Abstract
The process of sperm development in Phoronopsis harmeri was studied by electron microscopy. Developing spermatogenical cells are aggregated around the capillaries of the haemal plexus. The spermatogonia, which are situated around the capillary walls of the caeca, are remarkable for the presence of germ-line vesicles and contain their centrioles near the cell membrane. The spermatocytes and spermatids are flagellated cells arranged in clusters. During spermiogenesis the basal body/flagellum complex migrates to the apical pole of the spermatid. The acrosome-like structure arises from material produced by the Golgi complex. It lacks a surrounding membrane and has a fibrillar content. The nucleus elongates and the condensation of chromatin is caused by an activation of 'initiation centres'. The late spermatid and the spermatozoon appear as two-armed 'V'-shaped cells in which one arm contains the nucleus and posteriorly located mitochondria, and the other one is the axoneme. Spermatogenesis of P. harmeri is an interesting example of gamete differentiation where advanced sperm structure is combined with a plesiomorphic pattern of sperm development characterized as 'flagellate spermatogenesis'.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Present ultrastructural investigations in Lophophorata (Tentaculata) allow a general view of mature sperm structure in representatives of all five sub-groups: Phoronida, Brachiopoda, Bryozoa, Entoprocta and Cycliophora (see Herrmann 1997; James 1997; Mukai et al. 1997; Nielsen and Jespersen 1997). However, the data on spermatogenesis are insufficient, as the complete process has so far been studied only in two species of brachiopods (Hodgson and Reunov 1994).
Spermatozoa of Phoronida are typically 'V'-shaped (see Ikeda 1903; Cori 1939; Silen 1952; Franzén 1956; Zimmer 1967; Franzén and Ahlfors 1980; Herrmann 1997). In accordance with ultrastructural findings (Franzén and Ahlfors 1980) one arm of the V contains the flagellum, and the other the nucleus and two elongated mitochondria. In Phoronis muelleri Selys-Longchamps, 1903 the spermatozoon has a needle-like acrosome, a short, almost round nucleus and a flagellum (Herrmann 1997). An ultrastructural study of phoronid sperm development has been carried out on Phoronis pallida Schneider, 1862 with a consideration of spermatid development only (Franzén and Ahlfors 1980). The early stages of sperm development (spermatogonia and spermatocytes) have never been investigated in Phoronida. To fill this gap, spermatogenesis in Phoronopsis harmeri Pixell, 1912 has now been studied through all stages of sperm differentiation.
Methods
Samples of Phoronopsis harmeri were collected in August 1996 in the intertidal zone of 'Vostok' Biological Station (Japan Sea, Russia). The species is gonochoristic (Zimmer 1967; Herrmann 1997). The males were identified by dissection and the gametes were observed using light microscopy.
For the ultrastructural study the metasoma of three males were fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde in 0.1 M sodium cacodylate buffer (pH 7.4, fixative osmolarity=1100 mosmol) and in 2% osmium tetroxide buffered by filtered sea water. Following dehydration in a graded series of ethanol and acetone, the material was embedded in Epon-Araldite (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis). Sections were cut on an Ultracut-E ultramicrotome (Reichert-Jung, Austria) using glass and diamond knives, stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate, and examined with an EM 9S-2 transmission electron microscope (Zeiss, Germany). For scanning electron microscopical investigations, samples of P. harmeri were fixed as above, critical-point dried, coated with gold and photographed with a 35CF scanning electron microscope (Jeol, Japan). The examination of the specimens with the electron microscopes was carried out in the Zoological Institute at the University of Vienna.
Results
Male gamete forming tissue
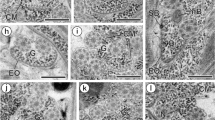
Developing spermatogenical cells are aggregated around the capillaries of the haemal plexus. The diameter of these vessels is quite small and corresponds to the size of a blood cell (Fig. 1). The wall of the capillaries consists of vasoperitoneal cells lined by an inner layer of extracellular matrix (Fig. 2). In some areas the projections of these cells do not join up and spermatogenical cells adhere to the matrix layer (Fig. 2). The vasoperitoneal tissue cells are spread among the forming gametes. The highly vacuolized cytoplasm of these cells has characteristic phagosome-shaped inclusions (Fig. 3).
Scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of fracture of vasoperitoneal tissue. Spermatogonia (Sg) and primary spermatocytes (Sc I) situated around the capillary blood vessel. Star shows a blood cell in the lumen of the vessel
Transmission electron migrograph (TEM) of the blood vessel wall. Asterisks show the vasoperitoneal tissue cells. Arrows indicate the inner matrix of the blood vessel. Triangles demonstrate an area of direct contact between spermatogenic cells and the matrix. Sc spermatogenical cells, B blood cell
TEM of vasoperitoneal tissue cells (V) surrounded by spermatogenical cells (Sc). P phagosome
TEM of spermatogonia (Sg) and spermatocytes (Sc). Arrows show vesicles of germ plasm
TEM of the centriolar complex in the spermatogonium. Arrow indicates the vesicles of germ plasm. Dc distal centriole, Pc proximal centriole, G Golgi complex, N nucleus
Spermatogonia
Groups of elongate spermatogonia are usually arranged around the capillary walls of the caeca (Fig. 1). These cells have an ovoid nucleus with small patches of chromatin. One prominent nucleolus is near the periphery of the nucleus. The cytoplasm of the spermatogonia contains electron-dense vesicles which supposedly represent the germ-line substance (Figs. 4, 5). Two perpendicularly oriented centrioles are near the cell membrane (Fig. 5).
Spermatocytes
Groups of spermatocytes usually cover the spermatogonia distally (Fig. 1), but sometimes they are connected to the capillary walls (Fig. 2). Developing spermatocytes are organized in multicellular clusters inside which the cells are connected by intercellular bridges (Fig. 6). The spermatocytes develop synchronously, i.e. the cells in each cluster are always at the same stage. The cytoplasm of the spermatocytes contains mitochondria, Golgi complexes, endoplasmic reticulum and vacuoles. The electron-dense vesicles, characteristic of spermatogonia, are no longer seen.
TEM of a cluster of primary spermatocytes. Asterisks show intercellular bridges
TEM of the synaptonemal complexes (arrowhead) in the chromatin of the primary spermatocyte in the zygotene-pachytene stage
TEM of the flagellum (F) in the primary spermatocyte. Arrows show daughter centrioles. D distal centriole, P proximal centriole, G Golgi complex, N nucleus
SEM of clusters of secondary spermatocytes (Sc II) and spermatids (St)
TEM of spermatocytes II. Arrow shows the daughter centriole. F flagellum, D distal centriole
TEM of early spermatids. Asterisks show intercellular bridges. Arrow indicates the flagellum
Primary spermatocytes are almost round (Fig. 1). One character of the primary spermatocytes is the presence of synaptonemal complexes in the zygotene-pachytene stage of meiosis (Fig. 7). The centriolar complexes consist of two maternal and two developing daughter centrioles during the pachytene period. Each primary spermatocyte has a single flagellum (Fig. 8).
The clusters of the secondary spermatocytes can be recognized in the vasoperitoneal tissues by the cell size intermediate between that of primary spermatocytes and early spermatids (Fig. 9). The secondary spermatocytes have one cilium and a single daughter centriole (Fig. 10).
Spermiogenesis
Early stage
Early spermatids are organized in clusters of cells (Fig. 9) connected by intercellular bridges (Fig. 11). The cells are monociliated and have an almost spherical nucleus with chromatin at the initial stage of condensation. From this stage, there is normally no other centriole in sperm cells except the basal body.
Middle stage
During this stage of spermiogenesis, the condensation of chromatin proceeds (Fig. 12) and the nucleus then becomes trapeziform (Fig. 13). The basal body/flagellum complex migrates to the apical pole of the spermatid (Figs. 12, 13). This displacement involves the formation of an invagination of the plasma membrane which forms a cytoplasmic channel through which the flagellum is passed (Fig. 14). The mitochondria tend to fuse at the lateral side of the nucleus and form two elongated ovoid mitochondria (Fig. 15). Golgi vesicles supply a substance for the formation of the acrosome-like structure (Figs. 16, 17). Finally, this organelle consists of fibrillar condensed material and is not surrounded by a membrane (Fig. 18). After the acrosome-like structure is formed, the Golgi complex is eliminated, along with residual cytoplasm (Fig. 19).
TEM of middle spermatid with flagellum (F) moving towards the apical cell pole. Arrow indicates a pericentriolar projection. N nucleus
TEM of a middle spermatid with trapeziform nucleus and apically located basal body/flagellum complex (arrowhead). Asterisk shows a mitochondrium
TEM of a middle spermatid with flagellum (arrows) inside cell channel
TEM of a middle spermatid with paired mitochondria (asterisks) situated laterally of the nucleus
TEM of a middle spermatid with Golgi complex (G) producing proacrosomal substance (arrow)
TEM of a middle spermatid with acrosome-like structure (arrowhead) produced by Golgi complex (G)
TEM of acrosome-like structure near cell membrane of a middle spermatid
TEM of a middle spermatid. The Golgi complex (G) is eliminated with residual cytoplasm (asterisk) after acrosome-like structure (arrowhead) has been formed
TEM of a longitudinal section of a late spermatid. 'Initiation centres' (arrow) in the nucleus (N)
TEM of cross-section of late spermatid. 'Initiation centres' (arrow) in the nucleus
TEM of acrosome-like structure (arrowhead) migrating anteriorly along the nucleus (N) in a late spermatid
Late stage
During the late stage of spermiogenesis, the nucleus elongates rapidly and the chromatin condensation, characterized by many 'initiation centres' proceeds (Figs. 20, 21). These 'initiation centres' gradually disappear during chromatin condensation. The acrosome-like structure migrates towards the anterior pole of the nucleus (Fig. 22). The two large mitochondrial masses move to the posterior cell pole and the flagellum becomes a 'free' sperm tail (Fig. 23). When late spermiogenesis has been completed, the acrosome-like structure is at the apical pole of the cell and the mitochondria adhere to the posterior end of the nucleus. The late spermatid appears as a two-armed V-shaped cell in which one arm is the nucleus with posteriorly located mitochondria whereas the other one is the axoneme (Fig. 24).
SEM of a late spermatid with mitochondria (arrowheads) migrating posteriorly and 'free' tail (T). Asterisks show nucleus
SEM of a spermatozoon. Arrowhead shows the acrosome-like structure. Asterisks show nucleus. T tail
TEM of the apical region of a spermatozoon. A acrosome-like structure, B basal body of tail (T), N nucleus
TEM of a cross-section of the tail
TEM of a longitudinal section of the nucleus of a spermatozoon
TEM of cross-sections of spermatozoa. Arrows show microtubules
TEM of a longitudinal section through the mitochondrial region of a spermatozoon. M mitochondria, N nucleus
TEM of a cross-section through the mitochondrial region of spermatozoon. M mitochondria
Spermatozoon
The morphology of the mature spermatozoon is similar to that of the late spermatid. The cell has a pointed apical projection consisting of an electron-dense fibrillar acrosome-like structure, and it widens near the basal body of the tail (Fig. 25). The tail, with the usual 9+2 axonemal pattern (Fig. 26), represents the longer arm of the spermatozoon (Fig. 24).
The apical part of the nucleus is close to the basal body of the tail (Fig. 25). The nucleus, full of electron-dense chromatin (Fig. 27), is kidney-shaped in cross section (Fig. 28). Two elongated mitochondria adhere to the posterior end of the nucleus (Fig. 29) and lie close to each other (Fig. 30).
Discussion
Early spermatogenesis
An outstanding feature of early spermatogenesis in Phoronopsis harmeri is the formation of a flagellum during the transformation of the spermatogonium into the primary spermatocyte. Thus, early sperm development in P. harmeri is an example of 'flagellate spermatogenesis' (see Reunov 2001) which is typical of Metazoa with external or external/internal fertilization and 'primitive' (sensu Franzén 1956) spermatozoa. This type of sperm development has been described for representatives of Porifera (Paulus 1989), Cnidaria (Larkman 1984), Priapulida (Adrianov et al. 1992), Nemertini (Reunov and Klepal 1997), Polychaeta (Eckelbarger 1984), Aplacophora (Hodgson et al. 1988), Bivalvia (Reunov and Hodgson 1994; Reunov et al. 1999), Echinodermata (Au et al. 1998), Brachiopoda (Hodgson and Reunov 1994), Tunicata (Villa and Tripepi 1983) and Cephalochordata (Welsch and Fang 1996).
On the other hand, it has been shown that the early germ cells of animals with internal fertilization and 'modified' (sensu Franzén 1956) sperms have no flagella; e.g. some Nemertini (Reunov and Chernishev 1992), Polychaeta (Lücht and Pfannenstiel 1989), Oligochaeta (Hodgson and Jamieson 1992), Cirripedia (Azevedo and Corral 1982), Gastropoda and Cephalopoda (Amor and Durfort 1990; Healy 1990) and Vertebrata (Sprando and Russel 1988; Phillips and Asa 1989; Sakai and Yamashina 1989; Bernardini et al. 1990).
The flagella in the early spermatogenic cells are obviously analogous to cilia arising in somatic epithelial cells. In the development of representatives of some taxa, including Phoronida (Herrmann 1997) and Brachiopoda (James 1997), such cells have been observed from the stage of blastula or gastrula, and then they participate in subsequent tissue differentiation. As suggested by Reunov (2001), the phenomenon of 'flagellate spermatogenesis' probably reflects plesiomorphic morphological similarity between somatic epithelial cells and early germ cells.
It is interesting that plesiomorphic flagellate spermatogenesis in P. harmeri seems to be accompanied by the formation of spermatozoa distinct from the 'primitive' pattern. In accordance with our approach (Reunov and Klepal 1997), sperm of this phoronid may be characterized as 'modified with element of aberration'. The aberration in this case is the anterior dislocation of the centriole/flagellum complex, which is distinct from the typical position of the basal body posteriorly to the nucleus. Such advanced sperm structure probably correlates with the quite complicated method of external/internal fertilization described for this species by Zimmer (1967). Thus, the present study highlights one more exception to the rule. Until now, the coexistence of flagella bearing in early spermatogenesis and advanced sperm type had only been found in some representatives of Insecta (Wolf and Kyburg 1989) and Tunicata (Holland 1989).
Spermiogenesis and spermatozoa
In general, spermatid formation and sperm ultrastructure of Phoronopsis harmeri are similar to those of Phoronis pallida (see Franzén and Ahlfors 1980), yet some distinct features have been found. As was shown for Phoronis pallida, the acrosome arises in early spermiogenesis from Golgi vesicles and then migrates anteriorly. The acrosome of the late spermatid and the spermatozoon is based on an additional pseudo-acrosomal structure composed of a band-like nuclear process and a parallel ribbon-like structure of condensed material (Franzén and Ahlfors 1980).
Similar to Phoronis pallida, the formation of acrosomal elements in Phoronopsis harmeri starts in the early spermatid with the aggregation of Golgi vesicles, but in the end the acrosome is simpler in Phoronopsis harmeri. This species has an acrosome-like structure consisting of electron-dense fibrillar material and without a surrounding membrane. The absence of a surrounding membrane and the fibrillar structure suggests that the material may be peri-acrosomal rather than representing an acrosome which is surrounded by a membrane and contains the electron-dense lytical substance (Baccetti and Afzelius 1976). It is likely that this peri-acrosomal material is a vestigial structure whereas the acrosomal vesicle has been lost in the course of evolution. The evolutional disappearance of acrosomes has been found as typical of aberrant sperm of many metazoan taxa (see Baccetti 1984).
There are also differences in the mode of chromatine condensation. In Phoronis pallida the condensation of chromatin is concentrated in one sector (Franzén and Ahlfors 1980). In Phoronopsis harmeri, in contrast, chromatin condensation involves the formation of 'initiation centres', which obviously means a different pattern. The type of chromatin condensation might be used as an additional character for phoronid phylogeny.
An interesting finding of spermiogenesis is the existence of only one centriole (basal body) instead of two as in the case in spermatids of many Metazoan representatives. Similarly, 'one centriolar' sperms have been described only in some Tunicata (Holland 1989).
Spermatological affinity of Phoronida and Brachiopoda
At the moment among the Lophophorata, the complete spermatogenesis has been studied only in representatives of the Phoronida and Brachiopoda (see Hodgson and Reunov 1994; present study). The monophyletic origin of Phoronida and Brachiopoda is confirmed by morphological and molecular data, and the Phoronida are generally regarded as the ancestral group (see Woollacott and Harrison 1997). It is interesting to compare the patterns of male sex cell differentiation in these two closely related groups.
The Brachiopoda are external fertilizers with 'primitive spermatozoa' (Reunov 1993) whereas the sperm of P. harmeri is characterized as 'modified with elements of aberration'. So the presumed basic taxon has a more complex sperm structure. The analysis of this fact forces us to consider two variants of conflicting views which are the subject of an ongoing debate.
The early theory postulates the general line of sperm evolution as a consistent transformation of primitive sperms to modified male gametes, which in turn gradually transformed to aberrant spermatozoa (see Baccetti and Afzelius 1976; Baccetti 1984).
However, the recent findings of modified sperms in the basal groups of some taxa suggest that internal fertilization and modified sperms are plesiomorphic in early Bilateria (see Jamieson 1991; Rouse and Fitzhugh 1994; Buckland-Nicks and Scheltema 1995).
Principally, both types of spermatozoa may have arisen from a prototype resembling a somatic ciliar cell (Reunov and Malakhov 1993). However, the hypothesis of evolutionary priority of modified sperm may meet some difficulties if extinct ancestors of basal taxa have had a primitive sperm.
Ultrastructural studies of sperm differentiation demonstrated that representatives of Brachiopoda such as Discinisca tenuis Davidson, 1888 (= D. laevis Sowerbey, 1822), Kraussina rubra Pallas, 1766 (see Hodgson and Reunov 1994) and the phoronid P. harmeri have a similar pattern of early spermatogenic cell differentiation which, according to a recent approach (Reunov 2001), may be characterized as plesiomorphic 'flagellar spermatogenesis' (Fig. 31). Thus, the pattern of sperm differentiation in Phoronida is not more advanced than in Brachiopoda. If the Phoronida are an ancestral taxon we should accept that 'primitive sperms' secondarily arose in Brachiopoda as it has been suggested for some other taxa (Buckland-Nicks and Sheltema 1995). As an alternative, ancestral extinct Phoronida might have had 'primitive' male gametes.
Schematic representation of typical spermatogenesis patterns in brachiopods (A–E) and phoronids (F–M). Brachiopod pattern: A spermatogonium; B primary spermatocyte; C secondary spermatocyte; D spermatid; E spermatozoon. Phoronid pattern: F spermatogonium; G primary spermatocyte; H secondary spermatocyte; I early spermatid; J middle spermatid; K, L stages of late spermiogenesis; M spermatozoon; m mitochondria, gp germ plasm substance, c centrioles, g Golgi complex, f flagellum, pv proacrosomal vesicle, v acrosomal vesicle, rc residual cytoplasm, a acrosome, n nucleus, as acrosome-like structure
References
Adrianov AV, Reunov AA, Malaknov VV (1992) Fine morphology of the gonads and spermatogenesis features of White Sea priapulids Halicryptus spinulosus (Cephalorhyncha, Priapulida) (in Russian with English summary). Zool Zh 71:31–39
Amor MJ, Durfort M (1990) Changes in nuclear structure during eupyrene spermatogenesis in Murex brandaris. Mol Reprod Dev 25:348–356
Au DWT, Reunov AA, Wu RSS (1998) Four lines of spermatid development and dimorphic spermatozoa in the sea urchin Anthocidaris crassispina (Echinodermata, Echinoida). Zoomorphology 118:159–168
Azevedo C, Corral L (1982) Ultrastructural study of spermatozoon and spermiogenesis of Pollicipes cornucopia (Crustacea; Cirripedia) with special reference to nucleus maturation. J Submicrosc Cytol 14:641–654
Baccetti B (1984) Evolution of the spermatozoon. Boll Zool 51:25–33
Baccetti B, Afzelius BA (1976) The biology of the sperm cell. Karger, Basel
Bernardini G, Podini P, Maci R, Camatini M (1990) Spermiogenesis in Xenopus laevis: from late spermatids to spermatozoa. Mol Reprod Dev 26:347–355
Buckland-Nicks J, Scheltema A (1995) Was internal fertilization an innovation of early Bilateria? Evidence from sperm structure of a mollusc. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 261:11–18
Cori CJ (1939) 'Phoronidea'. Bronn's Klassen und Ordnung des Tierreichs, 4th edn, vol 4, Buch 1. Leipzig
Eckelbarger KJ (1984) Ultrastructure of spermatogenesis in the reef-building polychaete Phragmatopoma lapidosa (Sabellariidae) with special reference to acrosome morphogenesis. J Ultrastruct Res 89:146–164
Franzén Å (1956) On spermiogenesis, morphology of the spermatozoon and biology of fertilization among invertebrates. Zool Bidr Uppsala 31:355–482
Franzén Å, Ahlfors K (1980) Ultrastructure of spermatids and spermatozoa in Phoronis, phylum Phoronida. J Submicrosc Cytol 12:585–597
Healy JM (1990) Ultrastructure of spermiogenesis in Vampyroteuthis infernalis Chun—a relict cephalopod mollusc. Helgol Meeresunters 44:95–107
Herrmann K (1997) Lophophorates, Entoprocta and Cycliophora. Phoronida. In: Harrison FW, Woollacot RM (eds) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates, vol 13. Wiley, New York, pp 207–235
Hodgson AN, Jamieson BGM (1992) Spermatogenesis in the earthworm Microchaetus pentheri (Oligochaeta, Microchaetidae). Zoomorphology 112:57–66
Hodgson AN, Reunov AA (1994) Ultrastructure of the spermatozoon and spermatogenesis of the brachiopods Discinisca tenuis (Inarticulata) and Kraussina rubra (Articulata). Invertebr Reprod Dev 25:23–31
Hodgson AN, Baxter JM, Sturrock MG, Bernard RTF (1988) Comparative spermatology of 11 species of Polyplacophora (Mollusca) from the suborders Lepidopleurina, Chitonina and Acanthochitonina. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 235:161–177
Holland LZ (1989) Fine structure of spermatids and sperm of Dollioletta gegenbauri and Doliolum nationalis (Tunicata: Thaliacea): implications for tunicate phylogeny. Mar Biol 101:83–95
Ikeda I (1903) On the development of the sexual organs and of their products in Phoronis. Annot Zool Jpn 4:23–31
James MA (1997) Lophophorates, Entoprocta and Cycliophora. Brachiopoda. In: Harrison FW, Woollacot RM (eds) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates, vol 13. Wiley, New York, pp 297–407
Jamieson BGM (1991) Fish evolution and systematics evidence from spermatozoa. Cambrige University Press, Cambridge
Larkman AU (1984) An ultrastructural study of the establishment of the testicular cysts during spermatogenesis in the sea anemone Actinia fragacea (Cnidaria: Anthozoa). Gamete Res 9:303–327
Lücht J, Pfannenstiel HD (1989) Spermatogenesis in Platynereis massiliensis (Polychaeta, Nereidae). Helgol Meeresunters 43:19–28
Mukai H, Terakado K, Reed CG (1997) Lophophorates, Entoprocta and Cycliophora. Bryozoa. In: Harrison FW, Woollacot RM (eds) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates, vol 13. Wiley, New York, pp 45–206
Nielsen C, Jespersen A (1997) Lophophorates, Entoprocta and Cycliophora. Entoprocta. In: Harrison FW, Woollacot RM (eds) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates, vol 13. Wiley, New York, pp 13–43
Paulus W (1989) Ultrastructural investigation of spermatogenesis in Spongilla lacustris and Ephydatia fluviatilis (Porifera, Spongillidae). Zoomorphology 109:123–130
Phillips DM, Asa CS (1989) Development of spermatozoa in the rhea. Anat Rec 223:276–282
Reunov AA (1993) Ultrastructural investigation of spermiogenesis in Rhynchonella psittacea (Tentaculata, Brachiopoda). Invertebr Reprod Dev 24:213–216
Reunov AA (2001) Is the "flagellate" pattern of spermatogenesis plesiomorphic in Metazoa? Invertebr Reprod Dev 40:239–242
Reunov AA, Chernishev AV (1992) The male gonad organization and spermatogenesis in the nemertean worm Tetrastemma nigrifrons Coe, 1904 (Haplonemertini, Tetrastemmatidae) (in Russian with English summary). Tsitologiya 34:13–20
Reunov AA, Hodgson AN (1994) Ultrastructure of the spermatozoa of five species of South African bivalves (Mollusca), and an examination of early spermatogenesis. J Morphol 219:275–283
Reunov AA, Klepal W (1997) Ultrastructural investigation of spermatogenesis in nemertine worm Procephalothrix sp. (Palaeonemertini, Anopla). Helgol Meeresunters 51:125–135
Reunov AA, Malakhov VV (1993) The evolution of spermatozoa in invertebrates (in Russian). Usp Sovrem Biol 113:3–18
Reunov AA, Au DWT, Wu RSS (1999) Spermatogenesis of the green-lipped mussel Perna viridis with dual patterns of acrosome and tail development in spermatids. Helgol Mar Res 53:62–69
Rouse GW, Fitzhugh K (1994) Broadcasting fables: is external fertilization really primitive? Sex, size, and larvae in sabellid polychaetes. Zool Scr 23:271–312
Sakai Y, Yamashina S (1989) Mechanism for the removal of residual cytoplasm from spermatids during mouse spermiogenese. Anat Rec 223:43–48
Silen L (1952) Researches on Phoronidea of the Gullmar Fiord area (west coast of Sweden). Ark Zool 4:95–140
Sprando RL, Russel LD (1988) Spermiogenesis in the bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana): a study of cytoplasmic events including cell volume changes and cytoplasmic elimination. J Morphol 198:303–319
Villa L, Tripepi S (1983) An electron microscope study of spermatogenesis and spermatozoa of Ascidia malaca, Ascidiella aspersa and Phallusia mamillata (Ascidiacea, Tunicata). Acta Embryol Morphol Exp 4:157–168
Welsch U, Fang YQ (1996) The reproductive organs of Branchiostoma. Isr J Zool 42:183–212
Wolf KW, Kyburg J (1989) The restructuring of the flagellar base and the flagellar necklace during spermatogenesis of Ephestia kuehniella Z. (Pyralidae, Lepidoptera). Cell Tissue Res 256:77–86
Woollacott RM, Harrison FW (1997) Lophophorates, Entoprocta and Cycliophora. Introduction. In: Harrison FW, Woollacot RM (eds) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates, vol 13. Wiley, New York, pp 1–11
Zimmer RL (1967) The morphology and function of accessory reproductive glands in the lophophore of Phoronis vancouverensis and Phoronopsis harmeri. J Morphol 121:159–178
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for grants from the University of Vienna ("Förderung von Auslandsbeziehungen"), from the President of the Russian Federation to A. Reunov (N 00-15-99354), from the Russian Fund of Basic Research: RFBR-primorye (N 01-04-96930); grant of Minpromnauka SS (N 1219.2003.4). Many thanks to Dr. V.I. Radashevsky and Dr. E.N. Temereva for their kind help in the collection of phoronids. We would also like to thank A. Losert, Mag. D. Gruber and Dr. M.L. Weidinger in the Department of Ultrastructural Research of the Zoological Institute of the University of Vienna for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H.-D. Franke
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reunov, A., Klepal, W. Ultrastructural study of spermatogenesis in Phoronopsis harmeri (Lophophorata, Phoronida). Helgol Mar Res 58, 1–10 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10152-003-0153-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10152-003-0153-3