Abstract
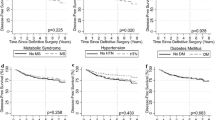
Higher body mass index (BMI) and diabetes are associated with worse breast cancer prognosis. However, few studies have focused on triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). The goal of this study is to examine this association in a cohort of patients with TNBC. We retrospectively reviewed 501 consecutive patients with TNBC seen at the Washington University Breast Oncology Clinic. Cox proportional hazard models were used to determine the relationship between BMI and diabetes at diagnosis with overall survival (OS) and disease free survival (DFS). Four hundred and forty-eight patients had BMI recorded and 71 patients had diabetes. The median age at diagnosis was 53 (23–98) years and follow-up was 40.1 months (IQR 25.2–62.9). Baseline BMI and diabetes were not associated with OS or DFS. OS hazard ratios (HRs) for patients who were overweight (BMI 25.0–29.99), with class I obesity (BMI 30–34.99), or BMI ≥35 were 1.22 (CI 0.78–1.91), 0.92 (CI 0.59–1.43), and 1.16 (CI 0.70–1.90), respectively. The HRs for DFS in patients who were overweight, with class I obesity, or BMI ≥35 were 1.01 (CI 0.65–1.56), 0.94 (CI 0.60–1.47), and 0.99 (CI 0.63–1.57), respectively. Similarly, the HRs for diabetics were 1.27 (CI 0.82–1.96) for OS and 0.98 (CI 0.64–1.51) for DFS. Obesity and diabetes did not significantly affect survival for patients with TNBC in this study.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM (2014) Prevalence of childhood and adult obesity in the United States, 2011–2012. JAMA 311(8):806–814
Guh DP, Zhang W, Bansback N, Amarsi Z, Birmingham CL, Anis AH (2009) The incidence of co-morbidities related to obesity and overweight: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC public health 9:88
Eliassen AH, Colditz GA, Rosner B, Willett WC, Hankinson SE (2006) Adult weight change and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer. JAMA 296(2):193–201
Suzuki R, Orsini N, Saji S, Key TJ, Wolk A (2009) Body weight and incidence of breast cancer defined by estrogen and progesterone receptor status–a meta-analysis. Int J Cancer 124(3):698–712
van den Brandt PA, Spiegelman D, Yaun SS, Adami HO, Beeson L, Folsom AR, Fraser G, Goldbohm RA, Graham S, Kushi L et al (2000) Pooled analysis of prospective cohort studies on height, weight, and breast cancer risk. Am J Epidemiol 152(6):514–527
Pierobon M, Frankenfeld CL (2013) Obesity as a risk factor for triple-negative breast cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 137(1):307–314
Key TJ, Appleby PN, Reeves GK, Roddam A, Dorgan JF, Longcope C, Stanczyk FZ, Stephenson HE Jr, Falk RT, Miller R et al (2003) Body mass index, serum sex hormones, and breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women. J Natl Cancer Inst 95(16):1218–1226
Li CI, Malone KE, Daling JR (2006) Interactions between body mass index and hormone therapy and postmenopausal breast cancer risk (United States). Cancer Causes Control 17(5):695–703
Endogenous Hormones and Breast Cancer Collaborative Group, Key TJ, Appleby PN, Reeves GK, Roddam AW (2010) Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1), IGF binding protein 3 (IGFBP3), and breast cancer risk: pooled individual data analysis of 17 prospective studies. Lancet Oncol 11(6):530–542
Gunter MJ, Hoover DR, Yu H, Wassertheil-Smoller S, Rohan TE, Manson JE, Li J, Ho GY, Xue X, Anderson GL et al (2009) Insulin, insulin-like growth factor-I, and risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women. J Natl Cancer Inst 101(1):48–60
Tworoger SS, Eliassen AH, Kelesidis T, Colditz GA, Willett WC, Mantzoros CS, Hankinson SE (2007) Plasma adiponectin concentrations and risk of incident breast cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(4):1510–1516
Lorincz AM, Sukumar S (2006) Molecular links between obesity and breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 13(2):279–292
Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ (2003) Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med 348(17):1625–1638
Conroy SM, Maskarinec G, Wilkens LR, White KK, Henderson BE, Kolonel LN (2011) Obesity and breast cancer survival in ethnically diverse postmenopausal women: the Multiethnic Cohort Study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 129(2):565–574
Imkampe AK, Bates T (2010) Impact of a raised body mass index on breast cancer survival in relation to age and disease extent at diagnosis. Breast J 16(2):156–161
Jiralerspong S, Kim ES, Dong W, Feng L, Hortobagyi GN, Giordano SH (2013) Obesity, diabetes, and survival outcomes in a large cohort of early-stage breast cancer patients. Ann Oncol 24(10):2506–2514
Kamineni A, Anderson ML, White E, Taplin SH, Porter P, Ballard-Barbash R, Malone K, Buist DS (2013) Body mass index, tumor characteristics, and prognosis following diagnosis of early-stage breast cancer in a mammographically screened population. Cancer Causes Control 24(2):305–312
Protani M, Coory M, Martin JH (2010) Effect of obesity on survival of women with breast cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 123(3):627–635
Sestak I, Distler W, Forbes JF, Dowsett M, Howell A, Cuzick J (2010) Effect of body mass index on recurrences in tamoxifen and anastrozole treated women: an exploratory analysis from the ATAC trial. J Clin Oncol 28(21):3411–3415
Xing P, Li JG, Jin F, Zhao TT, Liu Q, Dong HT, Wei XL (2013) Prognostic significance of body mass index in breast cancer patients with hormone receptor-positive tumours after curative surgery. Clini Invest Med 36(6):E297–E305
Ademuyiwa FO, Groman A, O’Connor T, Ambrosone C, Watroba N, Edge SB (2011) Impact of body mass index on clinical outcomes in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer 117(18):4132–4140
Dawood S, Lei X, Litton JK, Buchholz TA, Hortobagyi GN, Gonzalez-Angulo AM (2012) Impact of body mass index on survival outcome among women with early stage triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 12(5):364–372
Mowad R, Chu QD, Li BD, Burton GV, Ampil FL, Kim RH (2013) Does obesity have an effect on outcomes in triple-negative breast cancer? J Surg Res 184(1):253–259
Pajares B, Pollán M, Martín M, Mackey JR, Lluch A, Gavila J, Vogel C, Ruiz-Borrego M, Calvo L, Pienkowski T et al (2013) Obesity and survival in operable breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant anthracyclines and taxanes according to pathological subtypes: a pooled analysis. Breast Cancer Res 15(6):R105
Sparano JA, Wang M, Zhao F, Stearns V, Martino S, Ligibel JA, Perez EA, Saphner T, Wolff AC, Sledge GW Jr et al (2012) Obesity at diagnosis is associated with inferior outcomes in hormone receptor-positive operable breast cancer. Cancer 118(23):5937–5946
Turkoz FP, Solak M, Petekkaya I, Keskin O, Kertmen N, Sarici F, Arik Z, Babacan T, Ozisik Y, Altundag K (2013) The prognostic impact of obesity on molecular subtypes of breast cancer in premenopausal women. J BUON 18(2):335–341
De Bruijn KM, Arends LR, Hansen BE, Leeflang S, Ruiter R, van Eijck CH (2013) Systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between diabetes mellitus and incidence and mortality in breast and colorectal cancer. Br J Surg 100(11):1421–1429
Gold HT, Makarem N, Nicholson JM, Parekh N (2014) Treatment and outcomes in diabetic breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 143(3):551–570
Peairs KS, Barone BB, Snyder CF, Yeh HC, Stein KB, Derr RL, Brancati FL, Wolff AC (2011) Diabetes mellitus and breast cancer outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol 29(1):40–46
Bayraktar S, Hernadez-Aya LF, Lei X, Meric-Bernstam F, Litton JK, Hsu L, Hortobagyi GN, Gonzalez-Angulo AM (2012) Effect of metformin on survival outcomes in diabetic patients with triple receptor-negative breast cancer. Cancer 118(5):1202–1211
Bartucci M, Morelli C, Mauro L, Andò S, Surmacz E (2001) Differential insulin-like growth factor I receptor signaling and function in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive MCF-7 and ER-negative MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 61(18):6747–6754
Hartog H, Horlings HM, van der Vegt B, Kreike B, Ajouaou A, van de Vijver MJ, Marike Boezen H, de Bock GH, van der Graaf WT, Wesseling J (2011) Divergent effects of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor expression on prognosis of estrogen receptor positive versus triple negative invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat 129(3):725–736
Law JH, Habibi G, Hu K, Masoudi H, Wang MY, Stratford AL, Park E, Gee JM, Finlay P, Jones HE et al (2008) Phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor-i/insulin receptor is present in all breast cancer subtypes and is related to poor survival. Cancer Res 68(24):10238–10246
Litzenburger BC, Creighton CJ, Tsimelzon A, Chan BT, Hilsenbeck SG, Wang T, Carboni JM, Gottardis MM, Huang F, Chang JC et al (2011) High IGF-IR activity in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines and tumorgrafts correlates with sensitivity to anti-IGF-IR therapy. Clin Cancer Res 17(8):2314–2327
Peiró G, Adrover E, Sánchez-Tejada L, Lerma E, Planelles M, Sánchez-Payá J, Aranda FI, Giner D, Gutiérrez-Aviñó FJ (2011) Increased insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor mRNA expression predicts poor survival in immunophenotypes of early breast carcinoma. Mod Pathol 24(2):201–208
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank patients who participated in this study and physicians, nurses, and research coordinators at Washington University Breast Oncology Clinic for their care of these patients. The authors also wish to acknowledge the support of the Biostatistics Core, Siteman Cancer Center and National Cancer Institute Cancer Center Support Grant P30 CA091842.
Conflicts of Interest
All the authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was partly presented at the 2014 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, May 30–June 3, 2014, Chicago, IL, USA
S. Tait and J. M. Pacheco have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tait, S., Pacheco, J.M., Gao, F. et al. Body mass index, diabetes, and triple-negative breast cancer prognosis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 146, 189–197 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-014-3002-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-014-3002-y