Summary
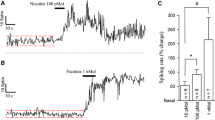
Effects of catecholamines, enkephalins and related compounds on electrical activity of the bed nucleus of stria terminalis (BST) were studied in vitro on thin BST sections prepared from guinea pig brains. Norepinephrine (NE) and epinephrine (E) suppressed field potentials elicited by a single shock to the stria terminalis (ST). The effects of NE and E were mimicked by phenylephrine and blocked by phenoxybenzamine. Isoproterenol and dichloroisoproterenol were without effect. NE and E suppressed the spontaneous firing of BST neurons and discharges elicited by ST stimulation. Dopamine was a less potent depressant. [D-Ala2]-Met-enkephalinamide (EKA) suppressed the field potentials and spike discharges elicited by ST stimulation. Spikes occurring spontaneously or during administration of glutamate were also suppressed by EKA. The action of EKA was blocked by naloxone. Late inhibition induced by stimulation of the lateral division of the ST was blocked by naloxone in about a third of the neurons examined. These results indicate that norepinephrine suppresses the activity of BST neurons by activating postsynaptic α-receptors. It is also suggested that opioid peptides mediate inhibitory control of the amygdala over the BST.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-Ari, Le Gal La Salle G, Barbin G, Schwarts JC, Garbarg M (1977) Histamine synthesizing afferents within the amygdaloid complex and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis of the rat. Brain Res 138: 285–294
De Olmos JS (1972) The amygdaloid projection field in the rat as studied with the cupric-silver method. In: Eleftheriou BE (ed) The neurobiology of the amygdala, Plenum Press, New York London, pp 145–204
Emery DE, Sachs BD (1976) Copulatory behavior in male rats with lesions in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Physiol Behav 17: 803–806
Garau L, Goconi S, Stefanini E, Trabucchi M, Spano PF (1978) Dopamine receptors: Pharmacological and anatomical evidences indicate that two distinct dopamine receptor populations are present in rat striatum. Life Sci 23: 1745–1750
Gent JP, Wolstencroft JH (1976) Effects of methionine-enkephalin and leucine-enkephalin compared with those of morphine on brainstem neurones in cat. Nature 261: 426–427
Gros C, Pradelles P, Humbert J, Dray F, Le Gal La Salle G, Ben-Ari Y (1978) Regional distribution of met-enkephalin within the amygdaloid complex and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Neurosci Lett 10: 193–196
Jhamandas K, Pinsky C, Phillis JW (1970) Effects of morphine and its antagonists on release of cerebral cortical acetylcholine. Nature 228: 176–177
Krettek JE, Price JL (1978) Amygdaloid projections to subcortical structures within the basal forebrain and brainstem in the rat and cat. J Comp Neurol 178: 225–254
Loh HH, Brase DA, Sampath-Khanna S, Mar JB, Way EL, Li EH (1976) β-Endorphin in vitro inhibition of striatal dopamine release. Nature 264: 567–568
Miczek KA, Brykczynski T, Grossman SO (1974) Differential effects of lesions in the amygdala, periamygdaloid cortex, and stria terminalis on aggressive behaviors in rats. J Comp Physiol Psychol 87: 760–771
Robison GA, Butcher RW, Sutherland EW (1967) Adenyl cyclase as an adrenergic receptor. Ann NY Acad Sci 139: 703–723
Rogawski MA, Aghajanian GK (1980) Activation of lateral geniculate neurons by norepinephrine: Mediation by an α-adrenergic receptor. Brain Res 182: 345–359
Satoh M, Zieglgansberger W, Herz A (1976) Actions of opiates upon single unit activity in the cortex of naive and tolerant rats. Brain Res 115: 99–110
Sawada S, Takada S, Yamamoto C (1980) Electrical activity recorded from thin sections of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, and the effects of neurotensin. Brain Res 188: 578–581
Segal M, Bloom FE (1974) The action of norepinephrine in the rat hippocampus. I. Iontophoretic studies. Brain Res 72: 79–97
Swanson LW, Cowan WM (1976) Autoradiographic studies of the development and connections of the septal area in the cat. In: DeFrance JF (ed) The septal nuclei. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 37–64
Swanson LW, Hartman B (1975) The central adrenergic system. An immunofmorescence study of the location of cell bodies and their efferent connections in the rat utilizing dopamine β-hydroxylases as a marker. J Comp Neurol 133: 467–506
Turner BH, Knapp ME (1976) Projections of the nucleus and tracts of the stria terminalis following lesions at the level of the anterior commissure. Exp Neurol 51: 468–479
Uhl GR, Kuhar MJ, Snyder SH (1978) Enkephaline-containing pathway: amygdaloid efferents in the stria terminalis. Brain Res 149: 223–228
Uhl GR, Snyder SH (1979) A neuronal pathway projecting from amygdala through stria terminalis. Brain Res 161: 522–526
Ungerstedt U (1971) Stereotaxic mapping of the monoamine pathways in the rat brain. Acta Physiol Scand [Suppl] 367: 1–48
Yamamoto C (1972) Activation of hippocampal neurons by mossy fiber stimulation in thin brain sections in vitro. Exp Brain Res 14: 423–435
Zieglgansberger W, Bayeri H (1976) The mechanism of inhibition of neuronal activity by opiates in the spinal cord of cat. Brain Res 115: 111–128
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by a grant from the Ministry of Education of Japan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sawada, S., Yamamoto, C. Postsynaptic inhibitory actions of catecholamines and opioid peptides in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Exp Brain Res 41, 264–270 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238883
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238883