Summary
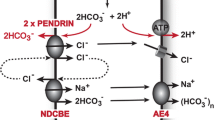
During the passed few years the cellular mechanisms responsible for the NaCl reabsorption in the thick ascending limb of the Henle loop of mammalian nephron and of the early distal tubule of amphibian kidney have been extensively studied. From these studies a new type of secondarily active transport mechanism, i.e. the Na+ - 2Cl− - K+ symport has emerged. Meanwhile it has been recognized that this system is also present in many other epithelia. All these epithelia share in common that they are sensitive to the so called loop diuretics. The present article summarizes our current knowledge of how the loop diuretics, by reversible interaction with the above cotransport system, inhibit the NaCl reabsorption in the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. It is shown that these drugs transfer the thick ascending limb cell to a state in which not only transepithelial NaCl reabsorption ceases but in which also very little energy is consumed since then K+ and Cl− “relax” to passive distribution across both cell membranes and Na+ entry into the cell is blocked.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakker-Grunwald T (1981) Hormon-induced diuretic sensitive potassium transport in turkey erythrocytes is anion dependent. Biochem Biophys Acta 641:427–431
Burg MB (1976) The renal handling of sodium chloride. In: Rector FC, Brenner BM (eds), The kidney, vol. I. Saunders, Philadelphia London Toronto, p 272
Burg MB (1982) Thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Kidney Int 22:454–464
Burg MB, Bourdeau JE (1978) Function of the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. In: Vogel HG, Ullrich KJ (eds), New aspects of renal function, vol 6. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam Oxford, pp 91 ff
Burg MB, Green N (1973) Function of the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Am J Physiol 224:659–668
Burg MB, Stoner L, Cardinal J, Green N (1973) Fuosemide effect on isolated perfused tubules. Am J Physiol 225:119–124
Eveloff J, Kinne R (1983) Sodium-chloride transport in the medullary, thick ascending limb of Henle's loop: Evidence for a sodium-chloride contransport system in plasma membrane vesicles. J Membrane Biol 72:173–181
Field M, Karnaky KJ Jr, Smith PL, Bolten JE, Kinter WB (1978) Ion transport across the isolated intestinal mucosa of the winter flounder, pseudopleuronectes americanus. J Membrane Biol 41:265–293
Geck P, Pietrzyk C, Burckhardt BC, Pfeiffer B, Heinz E (1980) Electrically silent cotransport of Na+, K+ and Cl− in Ehrlich cells. Biochem Biophys Acta 600:432–447
Goldberg M (1973) The renal physiology of diuretics. In: Orloff J, Berliner RB (eds). Handbook of Physiology, Sect 8. Renal Physiology. Am Physiol Soc, Washington, DC, pp 1003–1031
Greger R (1981) Cation selectivity of the isolated perfused cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit kidney. Pflügers Arch 390:30–37
Greger R (1981) Chloride reabsorption in the rabbit cortical thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. A sodium dependent process Pflügers Arch 390:38–43
Greger R (1981) Coupled transport of Na+ and Cl− in the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit nephron. Scand Audiol [Suppl] 14:1–15
Greger R (1984) The Na+-2Cl−-K+ carrier of the lumen membrane of the diluting segment of rabbit kidney. Fed Proc (in press)
Greger R, Schlatter E (1981) Presence of luminal K+, a prerequisitc for active NaCl transport in the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit kidney. Pflügers Arch 392:92–94
Greger R, Schlatter E (1983) Properties of the basolateral membrane of the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit kidney. Pflügers Arch 396:325–334
Greger R, Schlatter E (1983) Properties of the lumen membrane of the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit kidney. Pflügers Arch 396:315–324
Greger R, Oberleithner H, Schlatter E, Cassola AC (1983) Chloride activity in cells of isolated perfused cortical thick ascending limbs of rabbit kidney. Pflügers Arch [in press)
Greger R, Schlatter E, Lang F (1983) Evidence for electroneutral sodium chloride cotransport in the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit kidney. Pflügers Arch 396:308–314
Greger R, Weidtke C, Schlatter E, Wittner M, Gebler B (1984) Potassium activity in cells of isolated perfused cortical thick ascending limbs of rabbit kidney. Pflügers Arch (submitted)
Greven J (1982) Studies on the renal receptors of loop diuretics. Clin Exp Hypertens A 5:193–208
Guggino WB, Stanton BA, Giebisch G (1982) Electrical properties of isolated early distal tubule of the Amphiuma kidney. Fed Proc 41:1597
Halm DR, Krasny EJ, Frizzell RA (1983) Inhibition of K-indepenent NaCl uptake increases apical membrane K-conductance in flounder intestine. BMDIBL 22:80–82
Hannafin J, Friedman D, Kinne-Saffran E, Kinne R (1983) Ion fluxes and N-methylfuroscmide binding in squalus acanthias rectal gland plasma membrane vesicles. BMDIBL 22:69–72
Hebert SC, Culpepper RM, Andreoli TE (1981) NaCl transport in mouse medullary thick ascending limbs. I. Functional nephron heterogeneity and ADH-stimulated NaCl cotransport Am J Physiol 242:F412-F431
Hebert SC, Culpepper RM, Andreoli TE (1981) NaCl transport in mouse medullary thick ascending limbs. II. ADH enhancement of transcellular NaCl cotransport; origin of transepithelial voltage. Am J Physiol 241:F432-F442
Koenig B, Kinne R (1982) Sodium transport by plasma membranes isolated from cells of the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Fed Proc 41:1007
Nishimura H, Iami M (1981) Transepithelial voltage of proximal and distal renal tubules in the rainbow trout. VIIIth International Congress of Nephrology, Athen, p 31
Nishimura H, Imai M, Ogawa M (1983) Transepithelial voltage in reptilian and mammalian-types nephrons from japanese quail. Fed Proc 42:70
Oberleithner H, Greger R, Neumann S, Lang F, Giebisch G, Deetjen P (1983) Omission of luminal potassium reduces cellular chloride in early distal tubule of Amphibian kidney. Pflügers Arch 398:18–22
Oberleithner H, Guggino WB, Giebisch G (1982) Mechanism of distal tubular chloride transport in Amphiuma kidney. Am J Physiol 242:F331-F339
Oberleithner H, Lang F, Greger R, Wang W, Giebisch G (1983) Effect of luminal potassium on cellular sodium activity in the early distal tubule of Amphiuma kidney. Pflügers Arch 396:34–40
Oberleithner H, Giebisch G, Lang F, Wang W (1982) Cellular mechanism of the furosemide sensitive transport system in the kidney. Klin Wochenschr 60:1173–1179
Palfrey HC, Feit PW, Greengard P (1980) cAMP-stimulated cation cotransport in avian erythrocytes: inhibition by “loop” diuretics. Am J Physiol 238:C139-C148
Schlatter E, Greger R, Weidtke C (1983) Effect of “high ceiling” diuretics on active salt transport in the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit kidney. Correlation of chemical structure and inhibitory potency. Pflügers Arch 396:210–217
Wittner M, Schlatter E, Weidtke C, Greger R (1983) Aerobic glucose metabolism, the main energy source for active NAcl transport in the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop in rabbit nephron. Eur J Clin Invest 13:A6, 32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft: Gr 480/5-7
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greger, R., Schlatter, E. Cellular mechanism of the action of loop diuretics on the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Klin Wochenschr 61, 1019–1027 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01537500
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01537500