Abstract
Rationale
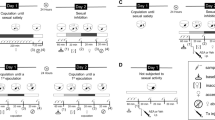
The influence of the main dopaminergic brain regions controlling copulation, the medial preoptic area (mPOA) and the nucleus accumbens (NAcc), on male rat sexual behavior expression has not been fully established.
Objective
This work analyzes the sexual effects of dopamine (DA) receptor activation in the mPOA or the NAcc of sexually active male rats, with an intact (sexually experienced) or a reduced (sexually exhausted) sexual motivation.
Methods
The non-specific DA receptor agonist apomorphine and the D2-like receptor agonist quinpirole were infused into the mPOA or the NAcc of sexually experienced or sexually exhausted male rats and their sexual behavior recorded.
Results
DA receptor activation neither in the mPOA nor in the NAcc modified the copulatory behavior of sexually experienced male rats. DA receptor stimulation in the NAcc, but not in the mPOA, reversed the characteristic sexual inhibition of sexually satiated rats, and D2-like receptors were found to participate in this effect.
Conclusion
The optimal sexual performance of sexually experienced male rats cannot be further improved by DA receptor activation at either brain region. In sexually satiated rats, which are sexually inhibited and have a diminished sexual motivation, NAcc DA receptor stimulation appears to play a key role in their capacity to respond to a motivational significant stimulus, the receptive female, with the participation of D2-like receptors. Activation of DA receptors with the same drug, at the same dose and in the same brain region, produces different effects on copulatory behavior that depend on the animal’s sexual motivational state.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CR:
-
Copulation resumption
- DA:
-
Dopamine
- DAergic:
-
Dopaminergic
- E:
-
Ejaculation
- EL:
-
Ejaculation latency
- I:
-
Intromission
- IL:
-
Intromission latency
- M:
-
Mount
- mPOA:
-
Medial preoptic area
- NAcc:
-
Nucleus accumbens
- VTA:
-
Ventral tegmental area
References
Agmo A, Turi AL, Ellingsen E, Kaspersen H (2004) Preclinical models of sexual desire: conceptual and behavioral analyses. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 78:379–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2004.04.013
Ahlenius S, Larsson K (1984) Apomorphine and haloperidol-induced effects on male rat sexual behavior: no evidence for actions due to stimulation of central dopamine autoreceptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 21:463–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-3057(84)80111-2
Baik JH (2013) Dopamine signaling in reward-related behaviors. Front Neural Circuits 7:152. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncir.2013.00152
Balfour ME, Yu L, Coolen LM (2004) Sexual behavior and sex-associated environmental cues activate the mesolimbic system in male rats. Neuropsycopharmacology 29:718–730. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300350
Beach FA, Jordan L (1956) Sexual exhaustion and recovery in the male rat. Q J Exp Psychol 8:121–133. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470215608416811
Berridge KC (2007) The debate over dopamine’s role in reward: the case for incentive salience. Psychopharmacology 191:391–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0578-x
Berridge KC, Kringelbach ML (2011) Building a neuroscience of pleasure and well-being. Psychol Well Being 1:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1186/2211-1522-1-3
Bitran D, Hull EM, Holmes GM, Lookingland KJ (1988) Regulation of male rat copulatory behavior by preoptic incertohypothalamic dopamine neurons. Brain Res Bull 20:323–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/0361-9230(88)90062-7
Blackburn JR, Pfaus JG, Phillips AG (1992) Dopamine functions in appetitive and defensive behaviours. Prog Neurobiol 39:247–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-0082(92)90018-A
Everitt B (1990) Sexual motivation: a neural and behavioural analysis of the mechanisms underlying appetitive and copulatory responses of male rats. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 14:217–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0149-7634(05)80222-2
Foreman M, Hall J (1987) Effects of D2-dopaminergic receptor stimulation on male rat sexual behavior. J Neural Transm 68:153–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02098495
Furmidge L, Tong Z-Y, Petry N, Clark D (1991) Effects of low, autoreceptor selective doses of dopamine agonists on the discriminative cue and locomotor hyperactivity produced by d-amphetamine. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 86:61–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01250376
Guadarrama-Bazante IL, Canseco-Alba A, Rodríguez-Manzo G (2014) Dopamine receptors play distinct roles in sexual behavior expression of rats with a different sexual motivational tone. Behav Pharmacol 25:684–694. https://doi.org/10.1097/FBP.0000000000000086
Hull EM, Rodríguez-Manzo G (2017) Male sexual behavior. In: Pfaff DW, Joëls M (eds) Hormones, brain and behavior, vol 1, chap. 1, 3rd edn. Academic Press, Oxford, pp 1–57
Hull EM, Bitran D, Pehek EA, Warner RK, Band LC, Holmes GM (1986) Dopaminergic control of male sex behavior in rats: effects of an intracerebrally-infused agonist. Brain Res 370:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(86)91106-6
Hull EM, Warner RK, Bazzett TJ, Eaton RC, Thompson JT, Scaletta LL (1989) D2/D1 ratio in the medial preoptic area affects copulation of male rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 251:422–427
Hull EM, Eaton RC, Markowski VP, Moses J, Lumley LA, Loucks JA (1992) Opposite influence of medial preoptic D1 and D2 receptors on genital reflexes: implications for copulation. Life Sci 51:1705–1713. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-3205(92)90299-5
Hull EM, Du J, Lorrain D, Matuszewich L (1995) Extracellular dopamine in the medial preoptic area: implications for sexual motivation and hormonal control of copulation. J Neurosci 15:7465–7471. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-11-07465.1995
Kalló I, Molnár CS, Szöke S, Fekete C, Hrabovszky E, Liposits Z (2015) Area-specific analysis of the distribution of hypothalamic neurons projecting to the rat ventral tegmental area, with special reference to the GABAergic and glutamatergic efferents. Front Neuroanat 9:112. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2015.00112
Kelley AE, Berridge KC (2002) The neuroscience of natural rewards: relevance to addictive drugs. J Neurosci 22:3306–3311. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-09-03306.2002
Kelliher KR, Liu YC, Baum MJ, Sachs BD (1999) Neuronal Fos activation in olfactory bulb and forebrain of male rats having erections in the presence of inaccessible estrous females. Neuroscience 92:1025–1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-4522(99)00050-0
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG (2013) Improving bioscience research reporting: the ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol 8:1–5
Kringelbach ML, Berridge KC (2009) Towards a functional neuroanatomy of pleasure and happiness. Trends Cogn Sci 13:479–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2009.08.006
Malsbury CW (1971) Facilitation of male rat copulatory behavior by electrical stimulation of the medial preoptic area. Physiol Behav 7:797–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9384(71)90042-4
Markowski VP, Hull EM (1995) Cholecystokinin modulates mesolimbic dopaminergic influence on male rat copulatory behavior. Brain Res 699:266–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(95)00918-G
Mas M, Fumero B, Perez-Rodriguez I (1995) Induction of mating behavior by apomorphine in sexually sated rats. Eur J Pharmacol 280:331–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-2999(95)00270-U
Melis M, Argiolas A (1995) Dopamine and sexual behavior. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 19:19–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/0149-7634(94)00020-2
Merari A, Ginton A (1975) Characteristics of exaggerated sexual behavior induced by electrical stimulation of the medial preoptic area in male rats. Brain Res 86:97–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(75)90641-1
Missale C, Nash SR, Robinson SW, Jaber M, Caron MG (1998) Dopamine receptors: from structure to function. Physiol Rev 78:190–212. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1998.78.1.189
Mitchell JB, Gratton A (1994) Involvement of mesolimbic dopamine neurons in sexual behaviors: implications for the neurobiology of motivation. Rev Neurosci 5:324–327. https://doi.org/10.1515/REVNEURO.1994.5.4.317
Moses J, Loucks JA, Watson HL, Matuszewich L, Hull EM (1984) Dopaminergic drugs in the medial preoptic area and nucleus accumbens: effects on motor activity, sexual motivation, and sexual performance. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 51:681–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/0091-3057(94)00437-N
Paglietti E, Pellegrini-Quarantotti B, Mereu G, Gessa G (1978) Apomorphine and L-DOPA lower ejaculation threshold in the male rat. Physiol Behav 20:559–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9384(78)90247-0
Paredes RG, Agmo A (2004) Has dopamine a physiological role in the control of sexual behavior? A critical review of the evidence. Prog Neurobiol 73:179–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2004.05.001
Paxinos G, Watson C (2009) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 6th edn. Elsevier, Oxford
Pehek EA, Warner RK, Bazzett TJ, Bitran D, Band LC, Eaton RC, Hull EM (1988) Microinjections of cis-flupenthixol, a dopamine antagonist, into the medial preoptic area impairs sexual behavior of male rats. Brain Res 443:70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(91)90505-P
Pehek EA, Thompson JT, Hull EM (1989) The effects of intracranial administration of the dopamine agonist apomorphine on penile reflexes and seminal emission in the rat. Brain Res 500:325–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(89)90328-4
Pfaus JG (2009) Pathways of sexual desire. J Sex Med 6:1506–1533. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1743-6109.2009.01309.x
Pfaus JG, Phillips AG (1989) Differential effects of dopamine receptor antagonists on the sexual behavior of male rats. Psychopharmacology 98:363–368. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00451688
Pfaus JG, Phillips AG (1991) Role of dopamine in anticipatory and consummatory aspects of sexual behavior in the male rat. Behav Neurosci 105:727–743. https://doi.org/10.1037/0735-7044.105.5.727
Robertson GS, Pfaus JG, Atkinson LJ, Matsumura H, Phillips AG, Fibiger HC (1991) Sexual behavior increases c-fos expression in the forebrain of the male rat. Brain Res 564:352–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(91)91477-I
Rodríguez-Manzo G (1999a) Yohimbine interacts with the dopaminergic system to reverse sexual satiation: further evidence for a role of sexual motivation in sexual exhaustion. Eur J Pharmacol 372(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-2999(99)00140-5
Rodríguez-Manzo G (1999b) Blockade of the establishment of the sexual inhibition resulting from sexual exhaustion by the Coolidge effect. Behav Brain Res 100:245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4328(98)00137-5
Rodríguez-Manzo G, Canseco-Alba A (2017) A new role for GABAergic transmission in the control of male rat sexual behavior expression. Behav Brain Res 320:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.11.041
Rodríguez-Manzo G, Fernández-Guasti A (1994) Reversal of sexual exhaustion by serotonergic and noradrenergic agents. Behav Brain Res 62:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-4328(94)90019-1
Rodríguez-Manzo G, Pellicer F (2007) Electrical stimulation of the ventral tegmental area exerts opposite effects on male rat sexual behaviour expression depending on the stimulated sub region. Behav Brain Res 179:310–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2007.02.006
Rodríguez-Manzo G, Pellicer F (2010) Electrical stimulation of dorsal and ventral striatum differentially alters the copulatory behavior of male rats. Behav Neurosci 124:686–694. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0020737
Rodríguez-Manzo G, Pellicer F, Larsson K, Fernández-Guasti A (2000) Stimulation of the medial preoptic area facilitates sexual behavior but does not reverse sexual satiation. Behav Neurosci 114:553–560. https://doi.org/10.1037/0735-7044.114.3.553
Rodríguez-Manzo G, Guadarrama-Bazante IL, Morales-Calderón A (2011) Recovery from sexual exhaustion-induced copulatory inhibition and drug hypersensitivity follow a same time course: two expressions of a same process? Behav Brain Res 217:253–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2010.09.014
Salamone JD, Correa M (2012) The mysterious motivational functions of mesolimbic dopamine. Neuron 76:470–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.10.021
Salamone JD, Pardo M, Yohn SE, López-Cruz L, SanMiguel N, Correa M (2016) Mesolimbic dopamine and the regulation of motivated behavior. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 27:231–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/7854_2015_383
Schultz W, Dayan P, Montague PR (1997) A neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science 275(5306):1593–1599. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.275.5306.1593
Stolzenberg DS, Numan M (2011) Hypothalamic interaction with the mesolimbic DA system in the control of the maternal and sexual behaviors in rats. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35:826–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.10.003
Tagliamonte A, Fratta W, Del Fiacco M, Gessa GL (1974) Possible stimulatory role of brain dopamine in the copulatory behavior of male rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2:257–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/0091-3057(74)90061-6
Van Dis H, Larsson K (1971) Induction of sexual arousal in the castrated male rat by intracranial stimulation. Physiol Behav 6:85–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9384(71)90021-7
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Marisol Guerra for the artwork design. The experiments here reported complied with the regulations established in the Mexican official norm for the use and care of laboratory animals NOM-062-ZOO-1999.
Funding
This work was supported by Conacyt Mexico (grant 220772 to G. R-M). The data here reported are part of the PhD thesis of I.L.G-B, who received a fellowship (grant 161083 Conacyt).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
Brain sections showing cannulae placements of the sexually experienced (left column) and sexually satiated animals (right column) infused into the medial preoptic area (mPOA) with different doses of apomorphine. Cannulae tips were in sections corresponding to − 0.0 to − 1.32 mm relative to bregma (Paxinos and Watson 2009). Asterisks indicate cannulae placement of vehicle-treated sexually experienced rats and filled diamonds vehicle-treated sexually satiated rats. Filled circles, triangles, and squares indicate the different apomorphine doses infused (PDF 719 kb)
Fig. S2
Brain sections showing cannulae placements of the sexually experienced (left column) and sexually satiated animals (right column) infused into the medial preoptic area (mPOA) with different doses of quinpirole. Cannulae tips were in sections corresponding to − 0.24 to − 1.32 mm relative to bregma (Paxinos and Watson 2009). Blank hexagons, circles, triangles, and squares indicate the different quinpirole doses infused (PDF 753 kb)
Fig. S3
Brain sections showing cannulae placements of the sexually experienced (left column) and sexually satiated animals (right column) infused into the nucleus accumbens (NAcc) with different doses of apomorphine. Cannulae tips were in sections corresponding to 0.72 to 2.16 mm relative to bregma (Paxinos and Watson 2009). Asterisks indicate cannulae placement of vehicle-treated sexually experienced male rats and filled diamonds those of vehicle-treated sexually satiated rats. Filled circles, triangles, and squares indicate the different apomorphine doses infused (PDF 753 kb)
Fig. S4
Brain sections showing cannulae placements of the sexually experienced (left column) and sexually satiated animals (right column) infused into the nucleus accumbens (NAcc) with different doses of quinpirole. Cannulae tips were in sections corresponding to 0.48 to 1.92 mm relative to bregma (Paxinos and Watson 2009). Blank circles, triangles, and squares indicate the different quinpirole doses infused (PDF 694 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guadarrama-Bazante, I.L., Rodríguez-Manzo, G. Nucleus accumbens dopamine increases sexual motivation in sexually satiated male rats. Psychopharmacology 236, 1303–1312 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-5142-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-5142-y