Abstract
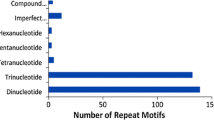
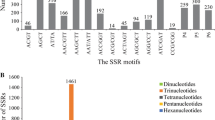
Expressed sequence tags derived simple sequence repeats (EST-SSRs), are different from traditional genomic SSR (gSSR) markers. They are more likely to be embedded in the functional gene sequences, less costly and time effective, and may provide abundant information. By analysis of 10,018 expressed sequence tags (ESTs) out of 10,829 for rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) available in public domain DNA databases, 799 SSR loci were found in the 643 non-redundant SSR-ESTs (SSR-containing ESTs), corresponding to one SSR in every 2.25 kb of the ESTs in rubber tree transcriptome. Of the total 799 SSRs in these ESTs, 673 (84.2%) contained simple repeat motifs while 126 (15.8%) represented compound motif types. Of the total EST-SSRs, 45.3% (362/799) were mononucleotide repeats (MNRs), 42.2% (337/799) were dinucleotide repeats (DNRs), 11.9% (95/799) were trinucleotide repeats (TNRs) and 0.6% (5/799) were tetranucleotide repeats (TTNRs) and hexanucleotide repeats (HNRs). The repeat motifs AAG and AG were the most abundant without regard to single nucleotide repeat. A total of 184 primer pairs were successful designed based on the non-redundant SSR-ESTs. Using 55°C as annealing temperature, 110 primer pairs successfully amplified 12 H. brasiliensis cultivated varieties and four related species. Analysis on 74 alleles amplified by 30 randomly selected primer pairs indicated the medium polymorphism of the EST-SSRs developed. Based on 272 alleles detected by 87 EST-SSR markers, an assessment of genetic diversity was carried out on 12 H. brasiliensis cultivated varieties and four related species. In addition, investigation based on five selected EST-SSRs by cloning and sequencing cross some cultivated species and related species provided evidence for cross-species/genera transferability of the EST-SSR markers developed in this study.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal RK, Hendre PS, Varshney RK, Bhat PR, Krishnakumar V, Singh L (2007) Identification, characterization and utilization of EST-derived genic microsatellite markers for genome analyses of coffee and related species. Theor Appl Genet 114:359–372. doi:10.1007/s00122-006-0440-x
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang JH, Zhang ZH, Miller W et al (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST:a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402. doi:10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Areshchenkova T, Ganal MW (2002) Comparative analysis of polymorphism and chromosomal location of tomato microsatellite markers isolated from different sources. Theor Appl Genet 104:229–235. doi:10.1007/s00122-001-0775-2
Baruah A, Naik V, Hendre PS, Rajkumar R, Rajendrakumar P, Aggarwal RK (2003) Isolation and characterization of nine microsatellite markers from Coffea arabica L., showing wide cross-species amplifications. Mol Ecol Notes 3:647–650. doi:10.1046/j.1471-8286.2003.00544.x
Besse P, Seguin M, Legrun P, Chevallier MH, Nicolas D, Lanaud C (1994) Genetic diversity among wild and cultivated populations of Hevea brasiliensis assessed by nuclear RFLP analysis. Theor Appl Genet 88:199–207. doi:10.1007/BF00225898
Bhat PR, Krishnakumar V, Hendre PS, Rajendrakumar P, Varshney RK, Aggarwal RK (2005) Identification and characterization of gene-derived EST-SSR markers from robusta coffee variety ‘CxR’ (an interspecific hybrid of Coffea canephora × Coffea congensis). Mol Ecol Notes 5:80–83. doi:10.1111/j.1471-8286.2004.00839.x
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Bozhko M, Riegel R, Schubert R, Muller-Starck GA (2003) A cyclophilin gene marker confirming geographical differentiation of Norway spruce populations and indicating viability response on excess soil-born salinit. Mol Ecol 12:3147–3155. doi:10.1046/j.1365-294X.2003.01983.x
Callow JA, Ford-Lloyd BV, Newbury HJ (1997) Biotechnology and plant genetic resources: conservation and use. CAB International, Wallingford, Oxon, UK, pp 49–76
Cardle L, Ramsay L, Milbourne D, Macaulay M, Marshall D, Waugh R (2000) Computational and experimental characterization of physically clustered simple sequence repeats in plants. Genetics 156:847–854
Chen X, Cho YG, McCouch SR (2002) Sequence divergence of rice microsatellites in Oryza and other plant species. Mol Genet Genomics 268:331–343. doi:10.1007/s00438-002-0739-5
Chen CX, Zhou P, Choi YA, Huang S, Gmitter FG Jr (2006) Mining and characterizing microsatellites from citrus ESTs. Theor Appl Genet 112:1248–1257. doi:10.1007/s00122-006-0226-1
Chow KS, Wan KL, Isa MN, Bahari A, Tan SH, Harikrishna K et al (2007) Insights into rubber biosynthesis from transcriptome analysis of Hevea brasiliensis latex. J Exp Bot 58(10):2429–2440. doi:10.1093/jxb/erm093
Clauss MJ, Cobban H, Mitchell-Olds T (2002) Crossspecies microsatellite markers for elucidating population genetic structure in Arabidopsis and Arabis (Brassicaceae). Mol Ecol 11:591–601. doi:10.1046/j.0962-1083.2002.01465.x
Combes MC, Andrzejewski S, Anthony F, Bertrand B, Rovelli P, Graziosi G et al (2000) Characterization of microsatellite loci in Coffea arabica and related coffee species. Genetics 156:847–854
Cordeiro GM, Casu R, McIntyre CL, Manners JM, Henry RJ (2001) Microsatellite markers from sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) ESTs cross transferable to erianthus and sorghum. Plant Sci 160:1115–1123. doi:10.1016/S0168-9452(01)00365-X
Davierwala AP, Ramakrishna W, Chowdari V, Ranjekar PK, Gupta VS (2001) Potential of (GATA)n microsatellites from rice for inter-and intraspecific variability studies. BMC Evol Biol 1:7. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-1-7
Decroocq V, Fave MG, Hagen L, Bordenave L, Decroocq S (2003) Development and transferability of apricot and grape microsatellite markers across taxa. Theor Appl Genet 106:912–922
Dreisigacker S, Zhang P, Warburton ML, Ginkel MV (2004) SSR and pedigree analyses of genetic diversity among CIMMYT wheat lines targeted to different megaenvironments. Crop Sci 44:381–388
Eujayl I, Sorrells ME, Baum M, Wolters P, Powell W (2002) Solation of EST-derived microsatellite markers for genotyping the A and B genomes of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 104:399–407. doi:10.1007/s001220100738
Ferguson ME, Burow MD, Schulze SR, Bramel PJ, Paterson AH, Kresovich S et al (2004) Microsatellite identification and characterization in peanut (A. hypogaea L.). Theor Appl Genet 108:1064–1070. doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1535-2
Fraser LG, Harvey CF, Crowhurst RN, De Silva HN (2004) EST-derived microsatellites from Actinidia species and their potential for mapping. Theor Appl Genet 108:1010–1016. doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1517-4
Gao LF, Tang J, Li H, Jia J (2003) Analysis of microsatellites in major crops assessed by computational and experimental approaches. Mol Breed 113:163–185
Gao LZ, Zhang CH, Jia JZ (2005) Cross-species transferability of rice microsatellites in its wild relatives and the potential for conservation genetic studies. Genet Resour Crop Evol 52:931–940. doi:10.1007/s10722-003-6124-3
Gonzalo MJ, Oliver M, Garcia-Mas J, Monfort A, Dolcet-Sanjuan R, Katzir N et al (2005) Simple-sequence repeat markers used in merging linkage maps of melon (Cucumis melo L.). Theor Appl Genet 110:802–811. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1814-6
Guen V, Lespinasse D, Oliver G, Rodier-Goud M, Pinard F, Seguin M (2003) Molecular mapping of genes conferring field resistance to South American Leaf Blight (Microcyclus ulei) in rubber tree. Theor Appl Genet 108:160–167. doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1407-9
Guo WZ, Wang W, Zhou BL, Zhang TZ (2006) Cross-species transferability of G. arboreum-derived EST-SSRs in the diploid species of Gossypium. Theor Appl Genet 112:1573–1581. doi:10.1007/s00122-006-0261-y
Gupta PK, Varshney RK (2000) The development and use of microsatellite markers fore genetic analysis and plant breeding with emphasis on bread wheat. Euphytica 113:163–185. doi:10.1023/A:1003910819967
Gutierrez MV, Vaz Patto MC, Huguet T, Cubero JI, Moreno MT, Torres AM (2005) Cross-species amplification of Medicago truncatula microsatellites across three major pulse crops. Theor Appl Genet 110:1210–1217. doi:10.1007/s00122-005-1951-6
Holton TA, Christopher JT, McClure L, Harker N, Henry RJ (2002) Identification and mapping of polymorphic SSR markers from expressed gene sequences of barley and wheat. Mol Breed 9:63–71. doi:10.1023/A:1026785207878
Huang WG, Cipriani G, Morgante M, Testolin R (1998) Microsatellite DNA in Actinidia chinensis: isolation, characterization, and homology in related species. Theor Appl Genet 97:1269–1278. doi:10.1007/s001220051019
Jung S, Albert A, Jesudurai C, Tomkins J, Main D (2005) Frequency, type, distribution and annotation of simple sequence repeats in Rosaceae ESTs. Funct Integr Genomics 5:136–143. doi:10.1007/s10142-005-0139-0
Kantety RM, Matthews DE, Sorrells ME (2002) Data mining for simple sequence repeats in expressed sequence tags from barley, maize, rice, sorghum and wheat. Plant Mol Biol 148:501–510. doi:10.1023/A:1014875206165
Ko JH, Chow KS, Han KH (2003) Transcriptome analysis reveals novel features of the molecular events occurring in the laticifers of Hevea brasiliensis (para rubber tree). Plant Mol Biol 53(4):479–492. doi:10.1023/B:PLAN.0000019119.66643.5d
Kota R, Varshney RK, Thiel T, Dehmer KJ, Graner A (2001) Generation and comparison of EST-derived SSRs and SNPs in barley (Houdeum Vulgare L.). Hereditas 135:145–151. doi:10.1111/j.1601-5223.2001.00145.x
Lespinasse D, Rodier-Goud M, Grivet L, Leconte A, Legnate H, Seguin M (2000) A saturated genetic linkage map of rubber tree (Hevea spp.) based on RFLP, AFLP, microsatellite, and isozyme markers. Theor Appl Genet 100:127–138. doi:10.1007/s001220050018
Liewlaksaneeyanawin C, Ritland CE, El-Kassaby YA, Ritland K (2004) Single-copy, species-transferable microsatellite markers developed from loblolly pine ESTs. Theor Appl Genet 109:361–369. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1635-7
Low FC, Gale MD (1996) Development of molecular markers for Hevea. J Nat Rubb Res 6:152–157
Luo H, Boutry M (1995) Phylogenetic relationships within Hevea brasiliensis as deduced from a polymorphic mitochondrial DNA region. Theor Appl Genet 91:876–884. doi:10.1007/BF00223895
Miller RT, Christoffels AG, Gopalakrishnan C, Burke J, Ptitsyn AA, Broveak TR et al (1999) A comprehensive approach to clustering of expressed human gene sequence: the sequence tag alignment and consensus knowledge base. Genome Res 9:1143–1155. doi:10.1101/gr.9.11.1143
Moncada P, McCouch S (2004) Simple sequence repeat diversity in diploid and tetraploid Coffea species. Genome 47:501–509. doi:10.1139/g03-129
Nicot N, Chiquet V, Gandon B, Amilhat L, Legeai F, Leroy P et al (2004) Study of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers from wheat expressed sequence tags (ESTs). Theor Appl Genet 109:800–805. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1685-x
Peakall R, Gilmore S, Keys W (1998) Cross-species amplification of soybean (Glycine max) simple sequence repeats (SSRs) within the genus and other legume genera: implications for the transferability of SSRs in plants. Mol Biol Evol 15:1275–1287
Pinto LR, Oliveira KM, Marconi T, Garcia AAF, Ulian EC, deSouza AP (2006) Characterization of novel sugarcane expressed sequence tag microsatellites and their comparison with genomic SSRs. Plant Breed 125:378–384. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0523.2006.01227.x
Ramakrishna W, Davierwala AP, Gupta VS, Ranjekar PK (1998) Expansion of (GA)n dinucleotide at a microsatellite locus associated repeats (SSRs) within the genus and other legume genera. Biochem Genet 36:323–327. doi:10.1023/A:1018793328896
Rota M, Kantety RV, Yu JK, Sorrells ME (2005) Non-random distribution and frequencies of genomic and EST-derived microsatellite markers in rice, wheat and barley. BMC Genomics 6:23. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-6-23
Rovelli P, Mettulio R, Anthony F (2000) Microsatellites in Coffea arabica L. In: Sera T, Soccol CR, Pandey A, Roussos S (eds) Coffee biotechnology and quality. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 123–133
Roy CB, Nazeer MA, Saha T (2004) Identification of simple sequence repeats in rubber (Hevea brasiliensis). Curr Sci 87(6)
Schubert R, Mueller-Starck G, Riegel R (2001) Development of EST-PCR markers and monitoring their intrapopulational genetic variation in Picea abies (L.) Karst. Theor Appl Genet 103:1223–1231. doi:10.1007/s001220000501
Scott KD, Eggler P, Seaton G, Rossetto M, Ablett EM, Lee LS et al (2000) Analysis of SSRs derived from grape ESTs. Theor Appl Genet 100:723–726. doi:10.1007/s001220051344
Stack S, Campbell L, Henderson K, Eujayl I, Hanafey M, Powell W et al (2000) Development of EST-derived microsatellite markers for mapping and germplasm analysis in wheat. Plant & Animal Genome VIII Conference January:9–12
Swanson T (1996) Global values of biological diversity: the public interest in the conservation of plant genetic resources for agriculture. Plant Genet Resour Newsl 105:1–3
Temnykh S, Declerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch S (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genome Res 11:1441–1452. doi:10.1101/gr.184001
Thiel T, Michalek W, Varshney RK, Graner A (2003) Exploiting EST database for the development and characterization of gen-derived SSR-markers in barley(Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 106:411–422
Varghese YA (1992) Germ plasm resources and genetic improvements. In: Sethuraj MR, Mathew NM (eds) Developments in crop science 23, natural rubber biology, cultivation and technology. Elsevier, Cambridge, pp 89–115
Varshney RK, Graner A, Sorrells ME (2005) Genic microsatellite markers in plants: features and applications. Trends Biotechnol 23:48–55. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2004.11.005
Venkatachalam P, Thomas S, Priya P, Thanseem I, Gireesh T, Saraswathyamma CK et al (2002) Identification of DNA polymorphism within the clones of Hevea brasiliensis (Muell.) Arg. using RAPD analysis. Indian J Nat Rubb Res 15:172–181
Venkatachalam P, Priya P, Gireesh T, Saraswathy Amma CK, Thulaseedharan A (2006) Molecular cloning and sequencing of a polymorphic band from rubber tree [Hevea brasiliensis (Muell.) Arg.]: the nucleotide sequence revealed partial homology with proline-specific permease gene sequence. Curr Sci 90(11):1510–1515
Wetmur JG (1991) DNA Probes: Applications of the Principles of Nucleic Acid Hybridization. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 26:227–259. doi:10.3109/10409239109114069
Xie H, Sui Y, Chang F-Q, Xu Y, Ma R-C (2006) SSR allelic variation in almond (Prunus dulcis Mill.). Theor Appl Genet 112:366–372. doi:10.1007/s00122-005-0138-5
Acknowledgements
Project support was provided by the National Non-profit Institute Research Grant. Prof. Jun Zhang of Shandong Academy of Agricultural Science and Prof. Xing-Quan Zhu of South China Agricultural University are thanked for their constructive comments on the content of the manuscript. Dr. Keng-See Chow of the Rubber Research Institute of Malaysia is thanked for the critical reading of the manuscript. Prof. John M. Woodruff, University of Georgia, is thanked for the English usage.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, S.P., Li, W.G., Huang, H.S. et al. Development, characterization and cross-species/genera transferability of EST-SSR markers for rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). Mol Breeding 23, 85–97 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-008-9216-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-008-9216-0