Abstract
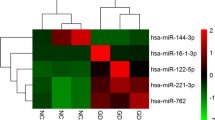
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding RNAs that regulate the expression of protein-coding genes. Recently, miRNA levels have been used as a novel non-invasive biomarker for the diagnosis of various diseases. We aimed to identify serum miRNAs elevated in patients with Kawasaki disease (KD) and to explore the potential biological function of identified candidate miRNAs. Serum specimens were collected from children with KD (n = 12) and healthy controls (n = 6). miRNA microarray assays were performed using the PANArray™ miRNA expression profiling kit (PANAGENE Co., Daejeon, Korea). We used TargetScan and the database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery program to obtain a list of enriched biological pathways targeted by miRNAs elevated in KD patients. As a result, miR-200c and miR-371-5p were significantly upregulated in the KD group compared with the control group (p = 0.032 in both). By using TargetScan, we obtained a list of 421 and 542 genes predicted to be targeted by miR-200c and miR-371, respectively, and these genes were significantly (p < 0.05) clustered in 17 and 3 pathways, respectively. Many of them are major pathways involved in inflammatory responses. The present data support the hypothesis that the inflammatory response is a crucial mechanism for pathogenesis of KD, and miRNAs might be the main regulators of this inflammatory response.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi T (2005) Interventions in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 26:206–212
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233
Belair C, Darfeuille F, Staedel C (2009) Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: possible role of microRNAs in this intimate relationship. Clin Microbiol Infect 15:806–812
Bihrer V, Waidmann O, Friedrich-Rust M, Forestier N, Susser S, Haupenthal J et al (2011) Serum microRNA-21 as marker for necroinflammation in hepatitis C patients with and without hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One 6:e26971
Brogan PA, Bose A, Burgner D, Shingadia D, Tulloh R, Michie C et al (2002) Kawasaki disease: an evidence based approach to diagnosis, treatment, and proposals for future research. Arch Dis Child 86:286–290
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K et al (2008) Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res 18:997–1006
Cortez MA, Calin GA (2009) MicroRNA identification in plasma and serum: a new tool to diagnose and monitor diseases. Expert Opin Biol Ther 9:703–711
Cui L, Guo X, Qi Y, Qi X, Ge Y, Shi Z et al (2010) Identification of microRNAs involved in the host response to enterovirus 71 infection by a deep sequencing approach. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:425939
Cui L, Qi Y, Li H, Ge Y, Zhao K, Qi X et al (2011) Serum microRNA expression profile distinguishes enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus 16 infections in patients with hand-foot-and-mouth disease. PLoS One 6:e27071
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs: microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:259–269
Fu Y, Yi Z, Wu X, Li J, Xu F (2011) Circulating microRNAs in patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol 49:4246–4251
Ghelani SJ, Sable C, Wiedermann BL, Spurney CF (2012) Increased incidence of incomplete Kawasaki disease at a pediatric hospital after publication of the 2004 American Heart Association guidelines. Pediatr Cardiol 33:1097–1103
Kawasaki T (1967) Acute febrile mucocutaneous syndrome with lymphoid involvement with specific desquamation of the fingers and toes in children. Arerugi 16:178–222
Kim VN (2005) Small RNAs: classification, biogenesis, and function. Mol Cells 19:1–15
Laupland KB, Dele Davies H (1999) Epidemiology, etiology, and management of Kawasaki disease: state of the art. Pediatr Cardiol 20:177–183
Liu RY, Diao CF, Zhang Y, Wu N, Wan HY, Nong XY et al (2013) miR-371-5p down-regulates pre mRNA processing factor 4 homolog B (PRPF4B) and facilitates the G1/S transition in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 335:351–360
Loveday EK, Svinti V, Diederich S, Pasick J, Jean F (2012) Temporal- and strain-specific host microRNA molecular signatures associated with swine-origin H1N1 and avian-origin H7N7 influenza A virus infection. J Virol 86:6109–6122
Magenta A, Cencioni C, Fasanaro P, Zaccagnini G, Greco S, Sarra-Ferraris G et al (2011) miR-200c is upregulated by oxidative stress and induces endothelial cell apoptosis and senescence via ZEB1 inhibition. Cell Death Differ 18:1628–1639
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC et al (2004) Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics 114:1708–1733
Othumpangat S, Walton C, Piedimonte G (2012) MicroRNA-221 modulates RSV replication in human bronchial epithelium by targeting NGF expression. PLoS One 7:e30030
Shimizu C, Kim J, Stepanowsky P, Trinh C, Lau HD, Akers JC et al (2013) Differential expression of miR-145 in children with Kawasaki disease. PLoS One 8:e58159
Skalsky RL, Cullen BR (2010) Viruses, microRNAs, and host interactions. Annu Rev Microbiol 64:123–141
Teraguchi M, Ogino H, Yoshimura K, Taniuchi S, Kino M, Okazaki H et al (2013) Steroid pulse therapy for children with intravenous immunoglobulin therapy-resistant Kawasaki disease: a prospective study. Pediatr Cardiol 34:959–963
Uehara R, Belay ED (2012) Epidemiology of Kawasaki disease in Asia, Europe, and the United States. J Epidemiol 22:79–85
Valladares-Ayerbes M, Reboredo M, Medina-Villaamil V, Iglesias-Diaz P, Lorenzo-Patino MJ, Haz M et al (2012) Circulating miR-200c as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer. J Transl Med 10:186
Vasilescu C, Rossi S, Shimizu M, Tudor S, Veronese A, Ferracin M et al (2009) MicroRNA fingerprints identify miR-150 as a plasma prognostic marker in patients with sepsis. PLoS One 4:e7405
Wang C, Yang S, Sun G, Tang X, Lu S, Neyrolles O et al (2011) Comparative miRNA expression profiles in individuals with latent and active tuberculosis. PLoS One 6:e25832
Wang HJ, Zhang PJ, Chen WJ, Feng D, Jia YH, Xie LX (2012) Four serum microRNAs identified as diagnostic biomarkers of sepsis. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 73:850–854
Wang H, Zhang P, Chen W, Feng D, Jia Y, Xie L (2012) Serum microRNA signatures identified by Solexa sequencing predict sepsis patients’ mortality: a prospective observational study. PLoS One 7:e38885
Wendlandt EB, Graff JW, Gioannini TL, McCaffrey AP, Wilson ME (2012) The role of microRNAs miR-200b and miR-200c in TLR4 signaling and NF-kappaB activation. Innate Immun 18:846–855
Zhu YK, Cheng N, Hu Y, Cen YZ (2012) The role of microRNAs in the pathogenesis of cervical cancer and its relationship to HPV. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan 43:251–256
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Ji Hye Yoon from PANAGENE Co., Ltd for help with miRNA microarrays and excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yun, K.W., Lee, J.Y., Yun, S.W. et al. Elevated Serum Level of MicroRNA (miRNA)-200c and miRNA-371-5p in Children with Kawasaki Disease. Pediatr Cardiol 35, 745–752 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-013-0846-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-013-0846-6