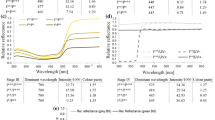
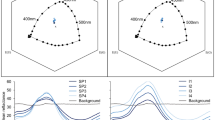
Abstract
Colour vision was first demonstrated with behavioural experiments in honeybees 100 years ago. Since that time a wealth of quality physiological data has shown a highly conserved set of trichromatic colour receptors in most bee species. Despite the subsequent wealth of behavioural research on honeybees and bumblebees, there currently is a relative dearth of data on stingless bees, which are the largest tribe of the eusocial bees comprising of more than 600 species. In our first experiment we tested Trigona cf. fuscipennis, a stingless bee species from Costa Rica in a field setting using the von Frisch method and show functional colour vision. In a second experiment with these bees, we use a simultaneous colour discrimination test designed for honeybees to enable a comparative analysis of relative colour discrimination. In a third experiment, we test in laboratory conditions Tetragonula carbonaria, an Australian stingless bee species using a similar simultaneous colour discrimination test. Both stingless bee species show relatively poorer colour discrimination compared to honeybees and bumblebees; and we discuss the value of being able to use these behavioural methods to efficiently extend our current knowledge of colour vision and discrimination in different bee species.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amano K, Nemoto T, Heard TA (2000) What are stingless bees, and why and how to use them as crop pollinators?—a review. Jpn Agr Res Q 34:183–190
Autrum H, Zwehl V (1964) Die spektrale Empfindlichkeit einzelner Sehzellen des Bienenauges. Z Vergl Physiol 48(4):357–384. doi:10.1007/BF00299270
Avarguès-Weber A, de Brito Sanchez MG, Giurfa M, Dyer AG (2010) Aversive reinforcement improves visual discrimination learning in free-flying honeybees. PLoS One 5(10):15370. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015370
Backhaus W (1991) Color opponent coding in the visual system of the honeybee. Vis Res 31(7–8):1381–1397
Barth FG (1985) Insects and flowers: the biology of a partnership. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Bischoff M, Lord JM, Robertson AW, Dyer AG (2013) Hymenopteran pollinators as agents of selection on flower colour in the New Zealand mountains: salient chromatic signals enhance flower discrimination. New Zeal J Bot 51(3):181–193. doi:10.1080/0028825X.2013.806933
Bispo dos Santos SA, Roselino AC, Hrncir M, Bego LR (2009) Pollination of tomatoes by the stingless bee Melipona quadrifasciata and the honey bee Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera, Apidae). Genet Mol Res 8(2):751–757
Briscoe AD, Chittka L (2001) The evolution of color vision in insects. Annu Rev Entomol 46:471–510. doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.46.1.471
Briscoe AD, Bernard GD, Szeto AS, Nagy LM, White RH (2003) Not all butterfly eyes are created equal: rhodopsin absorption spectra, molecular identification, and localization of ultraviolet-, blue-, and green-sensitive rhodopsin-encoding mRNAs in the retina of Vanessa cardui. J Comp Neurol 458(4):334–349. doi:10.1002/cne.10582
Bukovac Z, Dorin A, Dyer AG (2013) A-bees see: A simulation to assess social bee visual attention during complex search tasks. In: Liò et al (eds) Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Artificial Life (ECAL 2013). Taormina, Italy, 2-6 Sept, MIT Press, pp 276-283
Burns JG, Dyer AG (2008) Diversity of speed-accuracy strategies benefits social insects. Curr Biol 18(20):R953–R954
Chittka L (1992) The color hexagon—a chromaticity diagram based on photoreceptor excitations as a generalized representation of color opponency. J Comp Physiol A 170(5):533–543
Chittka L (1996a) Does bee color vision predate the evolution of flower color? Naturwissenschaften 83(3):136–138
Chittka L (1996b) Optimal sets of color receptors and color opponent systems for coding of natural objects in insect vision. J Theor Biol 181(2):179–196
Chittka L, Menzel R (1992) The evolutionary adaptation of flower colors and the insect pollinators’ color vision. J Comp Physiol A 171(2):171–181
Chittka L, Thomson JD, Waser NM (1999) Flower constancy, insect psychology, and plant evolution. Naturwissenschaften 86(8):361–377
Chittka L, Spaethe J, Schmidt A, Hickelsberger A (2001) Adaptation, constraint, and chance in the evolution of flower color and pollinator color vision. In: Chittka L, Thomson JD (eds) Cognitive ecology of pollination. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 106–126
Daumer K (1956) Reizmetrische Untersuchung des Farbensehens der Bienen. Z Vergl Physiol 38(5):413–478. doi:10.1007/BF00340456
Dyer AG (2006) Discrimination of flower colours in natural settings by the bumblebee species Bombus terrestris (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Entomol Gen 28(4):257–268
Dyer AG, Chittka L (2004) Fine colour discrimination requires differential conditioning in bumblebees. Naturwissenschaften 91(5):224–227. doi:10.1007/s00114-004-0508-x
Dyer AG, Neumeyer C (2005) Simultaneous and successive colour discrimination in the honeybee (Apis mellifera). J Comp Physiol A 191(6):547–557. doi:10.1007/s00359-005-0622-z
Dyer AG, Whitney HM, Arnold SEJ, Glover BJ, Chittka L (2007) Mutations perturbing petal cell shape and anthocyanin synthesis influence bumblebee perception of Antirrhinum majus flower colour. Arthropod Plant Interact 1(1):45–55. doi:10.1007/s11829-007-9002-7
Dyer AG, Spaethe J, Prack S (2008) Comparative psychophysics of bumblebee and honeybee colour discrimination and object detection. J Comp Physiol A 194(7):617–627. doi:10.1007/s00359-008-0335-1
Dyer AG, Paulk AC, Reser DH (2011) Colour processing in complex environments: insights from the visual system of bees. P Roy Soc B-Biol Sci 278(1707):952–959. doi:10.1098/rspb.2010.2412
Dyer AG, Boyd-Gerny S, McLoughlin S, Rosa MGP, Simonov V, Wong BBM (2012) Parallel evolution of angiosperm colour signals: common evolutionary pressures linked to hymenopteran vision. P Roy Soc B-Biol Sci 279(1742):3606–3615. doi:10.1098/rspb 2012.0827
Giurfa M (2004) Conditioning procedure and color discrimination in the honeybee Apis mellifera. Naturwissenschaften 91(5):228–231. doi:10.1007/s00114-004-0530-z
Giurfa M (2007) Behavioral and neural analysis of associative learning in the honeybee: a taste from the magic well. J Comp Physiol A 193(8):801–824. doi:10.1007/s00359-007-0235-9
Giurfa M, Núñez J, Chittka L, Menzel R (1995) Color preferences of flower-naive honeybees. J Comp Physiol A 177(3):247–259
Giurfa M, Vorobyev M, Kevan P, Menzel R (1996) Detection of coloured stimuli by honeybees: minimum visual angles and receptor specific contrasts. J Comp Physiol A 178(5):699–709
Goulson D, Cruise JL, Sparrow KR, Harris AJ, Park KJ, Tinsley MC, Gilburn AS (2007) Choosing rewarding flowers; perceptual limitations and innate preferences influence decision making in bumblebees and honeybees. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 61(10):1523–1529. doi:10.1007/s00265-007-0384-4
Green CL, Franck P, Oldroyd BP (2001) Characterization of microsatellite loci for Trigona carbonaria, a stingless bee endemic to Australia. Mol Ecol Notes 1:89–92. doi:10.1046/j.1471-8278.2001.00041.x
Gumbert A (2000) Color choices by bumble bees (Bombus terrestris): innate preferences and generalization after learning. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 48(1):36–43
Heard TA (1988) Propagation of hives of Trigona carbonaria SMITH (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Aust J Entomol 27(4):303–304. doi:10.1111/j.1440-6055.1988.tb01178.x
Heard TA (1994) Behaviour and pollinator efficiency of stingless bees and honey bees on Macadamia flowers. J Apic Res 33(4):191–198
Heard TA (1999) The role of stingless bees in crop pollination. Annu Rev Entomol 44:183–206. doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.44.1.183
Heard T, Hendrikz J (1993) Factors influencing flight activity of colonies of the stingless bee Trigona carbonaria (Hymenoptera, Apidae). Aust J Zool 41(4):343–353. doi:10.1071/ZO9930343
Hegland SJ, Nielsen A, Lázaro A, Bjerknes AL, Totland Ø (2009) How does climate warming affect plant-pollinator interactions? Ecol Lett 12(2):184–195. doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2008.01269.x
Hempel de Ibarra N, Giurfa M, Vorobyev M (2001) Detection of coloured patterns by honeybees through chromatic and achromatic cues. J Comp Physiol A 187(3):215–224
Hurvich LM (1981) Color vision. Sinauer, Sunderland
Jarau S, Morawetz L, Reichle C, Gruber MH, Huber W, Weissenhofer A (2009) Corbiculate bees of the Golfo Dulce region, Costa Rica. Verein zur Förderung der Tropenstation La Gamba, Vienna
Johnson LK, Hubbell SP (1975) Contrasting foraging strategies and coexistence of two bee species on a single resource. Ecology 56(6):1398–1406. doi:10.2307/1934706
Kaiser W, Liske E (1974) Die optomotorische Reaktion von fixiert fliegenden Bienen bei Reizung mit Spektrallichtern. J Comp Physiol A 89:391–408
Kakutani T, Inoue T, Tezuka T, Maeta Y (1993) Pollination of strawberry by the stingless bee, Trigona minangkabau, and the honey bee, Apis mellifera: an experimental study of fertilization efficiency. Res Popul Ecol 35:95–111
Kien J, Menzel R (1977) Chromatic properties of interneurons in the optic lobes of the bee. J Comp Physiol 113(1):35–53. doi:10.1007/BF00610452
Koshitaka H, Kinoshita M, Vorobyev M, Arikawa K (2008) Tetrachromacy in a butterfly that has eight varieties of spectral receptors. P Roy Soc B-Biol Sci 275(1637):947–954. doi:10.1098/rspb.2007.1614
Kühn A, Pohl R (1921) Dressurfähigkeit der Bienen auf Spektrallinien. Naturwissenschaften 9(37):738–740. doi:10.1007/BF01487183
Kulikowski JJ, Walsh V (1991) On the limits of colour detection and discrimination. In: Kulikowski JJ, Walsh V, Murray IJ, Cronly-Dillon JR (eds) Vision and visual dysfunction 5: limits of vision. Macmillian, London, pp 202–220
Lehrer M, Horridge GA, Zhang SW, Gadagkar R (1995) Shape vision in bees: innate preference for flower-like patterns. Phil Trans R Soc B 347:123–137
Lunau K (1990) Colour saturation triggers innate reactions to flower signals: flower dummy experiments with bumblebees. J Comp Physiol A 166(6):827–834. doi:10.1007/BF00187329
Menzel R (1967) Untersuchungen zum Erlernen von Spektralfarben durch die Honigbiene (Apis mellifica). Z Vergl Physiol 56(1):22–62. doi:10.1007/BF00333562
Menzel R, Steinmann E, De Souza J, Backhaus W (1988) Spectral sensitivity of photoreceptors and colour vision in the solitary bee Osmia rufa. J Exp Biol 136:35–52
Menzel R, Ventura DF, Werner A, Joaquim LCM, Backhaus W (1989) Spectral sensitivity of single photoreceptors and color-vision in the stingless bee, Melipona quadrifasciata. J Comp Physiol A 166:151–164
Michener CD (2007) The bees of the world, 2nd edn. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Morawetz L, Spaethe J (2012) Visual attention in a complex search task differs between honeybees and bumblebees. J Exp Biol 215:2515–2523. doi:10.1242/jeb.066399
Morawetz L, Svoboda A, Spaethe J, Dyer AG (2013) Blue colour preference in honeybees distracts visual attention for learning closed shapes. J Comp Physiol A. doi:10.1007/s00359-013-0843-5
Moreno AM, de Souza DdG, Reinhard J (2012) A comparative study of relational learning capacity in honeybees (Apis mellifera) and stingless bees (Melipona rufiventris). PLoS One 7(12):e51467. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0051467
Neumeyer C (1980) Simultaneous color contrast in the honeybee. J Comp Physiol 139(3):165–176. doi:10.1007/BF00657079
Neumeyer C (1981) Chromatic adaptation in the honeybee: successive color contrast and color constancy. J Comp Physiol A 144(4):543–553. doi:10.1007/BF01326839
Newhall SM, Burnham RW, Clark JR (1957) Comparison of successive with simultaneous color matching. J Opt Soc Am 47(1):43–54. doi:10.1364/JOSA.47.000043
Nieh JC, Tautz J, Spaethe J, Bartareau T (1999) The communication of food location by a primitive stingless bee, Trigona carbonaria. Zoology 102(4):238–246
Norgate M, Boyd-Gerny S, Simonov V, Rosa MGP, Heard TA, Dyer AG (2010) Ambient temperature influences Australian native stingless bee (Trigona carbonaria) preference for warm nectar. PLoS One 5(8):12000. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012000
Paulk AC, Dacks AM, Gronenberg W (2009) Color processing in the medulla of the bumblebee (Apidae: Bombus impatiens). J Comp Neurol 513(5):441–456. doi:10.1002/Cne.21993
Peitsch D, Fietz A, Hertel H, de Souza J, Ventura DF, Menzel R (1992) The spectral input systems of hymenopteran insects and their receptor-based colour vision. J Comp Physiol A 170(1):23–40
Potts SG, Biesmeijer JC, Kremen C, Neumann P, Schweiger O, Kunin WE (2010) Global pollinator declines: trends, impacts and drivers. Trends Ecol Evol 25(6):345–353. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2010.01.007
Raine NE, Chittka L (2007) The adaptive significance of sensory bias in a foraging context: floral colour preferences in the bumblebee Bombus terrestris. PLoS One 2(6):556. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000556
Rasmussen C, Cameron SA (2010) Global stingless bee phylogeny supports ancient divergence, vicariance, and long distance dispersal. Biol J Linn Soc 99(1):206–232. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8312.2009.01341.x
Reser DH, Wijesekara Witharanage R, Rosa MG, Dyer AG (2012) Honeybees (Apis mellifera) learn color discriminations via differential conditioning independent of long wavelength (green) photoreceptor modulation. PLoS One 7(11):e48577. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0048577
Romero J, Hita E, del Barco LJ (1986) A comparative study of successive and simultaneous methods in colour discrimination. Vis Res 26(3):471–476. doi:10.1016/0042-6989(86)90189-6
Roubik DW (1989) Ecology and natural history of tropical bees. Cambridge University Press, New York
Sánchez D, Vandame R (2012) Color and shape discrimination in the stingless bee Scaptotrigona mexicana Guérin (Hymenoptera, Apidae). Neotrop Entomol 41(3):171–177. doi:10.1007/s13744-012-0030-3
Shrestha M, Dyer AG, Boyd-Gerny S, Wong BBM, Burd M (2013) Shades of red: bird-pollinated flowers target the specific colour discrimination abilities of avian vision. New Phytol 198(1):301–310. doi:10.1111/nph.12135
Slaa EJ, Sánchez Chaves LA, Malagodi-Braga KS, Hofstede FE (2006) Stingless bees in applied pollination: practice and perspectives. Apidologie 37(2):293–315
Spaethe J, Briscoe AD (2005) Molecular characterization and expression of the UV opsin in bumblebees: three ommatidial subtypes in the retina and a new photoreceptor organ in the lamina. J Exp Biol 208:2347–2361. doi:10.1242/Jeb.01634
Spaethe J, Chittka L (2003) Interindividual variation of eye optics and single object resolution in bumblebees. J Exp Biol 206:3447–3453. doi:10.1242/Jeb.00570
Spaethe J, Tautz J, Chittka L (2001) Visual constraints in foraging bumblebees: flower size and color affect search time and flight behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(7):3898–3903
Srinivasan MV (2010) Honey bees as a model for vision, perception, and cognition. Annu Rev Entomol 55:267–284. doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.010908.164537
Stavenga DG, Smits RP, Hoenders BJ (1993) Simple exponential functions describing the absorbance bands of visual pigment spectra. Vis Res 33(8):1011–1017. doi:10.1016/0042-6989(93)90237-q
Stojcev M, Radtke N, D’Amaro D, Dyer AG, Neumeyer C (2011) General principles in motion vision: color blindness of object motion depends on pattern velocity in honeybee and goldfish. Vis Neurosci 28(4):361–370. doi:10.1017/S0952523811000101
Streinzer M, Brockmann A, Nagaraja N, Spaethe J (2013) Sex and caste-specific variation in compound eye morphology of five honeybee species. PLoS One 8(2):e57702. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0057702
Uchikawa K, Ikeda M (1981) Temporal deterioration of wavelength discrimination with successive comparison method. Vis Res 21(4):591–595. doi:10.1016/0042-6989(81)90106-1
von Frisch K (1914) Der Farbensinn und Formensinn der Biene. Zool Jahrb Allg Zool 35:1–188
von Frisch K (1967) The dance language and orientation of bees. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
von Helversen O (1972a) The relationship between difference in stimuli and choice frequency in training experiments with the honeybee. In: Wehner R (ed) Information processing in the visual system of anthropods. Springer, Berlin, pp 323–334
von Helversen O (1972b) Zur spektralen Unterschiedsempfindlichkeit der Honigbiene. J Comp Physiol 80(4):439–472. doi:10.1007/BF00696438
von Hess C (1913) Experimentelle Untersuchungen über den angeblichen Farbensinn der Bienen. G. Fischer, Jena
Vorobyev M, Brandt R, Peitsch D, Laughlin SB, Menzel R (2001) Colour thresholds and receptor noise: behaviour and physiology compared. Vis Res 41(5):639–653
Wakakuwa M, Kurasawa M, Giurfa M, Arikawa K (2005) Spectral heterogeneity of honeybee ommatidia. Naturwissenschaften 92(10):464–467. doi:10.1007/s00114-005-0018-5
Wertlen AM, Niggebrugge C, Vorobyev M, Hempel de Ibarra N (2008) Detection of patches of coloured discs by bees. J Exp Biol 211:2101–2104. doi:10.1242/Jeb.014571
Whitney HM, Dyer A, Chittka L, Rands SA, Glover BJ (2008) The interaction of temperature and sucrose concentration on foraging preferences in bumblebees. Naturwissenschaften 95(9):845–850. doi:10.1007/s00114-008-0393-9
Yang EC, Lin HC, Hung YS (2004) Patterns of chromatic information processing in the lobula of the honeybee. Apis mellifera L. J Ins Physiol 50(10):913–925. doi:10.1016/j.jinsphys.2004.06.010
Acknowledgments
We thank Werner Huber (University of Vienna) for logistical support, Christa Neumeyer for discussions, and the Tropical Research Station La Gamba, Costa Rica, for making available their laboratory facilities and tropical garden. The Costa Rican Ministerio de Ambiente y Energía kindly granted research permits. A.G.D. was supported by Australian Research Council DP0878968/DP0987989/DP130100015 and the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. A.G.D. and S.M. thank The Biological Sciences Department at Monash University for facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. Spaethe, M. Streinzer and A.G. Dyer contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spaethe, J., Streinzer, M., Eckert, J. et al. Behavioural evidence of colour vision in free flying stingless bees. J Comp Physiol A 200, 485–496 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-014-0886-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-014-0886-2