Abstract
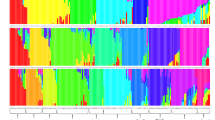
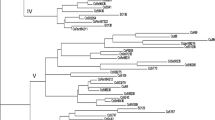
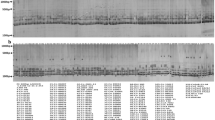
Eighteen sugarcane specific STMS markers developed from Genbank databases were used to analyze the genetic divergence of 54 Indian genetic stocks comprising of hybrids, inbreds, induced mutants and somaclones. Moderate genetic diversity was observed in 25 commercial hybrids. Eighteen inbreds, six each developed from three proven parents exhibited high levels of within-group genetic similarity. The mutants and somaclones derived from a variety exhibited highly similar molecular profiles. UPGMA dendrogram based on combined analysis of diversity based on 221 different bands revealed five distinct clusters, somaclones and mutants constituting cluster 1, commercial hybrids in cluster 2 and inbreds falling in clusters 3,4 and 5. The study revealed that genetic base of sugarcane germplasm used in varietal improvement in India is reasonably large. Based on diversity estimates, several genetically diverse combinations were identified. Inbreds constituted a more diverse genetic material for crossing programs to derive heterotic types.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berding, N. and Roach, B.T. 1987. Germplasm collection, maintenance and use. In: Heinz DJ. (Ed.), Sugarcane Improvement Through Breeding, pp: 143–210. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Cordeiro, GM. and Henry, R.J. 2001. Evaluation of microsatellite (simple sequence repeats) as genetic markers in sugarcane. Proc. Int. Soc. Sugar Cane Technol.24: 627–629.
D’Hont A., Lu, Y.H., Feldmn P. and Glaszmann, J.C. 1993. Cytoplasmic diversity in sugarcane revealed by heterologous probes. Sugar Cane1:12–15.
D’Hont A., Lu, Y.H., Leon D.GD., Grivet, L., Feldmann P., Lanaud, C. and Glaszmann J.C. 1994. A molecular approach to unravelling the genetics of sugarcane, a complex polyploid of the Andropogoneae tribe. Genome37: 222–230.
Glaszmann, J.C, Noyer J.L., Fautret A., Lanaud C. and Feldmann, P. 1989. Molecular genetic markers in sugarcane. Proc. Intern Soc Sugar Cane Technol.20: 872–881.
Harvey, M and Botha, F.C. 1996. Use of PCR based methodologies for determination of DNA diversity between Saccharum varieties. Euphytica89: 257–265.
Heinz. D. J. 1987. Sugarcane improvement through breeding. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Hemaprabha, G and Sree Rangasamy, S.R. 2001. Genetic similarity among five species of Saccharum based on isozyme and RAPD markers. Indian J. Genet.67(4): 341–347.
Hemaprabha, G, Natarajan, U.S. and Balasundaram, N. 2001. Isozyme diversity in identifying cross combinations for breeding elite cultivars in sugarcane. Diamond Jubilee Symposium on Hundred years of Post Mendelian Genetics and Plant Breeding held at New Delhi during November 6–9, 2001, p 264.
Hemaprabha, G, Natarajan, U.S. and Balasundaram, N. 2003. Breeding behaviour for juice quality through selfing and progeny evaluation in hybrid clones and inbred derivatives of sugarcane(Saccharum sp.). Sugar Tech.5(3): 177–180.
Jannoo, N., Forget, L. and Dookun, A. 2001. Contribution of microsatellites to sugarcane breeding program in Mauritius. Proc. Int. Soc. Sugarcane Technol.24:637–639.
Lu. Y.H., D’Hont, A. Paulet, F., Grivet, L., Arnaud M. and Glaszmann, J.C. 1994. Molecular diversity and genome structure in modern sugarcane varieties. Euphytica78: 217–226.
Murray, M. G and Thompson, W. F. 1980. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acid Research.8: 4321–4325.
Nair, N.V., Selvi. A., Sreenivasan, T.V. and Pushpalatha, K.N. 2002. Molecular diversity in Indian sugarcane cultivars as revealed by Random Amplified DNA polymorphism. Euphytica.127: 219–225.
Piperidis, G, 2003. Progress towards evaluation of SSR as a tool for sugarcane variety identification. ISSCT. IV Mol. Biol. Workshop, Montpellier, France.
Powell, W., Morgante, M., Andre, C., Hanafey, M., Vogel, J., Tingey, S. and Rafalski, A. 1996. A comparison of RFLP, RAPD, AFLP and SSR markers for germplasm analysis. Mol Breed2: 225–238.
Rafalski, J.A., Vogel, J.M., Morgante, M., Powell, W., Andre G and Tingey, S.V. 1996. Generating and using DNA markers in plants. In: B. Birren & E. Lai (Ed.). Non mammalian genomic analysis. A practical guide. pp. 75–134, Academic Press. San Diego, California.
Roach, B.T. 1972. Nobilization of sugarcane. Proc. Intern. Soc. Sugar Cane Technol.14: 206–216.
Rohlf, F.J. 1993. NTSYS- pc numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, version 2.0. Exeter software: Setauket, New York. 1990.
Sankaranarayanan, V., Natarajan, B. V. and Marimuthammal, S. 1986. Sugarcane varieties under cultivation in India. Indian Council of Agricultural research, New Delhi.
Selvi. A., Nair, N.V., Balasundaram N. and Mohapatra, T. 2003. Evaluation of maize microsatellite markers for genetic diversity analysis and fingerprinting in sugarcane. Genome46(3): 394–403.
Smith, S. and Helentjaris, T.1996. DNA fingerprinting and plant variety protection. In: A.H. Paterson (Ed.). Genome Mapping in Plants, pp, 95–110, R.G. Landes Company.
Sobral, B.W.S., Braga, D.P.V., LaHood, E.S. and Keim, P. 1994. Phylogenetic analysis of chloroplast restriction enzyme site mutations in the Saccharinae Griseb, subtribe of the Andropogoneae. Theor Appl Genet87: 843–853.
Stevenson, G.C. 1965. Genetics and Breeding of Sugarcane. Longmans. Green. London, pp 213–245.
Tautz, D. 1989. Hypervariability of simple sequences as a general source for polymorphic DNA. Markers. Nucleic Acids Res.17: 6463–6471.
Venkataraman, T.S.1942. The message of the sugarcane. Presidential address delivered at the Second Annual Meeting of the Indian Society of Genetics and Plant Breeding in January at Baroda.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hemaprabha, G., Govindaraj, P., Balasundaram, N. et al. Genetic diversity analysis of indian sugarcane breeding pool based on sugarcane specific STMS markers. Sugar Tech 7, 9–14 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02942521
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02942521