Abstract
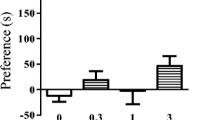
The importance of opiate receptors outside the central nervous system for the inhibitory actions of morphine on male rat sexual behavior was evaluated. Morphine (10 mg/kg) produced an almost complete inhibition of sexual behavior. This inhibition was antagonized by naloxone at a dose of 1 mg/kg but not at a dose of 0.25 mg/kg. The quaternary opioid antagonist methylnaloxone effectively blocked the inhibitory actions of morphine at a dose of 20 mg/kg but not at a dose of 5 mg/kg. Since the affinity of methylnaloxone for opiate receptors is about 5% of that of naloxone, it may be concluded that both antagonists were about equally effective in inhibiting the effects of morphine. Furthermore, the opiate-like drug loperamide was found to inhibit sexual behavior. This drug acts mainly outside the central nervous system. Its effect was blocked by both naloxone and methylnaloxone, suggesting that opiate receptors are involved. It was also shown that methylnaloxone is unable to block the reinforcing effects of morphine in the conditioned place preference procedure. Because the reinforcing effects of opiates seem to be localized to the central nervous system, it may be proposed that methylnaloxone does not antagonize morphine's central effects. Moreover, loperamide had no effect in the place preference procedure, suggesting that this drug does not act at central opioid receptors. Taken together, these data show that peripheral opioid receptors are responsible for at least some of the inhibitory actions of morphine on male sexual behavior. After treatment with morphine + methylnaloxone, ejaculatory mechanisms were facilitated, reflected in a reduced number of preejaculatory intromissions and a shortened ejaculation latency. It thus appears that central opioid receptors facilitate sexual behavior while peripheral receptors participate in inhibitory mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ågmo A (1976) Cholinergic mechanisms and sexual behavior in the male rabbit. Psychopharmacology 51:43–45
Ågmo A, Berenfeld R (1990) Reinforcing properties of ejaculation in the male rat: role of opioids and dopamine. Behav Neurosci 104:177–182
Ågmo A, Gomez M (1991) Conditioned place preference produced by infusion of met-enkephalin into the medial preoptic area. Brain Res 550:343–346
Ågmo A, Irazabal Y (1992) Enkephalinase inhibition facilitates sexual behavior in the male rat but does not produce conditioned place preference. Behav Neural Biol (in press)
Ågmo A, Paredes R (1988) Opioids and sexual behavior in the male rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 30:1021–1034
Band LC, Hull EM (1990) Morphine and dynorphin (1–13) microinjected into the medial preoptic area and nucleus accumbens: effects on sexual behavior in male rats. Brain Res 524:77–84
Bechara A, van der Kooy D (1985) Opposite motivational effects of endogenous opioids in brain and periphery. Nature 314:533–534
Bechara A, Zito KA, van der Kooy (1987) Peripheral receptors mediate the aversive conditioning effects of morphine in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 28:219–225
Bianchi C, Goi A (1977) On the antidiarrheal and analgesic properties of diphenoxylate, difenoxine and loperamide in mice and rats. Arzneimittelforschung 27:1040–1043
Brown DR, Goldberg LI (1985) The use of quaternary narcotic antagonists in opiate research. Neuropharmacology 24:181–191
Burleigh DE (1988) Opioid and non-opioid actions of loperamide on cholinergic nerve function in human isolated colon. Eur J Pharmacol 152:39–46
Colpaert FC, Niemegeers CJE, Lal H, Janssen PA (1975) Investigations on drug produced and subjectively experienced discriminative stimuli. 2. Loperamide, an antidiarrheal devoid of narcotic cue producing actions. Life Sci 16:717–728
Coulombe D (1984) Two-way ANOVA with and without repeated measurements, tests of simple main effects, and multiple comparisons for microcomputers. Behav Res Methods Instr Comp 16:397–398
Damassa DA, Smith ER, Tennent B, Davidson JM (1977) The relationship between circulating testosterone levels and male sexual behavior in rats. Horm Behav 8:275–286
Forsberg G, Bednar I, Eneroth P, Sodersten P (1987) Naloxone reverses post-ejaculatory inhibition of sexual behavior in female rats. J Endocrinal 113:429–434
Forsberg G, Bednar I, Eneroth P, Sodersten P (1990) β-endorphin acts on the reproductive tract of female rats to suppress sexual receptivity. Neurosci Lett 115:92–96
Giagnoni G, Casiraghi L, Senini R, Revel L, Parolaro D, Sala M, Gori E (1983) Loperamide: Evidence of interaction with μ and δ opioid receptors. Life Sci 33 [suppl 1]:315–318
Greene WA, Foote RH (1978) Release rate of testosterone and estrogen from polydimethylsiloxane implants for extended periods in vivo compared with loss in vitro. Int J Fertil 23:128–132
Harston CT, Spirtes MA, Dunlap WP, Coy DH (1980) Naloxone-reversible effects of d-ala2-met5-enkephalinamide induced behavioral activity in rats. Behav Neural Biol 30:1–19
Hughes AM, Everitt BJ, Herbert J (1987) Selective effects of β-endorphin infused into the hypothalamus, preoptic area and bed nucleus of stria terminalis on the sexual and ingestive behaviour of male rats. Neuroscience 23:1063–1073
Kalivas PW, Widerlow E, Stanley D, Breese G, Prange AJ Jr. (1983) Enkephalin action on the mesolimbic system: a dopamine-dependent and a dopamine-independent increase in locomotor activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227:229–237
Kumazawa T, Mizumura K, Sato J, Minagawa M (1989) Facilitatory effects of opioids on the discharges of visceral niciceptors. Brain Res 497:231–238
LeMaire S, Magnan J, Regoli B (1978) Rat was deferens: a specific bioassay for endogenous opioid peptides. Br J Pharmacol 64:372–329
Locke KW, Holtzman SG (1986) Behavioral effects of opioid peptides selective for mu or delta receptors. II. Locomotor activity in nondependent and morphine-dependent rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 238:997–1003
Malmnäs CO (1977) Short-latency effects of testosterone on copulatory behavior in sexually experienced male rats. J Reprod Fertil 51:351–354
Matuszweich L, Dornan WA (1990) Bilateral injections of morphiceptin into the medial preoptic nucleus produce a dramatic delay in the initation of sexual behavior in the male rat. Soc Neurosci Abstr 16:114.1
McIntosh TK, Vallano ML, Barfield RJ (1980) Effects of morphine, β-endorphin and naloxone on catecholamine levels and sexual behavior in the male rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 13:435–441
Meyerson BJ (1981) Comparison of the effects of β-endorphin and morphine on exploratory and socio-sexual behaviour in the male rat. Eur J Pharmacol 69:453–463
Meyerson BJ, Terenius L (1977) β-endorphin and male sexual behaviour. Eur J Pharmacol 42:191–192
Millan MJ, Herz A (1985) The endocrinology of opioids. Int Rev Neurobiol 26:1–84
Misra AL, Pontani RB, Vadlamani NL, Mule SJ (1976) Physiological disposition and biotransformation of allyl-1′-3′-14C naloxone in the rat and some comparative observations on nalorphine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 196:257–268
Mitchell JB, Stewart J (1990) Facilitation of sexual behavior in the male rat associated with intra-VTA injections of opiates. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 35:643–650
Mucha RF, Iversen SD (1984) Reinforcing properties of morphine and naloxone revealed by conditioned place preferences: a procedural examination. Psychopharmacology 82:241–247
Mumford L, Kumar R (1979) Sexual behavior of morphine-dependent and abstinent male rats. Psychopharmacology 65:179–185
Niemegeers CJE, Lenarts FM, Janssen PAJ (1974) Loperamide (R 18553), a novel type of antidiarrheal agent. Arzneimittelforschung 24:1636–1641
Oka T, Hosoya E (1977) The different effect of humoral modulators on the morphine and central nervous system stimulant-induced hyperactivity of rats. Neuropharmacology 16:115–119
Pellegrini Quarantotti B, Corda MG, Paglietti E, Biggio G, Gessa GL (1978) Inhibition of copulatory behavior byd-ala2-metenkephalinamide. Life Sci 23:673–678
Pfaus JG, Gorzalka BB (1987) Opioids and sexual behavior. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 11:1–34
Piercey MF, Ruwart MJ (1979) Naloxone inhibits the anti-diarrheal activity of loperamide. Br J Pharmacol 66:373–375
Ruiz E, Ågmo A (1988) Enkephalin infusion into the medial preoptic area and sexual behavior in the male rat. 20th Ann Conf Reprod Behav, Omaha, Nebraska, p 83
Schnur P, Bravo F, Trujillo M, Rocha S (1983) Biphasic effects of morphine on locomotor activity in hamsters. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 18:357–361
Tepperman FS, Hirst M, Smith P (1983) Brain and serum levels of naloxone following peripheral administration. Life Sci 33:1091–1096
van der Kooy D, Nagy JI (1985) Hyperalgesia mediated by peripheral opiate receptors in the rat. Behav Brain Res 17:203–211
van der Kooy D, Phillips AG (1977) Temporal analysis of naloxone attenuation of morphine-induced taste aversions. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 6:637–641
Wise RA (1989) Opiate reward: Sites and substrates. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 13:129–133
Wüster M, Herz A (1978) Opiate agonist action of antidiarrheal agents in vitro and in vivo — findings in support for selective action. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 301:187–194
Zito KA, Bechara A, Greenwood C, van der Kooy D (1988) The dopamine innervation of the visceral cortex mediates the aversive effects of opiates. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 30:693–699
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by funds from the Universidad Anáhuac. Part of these data was presented at the 22nd Annual Conference on Reproductive Behavior, Atlanta, Georgia, June 8–11, 1990.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ågmo, A., Rojas, J. & Vázquez, P. Inhibitory effect of opiates on male rat sexual behavior may be mediated by opiate receptors outside the central nervous system. Psychopharmacology 107, 89–96 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244971
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244971