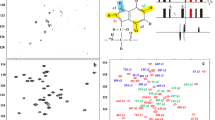
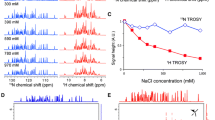
Abstract
The side-chain amide groups of asparagine and glutamine play important roles in stabilizing the structural fold of proteins, participating in hydrogen-bonding networks and protein interactions. Selective 15N-labeling of side-chain amides, however, can be a challenge due to enzyme-catalyzed exchange of amide groups during protein synthesis. In the present study, we developed an efficient way of selectively labeling the side chains of asparagine, or asparagine and glutamine residues with 15NH2. Using the biosynthesis pathway of tryptophan, a protocol was also established for simultaneous selective 15N-labeling of the side-chain NH groups of asparagine, glutamine, and tryptophan. In combination with site-specific tagging of the target protein with a lanthanide ion, we show that selective detection of 15N-labeled side-chains of asparagine and glutamine allows determination of magnetic susceptibility anisotropy tensors based exclusively on pseudocontact shifts of amide side-chain protons.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertini I, Luchinat C (1999) New applications of paramagnetic NMR in chemical biology. Curr Opin Chem Biol 3:145–151
Bertini I, Felli IC, Luchinat C (2000) Lanthanide induced residual dipolar couplings for the conformational investigation of peripheral 15NH2 moieties. J Biomol NMR 18:347–355
Bertini I, Luchinat C, Parigi G (2002) Paramagnetic constraints: an aid for quick solution structure determination of paramagnetic metalloproteins. Concepts Magn Reson 14:259–286
Boehlein SK, Richards NGJ, Schuster SM (1994) Glutamine-dependent nitrogen transfer in Escherichia coli asparagine synthetase B. J Biol Chem 269:7450–7457
Buck M, Schwalbe H, Dobson CM (1995) Structural determinants of protein dynamics: analysis of 15 N NMR relaxation measurements for main-chain and side-chain nuclei of hen egg white lysozyme. Biochemistry 34:4041–4055
Cai M, Huang Y, Clore GM (2001) Accurate orientation of the functional groups of asparagine and glutamine side chains using one- and two-bond dipolar couplings. J Am Chem Soc 123:8642–8643
Cedar H, Schwartz JH (1969) The asparagine synthetase of Escherichia coli I. Biosynthetic role of the enzyme, purification, and characterization of the reaction products. J Biol Chem 244:4112–4121
Clore GM (2011) Exploring sparsely populated states of macromolecules by diamagnetic and paramagnetic NMR relaxation. Protein Sci 20:229–246
Clore GM, Tang C, Iwahara J (2007) Elucidating transient macromolecular interactions using paramagnetic relaxation enhancement. Curr Opin Struct Biol 17:603–616
Creighton TE (1993) Proteins: structure and molecular properties, 2nd edn. Freeman, New York
Edwards KJ, Ollis DL, Dixon NE (1997) Crystal structure of cytoplasmic Escherichia coli peptidyl-prolyl isomerase: evidence for decreased mobility of loops upon Complexation. J Mol Biol 271:258–265
Etezady-Esfarjani T, Hiller S, Villalba C, Wüthrich K (2007) Cell-free synthesis of perdeuterated proteins for NMR studies. J Biomol NMR 39:229–238
Farmer BT, Venters RA (1996) Assignment of aliphatic side-chain 1HN/15N resonances in perdeuterated proteins. J Biomol NMR 7:59–71
Goddard TD, Kneller DG (2008) Sparky 3. University of California, San Francisco
Grzesiek S, Bax A (1993) Amino acid type determination in the sequential assignment procedure of uniformly 13C/15N-enriched proteins. J Biomol NMR 3:185–204
Higman VA, Boyd J, Smith LJ, Redfield C (2004) Asparagine and glutamine side chain conformation in solution and crystal: a comparison for hen egg-white lysozyme using residual dipolar couplings. J Biomol NMR 30:327–346
Huang XY, Holden HM, Raushel FM (2001) Channeling of substrates and intermediates in enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Annu Rev Biochem 70:149–180
Huang F, Pei YY, Zuo HH, Chen JL, Yang Y, Su XC (2013) Bioconjugation of proteins with a paramagnetic NMR and fluorescent tag. Chem Eur J 19:17141–17149
John M, Otting G (2007) Strategies for measurements of pseudocontact shifts in protein NMR spectroscopy. ChemPhysChem 8:2309–2313
Kainosho M, Güntert P (2010) SAIL—stereo-array isotope labeling. Q Rev Biophys 42:247–300
Kay WW (1971) Two aspartate transport systems in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 246:7373–7382
Keizers PH, Ubbink M (2011) Paramagnetic tagging for protein structure and dynamics analysis. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 58:88–96
Kigawa T, Muto Y, Yokoyama S (1995) Cell-free synthesis and amino acid-selective stable-isotope labelling of proteins for NMR analysis. J Biomol NMR 6:129–134
Lesk AM (2001) Introduction to protein architecture: the structural biology of proteins. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Liu A, Li Y, Yao L, Yan H (2006) Simultaneous NMR assignment of backbone and side chain amides in large proteins with IS-TROSY. J Biomol NMR 36:205–214
Liu A, Yao L, Li Y, Yan H (2007) TROSY of side chain amides in large proteins. J Magn Reson 186:319–326
Liu A, Lu Z, Wang J, Yao L, Li Y, Yan H (2008a) NMR detection of bifurcated hydrogen bonds in large proteins. J Am Chem Soc 130:2428–2429
Liu A, Wang J, Lu Z, Yao L, Li Y, Yan H (2008b) Hydrogen-bond detection, configuration assignment and rotamer correction of side chain amides in large proteins by NMR spectroscopy through protium/deuterium isotope effects. ChemBioChem 9:2860–2871
Löhr F, Rüterjans H (1997) H2NCO-E.COSY, a simple method for the sterospecific assignment of side-chain amide protons in proteins. J Magn Reson 124:255–258
Loscha KV, Otting G (2013) Biosynthetically directed 2H labelling for stereospecific resonance assignments of glycine methylene groups. J Biomol NMR 55:97–104
Marley J, Lu M, Bracken C (2001) A method for efficient isotopic labeling of recombinant proteins. J Biomol NMR 20:71–75
McIntosh LP, Dahlquist FW (1990) Biosynthetic incorporation of 15N and 13C for assignment and interpretation of nuclear-magnetic resonance spectra of proteins. Quart Rev Biophys 23:1–38
McIntosh LP, Brun E, Kay LE (1997) Stereospecific assignment of the NH2 resonances from the primary amides of asparagine and glutamine side chains in isotopically labeled proteins. J Biomol NMR 9:306–312
Mulder FA, Hon B, Mittermaier A, Dahlquist FW, Kay LE (2002) Slow internal dynamics in proteins: application of NMR relaxation dispersion spectroscopy to methyl groups in a cavity mutant of T4 lysozyme. J Am Chem Soc 124:1443–1451
Otting G (2010) Protein NMR using paramagnetic ions. Annu Rev Biophys 39:387–405
Ozawa K, Headlam MJ, Schaeffer PM, Henderson BR, Dixon NE, Otting G (2004) Optimization of an Escherichia coli system for cell-free synthesis of selectively 15N-labelled proteins for rapid analysis by NMR spectroscopy. Eur J Biochem 271:4084–4093
Pervushin K, Wider G, Wüthrich K (1997) Deuterium relaxation in a uniformly 15N-labeled homeodomain and its DNA complex. J Am Chem Soc 119:3842–3843
Pintacuda G, John M, Su XC, Otting G (2007) NMR structure determination of protein-ligand complexes by lanthanide labeling. Acc Chem Res 40:206–212
Radwanski ER, Last RL (1995) Tryptophan biosynthesis and metabolism: biochemical and molecular genetics. Plant Cell 7:921–934
Schmitz C, Stanton-Cook MJ, Su XC, Otting G, Huber T (2008) Numbat: an interactive software tool for fitting & #x0394;χ-tensors to molecular coordinates using pseudocontact shifts. J Biomol NMR 41:179–189
Shi J, Pelton JG, Cho HS, Wemmer DE (2004) Protein signal assignments using specific labeling and cell-free synthesis. J Biomol NMR 28:235–247
Sobhanifar S, Reckel S, Junge F, Schwarz D, Kai L, Karbyshev M, Löhr F, Bernhard F, Dötsch V (2010) Cell-free expression and stable isotope labelling strategies for membrane proteins. J Biomol NMR 46:33–43
Stadtman ER (2001) The story of glutamine synthetase regulation. J Biol Chem 276:44357–44364
Staunton D, Schlinker R, Zanetti G, Colebrook SA, Campbell ID (2006) Cell-free expression and selective isotope labelling in protein NMR. Magn Reson Chem 44:S2–S9
Studier FW (2005) Protein production by auto-induction in high-density shaking cultures. Protein Expr Purif 41:207–234
Su XC, Loh CT, Qi R, Otting G (2011) Suppression of isotope scrambling in cell-free protein synthesis by broadband inhibition of PLP enymes for selective 15N-labelling and production of perdeuterated proteins in H2O. J Biomol NMR 50:35–42
Sunnerhagen M, Nilges M, Otting G, Carey J (1997) Solution structure of the DNA-binding domain and model for the complex of multifunctional hexameric arginine repressor with DNA. Nat Struct Biol 4:819–826
Takeda M, Jee J, Ono AM, Terauchi T, Kainosho M (2011) Hydrogen exchange study on the hydroxyl groups of serine and threonine residues in proteins and structure refinement using NOE restraints with polar side-chain groups. J Am Chem Soc 133:17420–17427
Takeuchi K, Frueh DP, Sun ZY, Hiller S, Wagner G (2010) CACA-TOCSY with alternate 13C-12C labeling: a 13Cα direct detection experiment for main chain resonance assignment, dihedral angle information, and amino acid type identification. J Biomol NMR 47:55–63
Tate S, Tate NU, Ravera MW, Jaye M, Inagaki F (1992) A novel 15N-labeling method to selectively observe 15NH2 resonances of proteins in 1H-detected heteronuclear correlation spectroscopy. FEBS Lett 297:39–342
Tong KI, Yamamoto M, Tanaka T (2008) A simple method for amino acid selective isotope labeling of recombinant proteins in E. coli. J Biomol NMR 42:59–67
Tugarinov V, Kanelis V, Kay LE (2006) Isotope labeling strategies for the study of high-molecular-weight proteins by solution NMR spectroscopy. Nat Protoc 1:749–754
Vance CK, Kang YM, Miller AF (1997) Selective 15N labeling and direct observation by NMR of the active-site glutamine of Fe-containing superoxide dismutase. J Biomol NMR 9:201–206
Waugh DS (1996) Genetic tools for selective labeling of proteins with α-15N-amino acids. J Biomol NMR 8:184–192
Whittaker JW (2007) Selective isotopic labeling of recombinant proteins using amino acid auxotroph strains. Methods Mol Biol 389:175–187
Willis RC, Woolfolk CA (1974) Asparagine utilization in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 118:231–241
Willis RC, Woolfolk CA (1975) l-asparagine uptake in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 123:937–945
Woolfolk CA, Shapiro B, Stadtman ER (1966) Regulation of glutamine synthetase: I. Purification and properties of glutamine synthetase from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys 116:177–192
Zheng L, Kostrewa D, Bernèche S, Winkler FK, Li XD (2004) The mechanism of ammonia transport based on the crystal structure of AmtB of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci 49:17090–17095
Acknowledgments
Financial support by the 973 program (2013CB910200), the National Science Foundation of China (21073101, 21121002 and 21273121), and the Australian Research Council is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, C., Chen, JL., Yang, Y. et al. Selective 15N-labeling of the side-chain amide groups of asparagine and glutamine for applications in paramagnetic NMR spectroscopy. J Biomol NMR 59, 251–261 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-014-9844-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-014-9844-0