Abstract
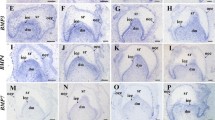
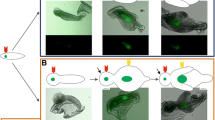
Tooth morphogenesis is regulated by sequential and reciprocal interaction between oral epithelium and neural-crest-derived ectomesenchyme. The interaction is controlled by various signal molecules such as bone morphogenetic protein (BMP), Hedgehog, fibroblast growth factor (FGF), and Wnt. Zeb family is known as a transcription factor, which is essential for neural development and neural-crest-derived tissues, whereas the role of the Zeb family in tooth development remains unclear. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the expression profiles of Zeb1 and Zeb2 during craniofacial development focusing on mesenchyme of palate, hair follicle, and tooth germ from E12.5 to E16.5. In addition, we examined the interaction between Zeb family and BMP4 during tooth development. Both Zeb1 and Zeb2 were expressed at mesenchyme of the palate, hair follicle, and tooth germ throughout the stages. In the case of tooth germ at the cap stage, the expression of Zeb1 and Zeb2 was lost in epithelium-separated dental mesenchyme. However, the expression of Zeb1 and Zeb2 in the dental mesenchyme was recovered by Bmp4 signaling via BMP4-soaked bead and tissue recombination. Our results suggest that Zeb1 and Zeb2, which were mediated by BMP4, play an important role in neural-crest-derived craniofacial organ morphogenesis, such as tooth development.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberg T, Wozney J, Thesleff I (1997) Expression patterns of bone morphogenetic proteins in the developing mouse tooth suggest roles in morphogenesis and cell differentiation. Dev Dyn 210:383–396
Barrallo-Gimeno A, Nieto MA (2005) The Snail genes as inducers of cell movement and survival: implications in development and cancer. Development 132:3151–3161
Bassez G, Camand OJ, Cacheux V, Kobetz A, Dastot-Le Moal F, Marchant D, Catala M, Abitbol M, Goossens M (2004) Pleiotropic and diverse expression of ZEB2 gene transcripts during mouse and human development supports the various clinical manifestations of the “Mowat-Wilson” syndrome. Neurobiol Dis 15:240–250
Cabanillas AM, Darling DS (1996) Alternative splicing gives rise to two isoforms of Zfhep, a zinc finger/homeodomain protein that binds T3-response elements. DNA Cell Biol 15:643–651
Cacheux V, Dastot-Le Moal F, Kaariainen H, Bondurand N, Rintala R, Boissier B, Wilson M, Mowat D, Goossens M (2001) Loss-of-function mutations in SIP1 Smad interacting protein 1 result in a syndromic Hirschsprung disease. Hum Mol Genet 10:1503–1510
Cate AR Ten (1998) Oral histology: development, structure, and function. 5th edn
Chen Y, Bei M, Woo I, Satokata I, Maas R (1996) Msx1 controls inductive signaling in mammalian tooth morphogenesis. Development 122:3035–3044
Chen D, Zhao M, Mundy GR (2004) Bone morphogenetic proteins. Growth Factors 22:233–241
Cho SW, Kwak S, Woolley TE, Lee MJ, Kim EJ, Baker RE, Kim HJ, Shin JS, Tickle C, Maini PK, Jung HS (2011) Interactions between Shh, Sostdc1 and Wnt signaling and a new feedback loop for spatial patterning of the teeth. Development 138:1807–1816
Darling DS, Stearman RP, Qi Y, Qiu MS, Feller JP (2003) Expression of Zfhep/deltaEF1 protein in palate, neural progenitors, and differentiated neurons. Gene Expr Patterns 3:709–717
Dassule HR, Lewis P, Bei M, Maas R, McMahon AP (2000) Sonic hedgehog regulates growth and morphogenesis of the tooth. Development 127:4775–4785
Dastot-Le Moal F, Wilson M, Mowa D, Collot N, Niel F, Goossens M (2007) ZEB2 mutations in patients with Mowat-Wilson syndrome. Hum Mutat 28:313–321
Fortini ME, Lai ZC, Rubin GM (1991) The Drosophila zfh-1 and zfh-2 genes encode novel proteins containing both zinc-finger and homeodomain motifs. Mech Dev 34:113–122
Funahashi J, Sekido R, Murai K, Kamachi Y, Kondoh H (1993) Delta-crystallin enhancer binding protein delta EF1 is a zinc finger-homeodomain protein implicated in postgastrulation embryogenesis. Development 119:433–446
Higashi Y, Maruhashi M, Nelles L, Van de Putte T, Verschueren K, Miyoshi T, Yoshimoto A, Kondoh H, Huylebroeck D (2002) Generation of the floxed allele of the SIP1 (Smad-interacting protein 1) gene for Cre-mediated conditional knockout in the mouse. Genesis 32:82–84
Jernvall J, Thesleff I (2000) Reiterative signaling and patterning during mammalian tooth morphogenesis. Mech Dev 92:19–29
Jernvall J, Kettunen P, Karavanova I, Martin LB, Thesleff I (1994) Evidence for the role of the enamel knot as a control center in mammalian tooth cusp formation: non-dividing cells express growth stimulating Fgf-4 gene. Int J Dev Biol 38:463–469
Jin JZ, Li Q, Higshi Y, Darling DS, Ding J (2008) Analysis of Zfhx1a mutant mice reveals palatal shelf contact-independent medial edge epithelial differentiation during palate fusion. Cell Tissue Res 333:29–38
Kaartinen V, Cui XM, Heisterkamp N, Groffen J, Shuler CF (1997) Transforming growth factor-beta3 regulates transdifferentiation of medial edge epithelium during palatal fusion and associated degradation of the basement membrane. Dev Dyn 209:255–260
Martinez-Alvarez C, Blanco MJ, Perez R, Rabadan MA, Aparicio M, Resel E, Martinez T, Nieto MA (2004) Snail family members and cell survival in physiological and pathological cleft palates. Dev Biol 265:207–218
Moribe H, Takagi T, Kondoh H, Higashi Y (2000) Suppression of polydactyly of the Gli3 mutant (extra toes) by deltaEF1 homozygous mutation. Dev Growth Differ 42:367–376
Nakatomi M, Wang XP, Key D, Lund JJ, Turbe Doan A, Kis R, Aw A, Chen Y, Maas RL, Peters H (2010) Genetic interactions between Pax9 and Msx1 regulate lip development and several stages of tooth morphogenesis. Dev Biol 340:438–449
Nawshad A, LaGamba D, Hay ED (2004) Transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta) signalling in palatal growth, apoptosis and epithelial mesenchymal transformation (EMT). Arch Oral Biol 49:675–689
Nishimura G, Manabe I, Tsushima K, Fujiu K, Oishi Y, Imai Y, Maemura K, Miyagishi M, Higashi Y, Kondoh H, Nagai R (2006) DeltaEF1 mediates TGF-beta signaling in vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation. Dev Cell 11:93–104
Pelton RW, Hogan BL, Miller DA, Moses HL (1990) Differential expression of genes encoding TGFs beta 1, beta 2, and beta 3 during murine palate formation. Dev Biol 141:456–460
Postigo AA (2003) Opposing functions of ZEB proteins in the regulation of the TGFbeta/BMP signaling pathway. EMBO J 22:2443–2452
Postigo AA, Dean DC (1997) ZEB, a vertebrate homolog of Drosophila Zfh-1, is a negative regulator of muscle differentiation. EMBO J 16:3935–3943
Shin JO, Lee JM, Cho KW, Kwak S, Kwon HJ, Lee MJ, Cho SW, Kim KS, Jung HS (2012a) MiR-200b is involved in Tgf-β signaling to regulate mammalian palate development. Histochem Cell Biol 137:67–78
Shin JO, Nakagawa E, Kim EJ, Cho KW, Lee JM, Cho SW, Jung HS (2012) MiR-200b regulates cell migration via Zeb family during mouse palate development. Histochem Cell biol (in press)
Takagi T, Moribe H, Kondoh H, Higashi Y (1998) DeltaEF1, a zinc finger and homeodomain transcription factor, is required for skeleton patterning in multiple lineages. Development 125:21–31
Thesleff I (2003) Epithelial-mesenchymal signaling regulating tooth morphogenesis. J Cell Sci 116:1647–1648
Thesleff I, Sharpe PT (1997) Signaling networks regulating dental development. Mech Dev 67:111–123
Tucker AS, Sharpe PT (2004) The cutting-edge of mammalian development; how the embryo makes teeth. Nat Rev Genet 5:499–508
Van de Putte T, Maruhashi M, Francis A, Nelles L, Kondoh H, Huylebroeck D, Higashi Y (2003) Mice lacking ZEB2, the gene that codes for Smad-interacting protein-1, reveal a role for multiple neural crest cell defects in the etiology of Hirschsprung disease-mental retardation syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 72:465–470
Vandewalle C, Van Roy F, Berx G (2009) The role of the ZEB family of transcription factors in development and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:773–787
Verschueren K, Remacle JE, Collart C, Kraft H, Baker BS, Tylzanowski P, Nelles L, Wuytens G, Su MT, Bodmer R, Smith JC, Huylebroeck D (1999) SIP1, a novel zinc finger/homeodomain repressor, interacts with Smad proteins and binds to 5′-CACCT sequences in candidate target genes. J Biol Chem 274:20489–20498
Wakamatsu N, Yamada Y, Yamada K, Ono T, Nomura N, Taniguchi H, Kitoh H, Mutoh N, Yamanaka T, Mushiake K, Kato K, Sonta S, Nagaya M (2001) Mutations in SIP1, encoding Smad interacting protein-1, cause a form of Hirschsprung disease. Nat Genet 27:369–370
Yamada K, Yamada Y, Nomura N, Miura K, Wakako R, Hayakawa C, Matsumoto A, Kumagai T, Yoshimura I, Miyazaki S, Kato K, Sonta S, Ono H, Yamanaka T, Nagaya M, Wakamatsu N (2001) Nonsense and frameshift mutations in ZEB2, encoding Smad-interacting protein 1, cause a complex developmental disorder with a great variety of clinical features. Am J Hum Genet 69:1178–1185
Yen G, Croci A, Dowling A, Zhang S, Zoeller RT, Darling DS (2001) Developmental and functional evidence of a role for Zfhep in neural cell development. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 96:59–67
Yu PB, Hong CC, Sachidanandan C, Babitt JL, Deng DY, Hoyng SA, Lin HY, Bloch KD, Peterson RT (2008) Dorsomorphin inhibits BMP signals required for embryogenesis and iron metabolism. Nat Chem Biol 4:33–41
Zhang ZY, Yu X, Zhang Y, Geronimo B, Lovlie A, Fromm SH, Chen YP (2000) Targeted misexpression of constitutively active BMP receptor-ΙB causes bifurcation and duplication and posterior transformation of digit in mouse limb. Dev Biol 220:154–167
Zimmerman LB, De Jesus-Escobar JM, Harland RM (1996) The Spemann organizer signal noggin binds and inactivates bone morphogenetic protein 4. Cell 86:599–606
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (R13-2003-013-05001-0).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jeong-Oh Shin and Eun-Jung Kim contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
418_2012_930_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary Figure 1 (a-d) Expression of Zeb1 and Zeb2 in 24-h-cultured tooth germ with NOGGIN-soaked bead. (e-h) Expression patterns of Zeb1 and Zeb2 in 24-h culture tooth germ after treatment of dorsomorphin. Expression of Zeb1 and Zeb2 were disappeared after treatment NOGGIN and dorsomorphin to inhibit BMP signals. M, mesenchyme (TIFF 3574 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, JO., Kim, EJ., Cho, KW. et al. BMP4 signaling mediates Zeb family in developing mouse tooth. Histochem Cell Biol 137, 791–800 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-012-0930-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-012-0930-7