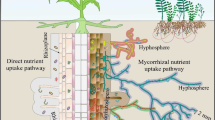
Abstract
The role of mycorrhizal fungi in acquisition of mineral nutrients by host plants is examined for three groups of mycorrhizas. These are; the ectomycorrhizas (ECM), the ericoid mycorrhizas (EM), and the vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizas (VAM). Mycorrhizal infection may affect the mineral nutrition of the host plant directly by enhancing plant growth through nutrient acquisition by the fungus, or indirectly by modifying transpiration rates and the composition of rhizosphere microflora.
A capacity for the external hyphae to take up and deliver nutrients to the plant has been demonstrated for the following nutrients and mycorrhizas; P (VAM, EM, ECM), NH4 + (VAM, EM, ECM), NO3 - (ECM), K (VAM, ECM), Ca (VAM, EM), SO4 2- (VAM), Cu (VAM), Zn (VAM) and Fe (EM). In experimental chambers, the external hyphae of VAM can deliver up to 80% of plant P, 25% of plant N, 10% of plant K, 25% of plant Zn and 60% of plant Cu. Knowledge of the role of mycorrhiza in the uptake of nutrients other than P and N is limited because definitive studies are few, especially for the ECM. Although further quantification is required, it is feasible that the external hyphae may provide a significant delivery system for N, K, Cu and Zn in addition to P in many soils. Proposals that ECM and VAM fungi contribute substantially to the Mg, B and Fe nutrition of the host plant have not been substantiated.
ECM and EM fungi produce ectoenzymes which provide host plants with the potential to access organic N and P forms that are normally unavailable to VAM fungi or to non mycorrhizal roots. The relative contribution of these nutrient sources requires quantification in the field.
Further basic research, including the quantification of nutrient uptake and transport by fungal hyphae in soil and regulation at the fungal-plant interface, is essential to support the selection and utilization of mycorrhizal fungi on a commercial scale.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AbbottL K and RobsonA D 1985 Formation of external hyphae in soil by four species of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 99, 245–255.
AbuzinadahR A and ReadD J 1989 The role of proteins in the nitrogen nutrition of ectomycorrhizal plants IV. The utilization of peptides by birch (Betula pendula L) infected with different mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 112, 55–60.
AhmadI, CarletonT J, MallochD W and HellebustJ.A. 1990 Nitrogen metabolism in the ectomycorrhizal fungus Laccaria bicolor (R. Mre.) Orton. New Phytol. 116, 431–441.
AmesR N, ReidC P P, PorterL K and CambardellaC 1983 Hyphal uptake and transport of nitrogen from two 15N labelled sources by Glomus mosseae, a vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus. New Phytol. 95, 381–396.
AzeonR and BareaJ M 1992 Nodulation, N2 fixation (15N) and N nutrition relationships in mycorrhizal or phosphateamended alfalfa plants. Symbiosis 12, 33–41.
BaathE and SpokesJ 1989 The effect of added nitrogen and phosphorus on mycorrhizal growth response and infection in Allium schoenoprasum. Can. J. Bot. 67, 3227–3232.
BajwaR and ReadD J 1985 The biology of mycorrhiza in the Ericaceae. IX. Peptides as nitrogen sources for the erecoid endophyte and for mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal plants. New Phytol. 101, 459–467.
BertaG, FusconiA, TrottaA and ScanneriniS 1990 Morphogenetic modifications induced by the mycorrhizal fungus Glomus strain E3 in the root system of Allium porrum L. New Phytol. 114, 207–215.
BethlenfalvayG J and FransonR L 1989 Manganese toxicity alleviated by mycorrhizae in soybean. J. Plant Nutr. 12, 953–970.
BethlenfalvayG J, UlrichJ M and BrownM S 1985 Plant response to mycorrhizal fungi: host, endophyte, and soil effects. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 49, 1164–1168.
BethlenfalvayG J, FransonR L, BrownM S and MiharaK L 1989 The Glycine-Glomus-Bradyrhizobium symbiosis. IX. Nutritional morphological and physiological responses of nodulated soybean to geographic isolates of the mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae. Physiol. Plant 76, 226–232.
BethlenfalvayG J, Reyes-SolisM G, CamelS B and Ferrera-CerratoR 1991 Nutrient transfer between the root zones of soybean and maize plants connected by a common mycorrhizal mycelium. Physiol. Plant. 82, 423–432.
BolanN S 1991 A critical review of the role of mycorrhizal fungi in the uptake of phosphorus by plants. Plant Soil 134, 189–207.
BolanN S, RobsonA D, BarrowN J and AylmoreL A G 1983 Specific activity of phosphorus in mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal plants in relation to the availability of phosphorus to plants. Soil Biol. Biochem. 16, 299–304.
BolanN S, RobsonA D and BarrowN J 1987 Effects of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza on the availability of iron phosphates to plants. Plant Soil 22, 401–410.
BougherN L, GroveT S and MalajczukN 1990 Growth and phosphorus acquisition of karri (Eucalyptus diyersicolor F. Muell.) seedlings inoculated with ectomycorrhizal fungi in relation to phosphorus supply. New Phytol. 114, 77–85.
BrownM S, ThamsurakulS and BethlenfalvayG J 1988 The Glycine-Glomus-Bradyrhizobium symbiosis. IX. Phosphorus-use efficiency of CO2 and N2 fixation in mycorrhizal soybean. Physiol. Plant. 74, 159–163.
BrundrettM C and AbbottL K 1991 Roots of jarrah forest plants. I. Mycorrhizal associations of shrubs and herbaceous plants. Aust. J. Bot. 39, 445–457.
BrylaD R and KoideR T 1990 Role of mycorrhizal infection in the growth and reproduction of wild vs. cultivated plants. II. Eight wild accessions and two cultivars of Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. Oecologia 84, 82–92.
CairneyJ W G and AshfordA E 1989 Reducing activity at the root surface in Eucalyptus pilularis-Pisolithus tinctorius ectomycorrhizas. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 16, 99–105.
CairneyJ W G and AshfordA E 1991 Release of a reducing substance by the ectomycorrhizal fungi Pisolithus tinctorius and Paxillus involutus. Plant Soil 135, 147–150.
ChalotM, BrunA, KhalidA, DellB, RohR and BottonB 1990 Occurrence and distribution of aspartate aminotransferases in spruce and beech ectomycorrhizas. Can. J. Bot. 68, 1756–1762.
ChalotM, StewartG R, BrunA, MartinF and BottonB 1991 Ammonium assimilation by spruce-Hebeloma sp. ectomycorrhizas. New Phytol. 119, 541–550.
CooperK M and TinkerP B 1978 Translocation and transfer of nutrients in vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizas. II. Uptake and translocation of phosphorus, zinc and sulphur. New Phytol. 81, 43–52.
CressW A, JohnsonG V and BartonL L 1986 The role of endomycorrhizal fungi in iron uptake by Hilaria jamesii. J. Plant Nutr. 2, 547–556.
CromackK, SollinsP, CransteinW C, SpeidelK, ToddA W, SpycherG, ChingY-Li and ToddR L 1979 Calcium oxalate accumulation and soil weathering in mats of the hypogeous fungus Hysterangium crassum. Soil Biol. Biochem 11, 463–468.
DaviesF TJr, PotterJ R and LindermanR G 1992 Mycorrhiza and repeated drought exposure affect drought resistance and extraradical hyphae development of pepper plants independent of plant size and nutrient content. J. Plant Physiol. 132, 289–294.
DellB, BottonB, MartinF and LeTaconF 1989 Glutamate dehydrogenases in ectomycorrhizas of spruce (Picea excelsa L) and beech (Fagus sylvatica L). New Phytol. 111, 683–692.
DennyH J and WilkinsD A 1987 Zinc tolerance in Betula spp. IV. The mechanism of ectomycorrhizal amelioration of zinc toxicity. New Phytol. 106, 545–553.
DoddJ C, BurtonC C, BurnsR G and JeffriesP 1987 Phosphatase activity associated with the roots and the rhizosphere of plants infected with vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 107, 163–171.
DoudsD DJr, JohnsonC R and KochK E 1988 Carbon cost of the fungal symbiont relative to net leaf P accumulation in a split-root VA mycorrhizal symbiosis. Plant Physiol. 86, 491–496.
FinlayR D and ReadD J 1986 The structure and function of the vegetative mycelium of ectomycorrhizal plants. II. The up-take and distribution of phosphorus by mycelial strands in the connecting host plants. New Phytol. 103, 157–165.
FinlayR D, EkH, OdhamG and SöderströmB 1988 Mycelial uptake translocation and assimilation of nitrogen from 15N-labelled ammonium by Pinus sylvestris plants infected with four different ectomycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 110, 59–66.
FinlayR D, EkH, OdhamG and SöderströmB 1989 Uptake, translocation and assimilation of nitrogen from 15N-labelled ammonium nitrate sources by intact ectomycorrhizal systems of Fagus sylvatica infected with Paxillus involutus. New Phytol. 113, 47–55.
FinlayR D, FrostegardA and SonnerfeldtA M 1992 Utilization of organic and inorganic nitrogen sources by ectomycorrhizal fungi in pure culture and in symbiosis with Pinus contorta Dougl. ex. Loud. New Phytol. 120, 105–115.
GeorgeE, HausslerK U, VetterleinD, GorgusE and MarschnerH 1992 Water and nutrient translocation by hyphae of Glomus mosseae. Can. J. Bot. 70, 2130–2137.
GreyW E 1991 Influence of temperature on colonization of spring barleys by vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Plant Soil 137, 181–190.
GriffithR P, CastellanoM A and CaldwellB A 1991 Hyphal mats formed by two ectomycorrhizal fungi and their association with Douglas-fir seedlings. A case study. Plant Soil 134, 255–259.
Hilger A B and KrauseH H 1989 Growth characteristics of Laccaria laccata and Paxillus involutus in liquid culture media with inorganic and organic phosphorus sources. Can. J. Bot. 67, 1782–1789.
HoI 1989 Acid phosphatase, alkaline phosphatase, and nitrate reductase activity of selected ectomycorrhizal fungi. Can. J. Bot. 67, 750–753.
HogbergP 1989 Growth and nitrogen inflow rates in mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal seedlings of Pinus sylvestris. Forest Ecol. Manag. 28, 7–17.
JakobsenI and RosendahlL 1990 Carbon flow into soil and external hyphae from roots of mycorrhizal cucumber plants. New Phytol. 115, 77–83.
JakobsenI, AbbottL K and RobsonA D 1992 External hyphae of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi associated with Trifolium subterraneum L I. Spread of hyphae and phosphorus inflow into roots. New Phytol. 120, 371–380.
JonesM D, DurallD M and TinkerP B 1990 Phosphorus relationships and production of extramatrical hyphae by two types of willow ectomycorrhizas at different soil phosphorus levels. New Phytol. 115, 259–267.
JongbloedR H, ClementJ M A M and Borst-PauwelsG W F H 1991 Kinetics of NH4 + and K+ uptake by ectomycorrhizal fungi. Effect of NH4 + on K+ uptake. Physiol. Plant 83, 437–432.
JungkA and ClaassenN 1989 Availability in soil and acquisition by plants as the basis for phosphorus and potassium supply to plants. Z Pflanzenernaehr. Bodenkd. 152, 151–157.
KammerbauerH, AgererR and SandermannHJr 1989 Studies on ectomycorrhiza XXII. Mycorrhizal rhizomorphs of Telephora terrestris and Pisolithus tinctorius in association with Norway spruce (Picea abies): formation in vitro and translocation of phosphate. Trees 3, 78–84.
KoideR 1991 Nutrient supply, nutrient demand and plant response to mycorrhizal infection. New Phytol. 117, 365–386.
KothariS K, MarschnerH and RömheldV 1990a Direct and indirect effects of VA mycorrhiza and rhizosphere microorganisms on mineral nutrient acquisition by maize (Zea mays L) in-a calcareous soil. New Phytol. 116, 637–645.
KothariS K, MarschnerH and GeorgeE 1990b Effect of VA mycorrhizal fungi and rhizosphere microorganisms on root and shoot morphology, growth and water relations in maize. New Phytol. 116, 303–311.
KothariS K, MarschnerH and RömheldV 1991a Contribution of VA mycorrhizal hyphae in acquisition of phosphorus and zinc by maize grown in a calcareous soil. Plant Soil 131, 177–185.
KothariS K, MarschnerH and RömheldV 1991b Effect of a vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and rhizosphere microorganisms on managenese reduction in the rhizosphere and manganese concentrations in maize (Zea mays L). New Phytol. 117, 649–655.
LambertD H and WeidensaulT C 1991 Element uptake by mycorrhizal soybean from sewage-sludge-treated soil. Soil Sci. Am. J. 55, 393–398.
LapeyrieF 1990 The role of ectomycorrhizal fungi in calcareous soil tolerance by ‘symbiocalcicole’ woody plants. Ann. Sci. For. 21, 579–589.
LapeyrieF, PicattoC, GerardJ and DexheimerJ 1990 T.E.M. study of intracellular and extracellular calcium oxalate accumulation by ectomycorrhizal fungi in pure culture or in association with Eucalyptus seedlings. Symbiosis 2, 163–166.
LeakeJ R and ReadD J 1989 The biology of mycorrhiza in the Ericaceae XV. The effect of mycorrhizal infection on calcium uptake by Calluna vulgris (L) Hull. New Phytol. 113, 535–544.
LeakeJ R and ReadD J 1990 Proteinase activity in mycorrhizal fungi I. The effect of extracellular pH on the production and activity of proteinase by ericoid endophytes from soils of contrasted pH. New Phytol. 115, 243–250.
LiX-L, GeorgeE and MarschnerH 1991a Extension of the phosphorus depletion zone in VA-mycorrhizal white clover in a calcareous soil. Plant Soil 136, 41–48.
LiX-L, GeorgeE and MarschnerH 1991b Phosphorus depletion and pH decrease at the root-soil and hyphae-soil interfaces of VA mycorrhizal white clover fertilized with ammonium. New Phytol. 119, 397–404.
LiX-L, MarschnerH and GeorgeE 1991c Acquisition of phosphorus and copper by VA-mycorrhizal hyphae and root-to-shoot transport in white clover. Plant Soil 136, 49–57.
LindermanR G 1988 Mycorrhizal interactions with the rhizosphere microflora: the mycorrhizosphere effect. Phytopathology 78, 366–371.
MaijalaP, FagerstedtK F and RaudaskoskiM 1991 Detection of extracellular cellulolytic and proteolytic activity in ectomycorrhizal fungi and Heterobasidion annosum (Fr.) Bref. New Phytol. 117, 643–648.
MartinF, StewartG, GenetetI and LeTaconF 1986 Assimilation of 15NH4 + by beech (Fagus sylvatica L) ectomycorrhizas. New Phytol. 102, 85–94.
MartinF, StewartG R, GenetetI and MourotB 1988 The involvement of glutamate dehydrogenase and glutamine synthetase in ammonia assimilation by the rapidly growing ectomycorrhizal ascomycete, Conococcum geophilum Fr. New Phytol. 110, 541–550.
MitchellR J, H EGarrett, CoxG S and AtalayA 1990 Boron and ectomycorrhizal influences on mineral nutrition of container-grown Pinus ehinata Mill. J. Plant Nutr. 13, 1555–1574.
NewmanE I, EasonW R, EissenstatD M and RamosM I R F 1992 Interactions between plants: the role of mycorrhizae. Mycorrhiza 1, 47–53.
PerrinR 1990 Interactions between mycorrhizae and diseases caused by soil-borne fungi. Soil Use Manag. 6, 189–195.
PaulitzT C and LindermanR G 1989 Interactions between fluorescent pseudomonads and VA mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 113, 37–45.
PicciniD, OcampoJ A and BedmarE J 1988 Possible influence of Rhizobium on VA mycorrhiza metabolic activity in double symbiosis of alfalfa plants (Medicago sativa L) grown in a pot experiment. Biol. Fert. Soils 6, 65–67.
PowellP E, SzaniszloP J, ClineG R and ReidC P P 1982 Hydroxamate siderophores in the iron nutrition of plants. J. Plant Nutr. 5, 653–573.
RajuP S, ClarkR B, EllisJ R and MaranvilleJ W 1990 Mineral uptake and growth of sorghum colonized with VA mycorrhiza at varied soil phosphorus levels. J. Plant Nutr. 13, 843–859.
ReadD J 1984 The structure and function of the vegetative mycelium of mycorrhizal roots. In The Ecology and Physiology of the Fungal Mycelium. Ed. D HJennings and A D MRayner. pp 215–240. Cambridge University Press. Cambridge.
RhodesL H and GerdemannJ W 1978 Translocation of calcium and phosphate by external hyphae of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae. Soil Sci. 126, 125–126.
RobsonA D, O'HaraG W and AbbottL K 1981 Involvement of phosphorus in nitrogen fixation by subterranean clover (Trifolium subterraneum L). Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 8, 427–436.
RygiewiczP T and BledsoeC S 1984 Mycorrhizal effects on potassium fluxes by northwest coniferous seedlings. Plant Physiol. 76, 918–923.
SandersF E and TinkerP B 1973 Phosphate inflow into mycorrhizal roots. Pestic. Sci. 4, 385–395.
ScherommP, PlassardC and SalsacL 1990 Nitrate nutrition of maritime pine (Pinus pinaster Soland in Ait.) ectomycorrhizal with Hebeloma cylindrosporum Romagn. New Phytol. 114, 93–89.
SchulerR and HaselwandterK 1988 Hydroxamate siderophore production by ericoid mycorrhizal fungi. J. Plant Nutr. 11, 907–913.
SeciliaJ and BagyarajD J 1987 Bacteria and actinomycetes associated with pot cultures of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizas. Can. J. Bot. 33, 1069–1073.
ShawG, LeakeJ R, BakerA J M and ReadD J 1990 The biology of mycorrhiza in the Ericaceae. XVII. The role of mycorrhizal infection in the regulation of iron uptake by ericaceous plants. New Phytol. 115, 251–258.
SieverdingE and ToroS 1988 Influence of soil water regime on VA mycorrhiza. V. Performance of different VAM fungal species with cassava. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 161, 322–332.
StoneE L 1990 Boron deficiency and excess in forest trees: A review. For. Ecol. Manag. 37, 49–75.
StrakerC J and MitchellD T 1986 The activity and characterization of acid phosphatases in endomycorrhizal fungi of the Ericaceae. New Phytol. 104, 243–256.
SylviaD 1988 Activity of external hyphae of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Soil Biol. Biochem. 20, 39–43.
VierheiligH and OcampoJ A 1991 Receptivity of various wheat cultivars to infection by VA-mycorrhizal fungus influenced by inoculum potential and the relation of VAM-effectiveness to succinic dehydrogenase activity of the mycelium in the root. Plant Soil 133, 291–296.
VogtK A, PublicoverD A and VogtD J 1991 A critique of the role of ectomycorrhizas in forest ecology. Agric. Ecos. Environ. 35, 171–190.
WhiteJ A and BrownM F 1979 Ultrastructural and X-ray analysis of phosphorus granules in a vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus. Can. J. Bot. 57, 2812–2818.
WilkinsD A 1991 The influence of sheathing (ecto-) mycorrhizas of trees on the uptake and toxicity of metals. Agric. Ecos. Environ. 35, 145–260.
ZhuH, GuoD and DancikB P 1990 Purification and characterization of an extracellular acid proteinase from the ectomycorrhizal fungus Hebeloma crustuliniforme. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56, 837–843.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marschner, H., Dell, B. Nutrient uptake in mycorrhizal symbiosis. Plant Soil 159, 89–102 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00000098
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00000098