy mediated by TrkB in neuroblastomas. Cancer Res 62:6462–6466
Lee J, Jiffar T, Kupferman ME (2012) A novel role for BDNF-TrkB in the regulation of chemotherapy resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One 7, e30246. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030246
Manavalan TT, Teng Y, Appana SN, Datta S, Kalbfleisch TS, Li Y, Klinge CM (2011) Differential expression of microRNA expression in tamoxifen-sensitive MCF-7 versus tamoxifen-resistant LY2 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett 313:26–43
Manavalan TT, Teng Y, Litchfield LM, Muluhngwi P, Al-Rayyan N, Klinge CM (2013) Reduced expression of miR-200 family members contributes to antiestrogen resistance in LY2 human breast cancer cells. PLoS One 8, e62334. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062334
Flaherty KT, Infante JR, Daud A, Gonzalez R, Kefford RF, Sosman J, Hamid O, Schuchter L, Cebon J, Ibrahim N et al (2012) Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition in melanoma with BRAF V600 mutations. N Engl J Med 367:1694–1703
Liu S, Tetzlaff MT, Wang T, Yang R, Xie L, Zhang G, Krepler C, Xiao M, Beqiri M, Xu W et al (2015) miR-200c/Bmi1 axis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition contribute to acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitor treatment. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 28:431–441
Gao C, Peng FH, Peng LK (2014) MiR-200c sensitizes clear-cell renal cell carcinoma cells to sorafenib and imatinib by targeting heme oxygenase-1. Neoplasma. doi:10.4149/neo_2014_083
Lin J, Liu C, Gao F, Mitchel RE, Zhao L, Yang Y, Lei J, Cai J (2013) miR-200c enhances radiosensitivity of human breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem 114:606–615
Sun Q, Liu T, Yuan Y, Guo Z, Xie G, Du S, Lin X, Xu Z, Liu M, Wang W et al (2015) MiR-200c inhibits autophagy and enhances radiosensitivity in breast cancer cells by targeting UBQLN1. Int J Cancer J Int du Cancer 136:1003–1012
Cui FB, Liu Q, Li RT, Shen J, Wu PY, Yu LX, Hu WJ, Wu FL, Jiang CP, Yue GF et al (2014) Enhancement of radiotherapy efficacy by miR-200c-loaded gelatinase-stimuli PEG-Pep-PCL nanoparticles in gastric cancer cells. Int J Nanomedicine 9:2345–2358
Singh A, Settleman J (2010) EMT, cancer stem cells and drug resistance: an emerging axis of evil in the war on cancer. Oncogene 29:4741–4751
Raza U, Zhang JD, Sahin O (2014) MicroRNAs: master regulators of drug resistance, stemness, and metastasis. J Mol Med (Berl) 92:321–336
Ceppi P, Mudduluru G, Kumarswamy R, Rapa I, Scagliotti GV, Papotti M, Allgayer H (2010) Loss of miR-200c expression induces an aggressive, invasive, and chemoresistant phenotype in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer Res: MCR 8:1207–1216
Puhr M, Hoefer J, Schafer G, Erb HH, Oh SJ, Klocker H, Heidegger I, Neuwirt H, Culig Z (2012) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition leads to docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer and is mediated by reduced expression of miR-200c and miR-205. Am J Pathol 181:2188–2201
Li Y, VandenBoom TG 2nd, Kong D, Wang Z, Ali S, Philip PA, Sarkar FH (2009) Up-regulation of miR-200 and let-7 by natural agents leads to the reversal of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 69:6704–6712
Bao B, Wang Z, Ali S, Ahmad A, Azmi AS, Sarkar SH, Banerjee S, Kong D, Li Y, Thakur S et al (2012) Metformin inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion by attenuating CSC function mediated by deregulating miRNAs in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Prev Res 5:355–364
Ma C, Huang T, Ding YC, Yu W, Wang Q, Meng B, Luo SX (2015) microRNA-200c overexpression inhibits chemoresistance, invasion and colony formation of human pancreatic cancer stem cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:6533–6539
Brozovic A, Duran GE, Wang YC, Francisco EB, Sikic BI (2015) The miR-200 family differentially regulates sensitivity to paclitaxel and carboplatin in human ovarian carcinoma OVCAR-3 and MES-OV cells. Mol Oncol 9:1678–1693
Siebzehnrubl FA, Silver DJ, Tugertimur B, Deleyrolle LP, Siebzehnrubl D, Sarkisian MR, Devers KG, Yachnis AT, Kupper MD, Neal D et al (2013) The ZEB1 pathway links glioblastoma initiation, invasion and chemoresistance. EMBO Mol Med 5:1196–1212
Fischer KR, Durrans A, Lee S, Sheng J, Li F, Wong ST, Choi H, El Rayes T, Ryu S, Troeger J et al (2015) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance. Nature 527:472–476
Adam L, Zhong M, Choi W, Qi W, Nicoloso M, Arora A, Calin G, Wang H, Siefker-Radtke A, McConkey D et al (2009) miR-200 expression regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in bladder cancer cells and reverses resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor therapy. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 15:5060–5072
Shien K, Toyooka S, Yamamoto H, Soh J, Jida M, Thu KL, Hashida S, Maki Y, Ichihara E, Asano H et al (2013) Acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors is associated with a manifestation of stem cell-like properties in cancer cells. Cancer Res 73:3051–3061
Cufi S, Bonavia R, Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Corominas-Faja B, Cuyas E, Martin-Castillo B, Barrajon-Catalan E, Visa J, Segura-Carretero A et al (2013) Silibinin suppresses EMT-driven erlotinib resistance by reversing the high miR-21/low miR-200c signature in vivo. Sci Rep 3:2459
Bryant JL, Britson J, Balko JM, Willian M, Timmons R, Frolov A, Black EP (2012) A microRNA gene expression signature predicts response to erlotinib in epithelial cancer cell lines and targets EMT. Br J Cancer 106:148–156
Izumchenko EG, Chang X, Michailidi C, Kagohara LT, Ravi R, Paz K, Brait M, Hoque MO, Ling S, Bedi A et al (2014) The TGFbeta-miR200-Mig6 pathway orchestrates the EMT-associated kinase switch that induces resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Cancer Res. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0110
Bai WD, Ye XM, Zhang MY, Zhu HY, Xi WJ, Huang X, Zhao J, Gu B, Zheng GX, Yang AG et al (2014) MiR-200c suppresses TGF-beta signaling and counteracts trastuzumab resistance and metastasis by targeting ZNF217 and ZEB1 in breast cancer. Int J Cancer J Int du Cancer. doi:10.1002/ijc.28782
Shi SJ, Wang LJ, Yu B, Li YH, Jin Y, Bai XZ (2015) LncRNA-ATB promotes trastuzumab resistance and invasion-metastasis cascade in breast cancer. Oncotarget 6:11652–11663
Rebustini IT, Hayashi T, Reynolds AD, Dillard ML, Carpenter EM, Hoffman MP (2012) miR-200c regulates FGFR-dependent epithelial proliferation via Vldlr during submandibular gland branching morphogenesis. Development 139:191–202
Cao H, Jheon A, Li X, Sun Z, Wang J, Florez S, Zhang Z, McManus MT, Klein OD, Amendt BA (2013) The Pitx2:miR-200c/141:noggin pathway regulates Bmp signaling and ameloblast differentiation. Development 140:3348–3359
Li H, Xu L, Li C, Zhao L, Ma Y, Zheng H, Li Z, Zhang Y, Wang R, Liu Y et al (2014) Ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b represses IGF-I-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition via ZEB2 and microRNA-200c regulation in gastric cancer cells. Mol Cancer 13:136
Song C, Liu LZ, Pei XQ, Liu X, Yang L, Ye F, Xie X, Chen J, Tang H, Xie X (2015) miR-200c inhibits breast cancer proliferation by targeting KRAS. Oncotarget
Park JT, Kato M, Yuan H, Castro N, Lanting L, Wang M, Natarajan R (2013) FOG2 protein down-regulation by transforming growth factor-beta1-induced microRNA-200b/c leads to Akt kinase activation and glomerular mesangial hypertrophy related to diabetic nephropathy. J Biol Chem 288:22469–22480
Howe EN, Cochrane DR, Cittelly DM, Richer JK (2012) miR-200c targets a NF-kappaB up-regulated TrkB/NTF3 autocrine signaling loop to enhance anoikis sensitivity in triple negative breast cancer. PLoS One 7:e49987
Schickel R, Park SM, Murmann AE, Peter ME (2010) miR-200c regulates induction of apoptosis through CD95 by targeting FAP-1. Mol Cell 38:908–915
Ren Y, Han X, Yu K, Sun S, Zhen L, Li Z, Wang S (2014) microRNA-200c downregulates XIAP expression to suppress proliferation and promote apoptosis of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Mol Med Rep 10:315–321
Huang HN, Chen SY, Hwang SM, Yu CC, Su MW, Mai W, Wang HW, Cheng WC, Schuyler SC, Ma N et al (2014) miR-200c and GATA binding protein 4 regulate human embryonic stem cell renewal and differentiation. Stem Cell Res 12:338–353
Lu YX, Yuan L, Xue XL, Zhou M, Liu Y, Zhang C, Li JP, Zheng L, Hong M, Li XN (2014) Regulation of colorectal carcinoma stemness, growth, and metastasis by an miR-200c-Sox2-negative feedback loop mechanism. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 20:2631–2642
Klein D, Misawa R, Bravo-Egana V, Vargas N, Rosero S, Piroso J, Ichii H, Umland O, Zhijie J, Tsinoremas N et al (2013) MicroRNA expression in alpha and beta cells of human pancreatic islets. PLoS One 8, e55064. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0055064
Luo X, Dong Z, Chen Y, Yang L, Lai D (2013) Enrichment of ovarian cancer stem-like cells is associated with epithelial to mesenchymal transition through an miRNA-activated AKT pathway. Cell Prolif 46:436–446
Vallejo DM, Caparros E, Dominguez M (2011) Targeting Notch signalling by the conserved miR-8/200 microRNA family in development and cancer cells. EMBO J 30:756–769
Bao B, Wang Z, Ali S, Kong D, Li Y, Ahmad A, Banerjee S, Azmi AS, Miele L, Sarkar FH (2011) Notch-1 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition consistent with cancer stem cell phenotype in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett 307:26–36
Mezquita B, Mezquita J, Barrot C, Carvajal S, Pau M, Mezquita P, Mezquita C (2014) A truncated-Flt1 isoform of breast cancer cells is upregulated by Notch and downregulated by retinoic acid. J Cell Biochem 115:52–61
Mezquita B, Mezquita P, Pau M, Mezquita J, Mezquita C (2014) Unlocking doors without keys: activation of Src by truncated C-terminal ıntracellular receptor tyrosine kinases lacking tyrosine kinase activity. Cells 3:92–111
Wendlandt EB, Graff JW, Gioannini TL, McCaffrey AP, Wilson ME (2012) The role of microRNAs miR-200b and miR-200c in TLR4 signaling and NF-kappaB activation. Innate Immun 18:846–855
Rokavec M, Wu W, Luo JL (2012) IL6-mediated suppression of miR-200c directs constitutive activation of inflammatory signaling circuit driving transformation and tumorigenesis. Mol Cell 45:777–789
Chuang TD, Khorram O (2014) miR-200c regulates IL8 expression by targeting IKBKB: a potential mediator of ınflammation in leiomyoma pathogenesis. PLoS One 9:e95370
Lobert S, Graichen ME, Morris K (2013) Coordinated regulation of beta-tubulin isotypes and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition protein ZEB1 in breast cancer cells. Biochemistry 52:5482–5490
Hur K, Toiyama Y, Takahashi M, Balaguer F, Nagasaka T, Koike J, Hemmi H, Koi M, Boland CR, Goel A (2013) MicroRNA-200c modulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human colorectal cancer metastasis. Gut 62:1315–1326
Oishi N, Kumar MR, Roessler S, Ji J, Forgues M, Budhu A, Zhao X, Andersen JB, Ye QH, Jia HL et al (2012) Transcriptomic profiling reveals hepatic stem-like gene signatures and interplay of miR-200c and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 56:1792–1803
Karakatsanis A, Papaconstantinou I, Gazouli M, Lyberopoulou A, Polymeneas G, Voros D (2013) Expression of microRNAs, miR-21, miR-31, miR-122, miR-145, miR-146a, miR-200c, miR-221, miR-222, and miR-223 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma or intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and its prognostic significance. Mol Carcinog 52:297–303
Lahat G, Lubezky N, Loewenstein S, Nizri E, Gan S, Pasmanik-Chor M, Hayman L, Barazowsky E, Ben-Haim M, Klausner JM (2014) Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN) is associated with high tumor grade and adverse outcomes. Ann Surg Oncol. doi:10.1245/s10434-014-3946-5
Kim MK, Jung SB, Kim JS, Roh MS, Lee JH, Lee EH, Lee HW (2014) Expression of microRNA miR-126 and miR-200c is associated with prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Virchows Archiv: Int J Pathol. doi:10.1007/s00428-014-1640-4
Tejero R, Navarro A, Campayo M, Vinolas N, Marrades RM, Cordeiro A, Ruiz-Martinez M, Santasusagna S, Molins L, Ramirez J et al (2014) miR-141 and miR-200c as markers of overall survival in early stage non-small cell lung cancer adenocarcinoma. PLoS One 9:e101899
Pacurari M, Addison JB, Bondalapati N, Wan YW, Luo D, Qian Y, Castranova V, Ivanov AV, Guo NL (2013) The microRNA-200 family targets multiple non-small cell lung cancer prognostic markers in H1299 cells and BEAS-2B cells. Int J Oncol 43:548–560
Zhang HH, Zhang ZY, Che CL, Mei YF, Shi YZ (2013) Array analysis for potential biomarker of gemcitabine identification in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 6:1734–1746
Leskela S, Leandro-Garcia LJ, Mendiola M, Barriuso J, Inglada-Perez L, Munoz I, Martinez-Delgado B, Redondo A, de Santiago J, Robledo M et al (2011) The miR-200 family controls beta-tubulin III expression and is associated with paclitaxel-based treatment response and progression-free survival in ovarian cancer patients. Endocrine-Related Cancer 18:85–95
Marchini S, Cavalieri D, Fruscio R, Calura E, Garavaglia D, Nerini IF, Mangioni C, Cattoretti G, Clivio L, Beltrame L et al (2011) Association between miR-200c and the survival of patients with stage I epithelial ovarian cancer: a retrospective study of two independent tumour tissue collections. Lancet Oncol 12:273–285
White NM, Bao TT, Grigull J, Youssef YM, Girgis A, Diamandis M, Fatoohi E, Metias M, Honey RJ, Stewart R et al (2011) miRNA profiling for clear cell renal cell carcinoma: biomarker discovery and identification of potential controls and consequences of miRNA dysregulation. J Urol 186:1077–1083
Fridman E, Dotan Z, Barshack I, David MB, Dov A, Tabak S, Zion O, Benjamin S, Benjamin H, Kuker H et al (2010) Accurate molecular classification of renal tumors using microRNA expression. J Mol Diagn: JMD 12:687–696
Wotschofsky Z, Busch J, Jung M, Kempkensteffen C, Weikert S, Schaser KD, Melcher I, Kilic E, Miller K, Kristiansen G et al (2013) Diagnostic and prognostic potential of differentially expressed miRNAs between metastatic and non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma at the time of nephrectomy. Clin Chim Acta 416:5–10
Mahdavinezhad A, Mousavi-Bahar SH, Poorolajal J, Yadegarazari R, Jafari M, Shabab N, Saidijam M (2015) Evaluation of miR-141, miR-200c, miR-30b expression and clinicopathological features of bladder cancer. Int J Mol Cell Med 4:32–39
Berber U, Yilmaz I, Narli G, Haholu A, Kucukodaci Z, Demirel D (2014) miR-205 and miR-200c: predictive micro RNAs for lymph node metastasis in triple negative breast cancer. J Breast Cancer 17:143–148
Toiyama Y, Hur K, Tanaka K, Inoue Y, Kusunoki M, Boland CR, Goel A (2014) Serum miR-200c is a novel prognostic and metastasis-predictive biomarker in patients with colorectal cancer. Ann Surg 259:735–743
Paraskevi A, Theodoropoulos G, Papaconstantinou I, Mantzaris G, Nikiteas N, Gazouli M (2012) Circulating MicroRNA in inflammatory bowel disease. JCrohn’s Colitis 6:900–904
Valladares-Ayerbes M, Reboredo M, Medina-Villaamil V, Iglesias-Diaz P, Lorenzo-Patino MJ, Haz M, Santamarina I, Blanco M, Fernandez-Tajes J, Quindos M et al (2012) Circulating miR-200c as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer. J Transl Med 10:186
Yun KW, Lee JY, Yun SW, Lim IS, Choi ES (2014) Elevated serum level of microRNA (miRNA)-200c and miRNA-371-5p in children with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 35:745–752
Liu XG, Zhu WY, Huang YY, Ma LN, Zhou SQ, Wang YK, Zeng F, Zhou JH, Zhang YK (2012) High expression of serum miR-21 and tumor miR-200c associated with poor prognosis in patients with lung cancer. Med Oncol 29:618–626
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C (2008) MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 110:13–21
Kan CW, Hahn MA, Gard GB, Maidens J, Huh JY, Marsh DJ, Howell VM (2012) Elevated levels of circulating microRNA-200 family members correlate with serous epithelial ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 12:627
Cheng HH, Mitchell PS, Kroh EM, Dowell AE, Chery L, Siddiqui J, Nelson PS, Vessella RL, Knudsen BS, Chinnaiyan AM et al (2013) Circulating microRNA profiling identifies a subset of metastatic prostate cancer patients with evidence of cancer-associated hypoxia. PLoS One 8, e69239. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0069239
Lv LL, Cao Y, Liu D, Xu M, Liu H, Tang RN, Ma KL, Liu BC (2013) Isolation and quantification of microRNAs from urinary exosomes/microvesicles for biomarker discovery. Int J Biol Sci 9:1021–1031
Zuberi M, Mir R, Das J, Ahmad I, Javid J, Yadav P, Masroor M, Ahmad S, Ray PC, Saxena A (2015) Expression of serum miR-200a, miR-200b, and miR-200c as candidate biomarkers in epithelial ovarian cancer and their association with clinicopathological features. Clin Transl Oncol 17:779–787
Hong L, Han Y, Zhang H, Fan D (2015) Prognostic markers in esophageal cancer: from basic research to clinical use. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 9:887–889
Pantel K, Alix-Panabieres C (2010) Circulating tumour cells in cancer patients: challenges and perspectives. Trends Mol Med 16:398–406
Perez-Hernandez J, Forner MJ, Pinto C, Chaves FJ, Cortes R, Redon J (2015) Increased urinary exosomal micrornas in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS One 10, e0138618. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0138618
Yuan JH, Yang F, Wang F, Ma JZ, Guo YJ, Tao QF, Liu F, Pan W, Wang TT, Zhou CC et al (2014) A long noncoding RNA activated by TGF-beta promotes the invasion-metastasis cascade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 25:666–681
Xiao X, Yu S, Li S, Wu J, Ma R, Cao H, Zhu Y, Feng J (2014) Exosomes: decreased sensitivity of lung cancer A549 cells to cisplatin. PLoS One 9, e89534. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0089534
Chen Y, Gao DY, Huang L (2015) In vivo delivery of miRNAs for cancer therapy: challenges and strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 81:128–141
Esposito CL, Cerchia L, Catuogno S, De Vita G, Dassie JP, Santamaria G, Swiderski P, Condorelli G, Giangrande PH, de Franciscis V (2014) Multifunctional aptamer-miRNA conjugates for targeted cancer therapy. Mol Ther: J Am Soc Gene Ther 22:1151–1163
Cortez MA, Valdecanas D, Zhang X, Zhan Y, Bhardwaj V, Calin GA, Komaki R, Giri DK, Quini CC, Wolfe T et al (2014) Therapeutic delivery of miR-200c enhances radiosensitivity in lung cancer. Mol Ther: J Am Soc Gene Ther. doi:10.1038/mt.2014.79
Li XJ, Ren ZJ, Tang JH (2014) MicroRNA-34a: a potential therapeutic target in human cancer. Cell Death Dis 5, e1327. doi:10.1038/cddis.2014.270
Acknowledgments and funding information
We would like to thank Suhail Ansari and Rasmi Mishra for their critical reading of the manuscript and valuable suggestions. This work is, in part, supported by the European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO) Installation Grant (Grant No. 2791) and TUBITAK (Grant No. 214S104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mutlu, M., Raza, U., Saatci, Ö. et al. miR-200c: a versatile watchdog in cancer progression, EMT, and drug resistance. J Mol Med 94, 629–644 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-016-1420-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-016-1420-5