Abstract
Rationale
Endocannabinoids (eCN) exert biphasic effects on several behaviours; however, they have only been reported to inhibit male sexual behaviour. eCN, the endogenous ligands for CB1 receptors, are released in response to neuronal stimulation and regulate the functioning of the mesocorticolimbic system (MCL), which is activated by male sexual behaviour. We hypothesised that eCN might exert biphasic effects on male rat copulatory behaviour and be released during copulation to satiation as a result of the repeated activation of the MCL system.
Objectives
The study was conducted to determine if the eCN anandamide exerts biphasic effects on sexual behaviour expression of sexually experienced and sexually satiated male rats and to establish the possible participation of eCN in the sexual satiation phenomenon.
Methods
The eCN anandamide and the CB1 receptor antagonist AM251 were systemically administered to sexually experienced or sexually satiated rats and their effects on copulatory behaviour analysed.
Results
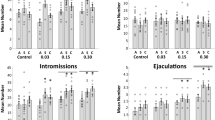
Low anandamide doses facilitated sexual behaviour expression in sexually experienced and in sexually satiated rats by acting at CB1 receptors. AM251 blocked the establishment of the sexual inhibition that characterises sexual satiation, but did not reverse it once established.
Conclusions
Anandamide exerts dose-based biphasic effects on copulatory behaviour of sexually experienced male rats and facilitates sexual behaviour expression of sexually satiated animals at low doses. eCN participate in the establishment, but not in the maintenance of the sexual inhibitory state that characterises the sexual satiation phenomenon.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alger BE, Kim J (2011) Supply and demand for endocannabinoids. Trends Neurosci 34:304–315
Balfour M, Yu L, Coolen L (2004) Sexual behavior and sex-associated environmental cues activate the mesolimbic system in male rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:718–730
Beach F, Jordan L (1956) Sexual exhaustion and recovery in the male rat. Q J Exp Psychol 8:121–133
Berridge KC (2007) The debate over dopamine’s role in reward: the case for incentive salience. Psychopharmacology 191:391–431
Canseco-Alba A, Rodríguez-Manzo G (2013) Anandamide transforms non copulating rats into sexually active animals. J Sex Med 10:686–693
Damsma G, Pfaus JG, Wenkstern D, Phillips AG, Fibiger HC (1992) Sexual behavior increases dopamine transmission in the nucleus accumbens and striatum of male rats: comparison with novelty and locomotion. Behav Neurosci 106:181–191
Di Marzo V, Melck D, Bisogno T, De Petrocellis L (1998) Endocannabinoids: endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligands with neuromodulatory action. Trends Neurosci 21:521–528
Ferrari F, Ottani D, Giuliani D (2000) Inhibitory effects of the cannabinoid agonist HU 210 on rat sexual behavior. Physiol Behav 69:547–554
Fiorino DF, Coury A, Phillips AG (1997) Dynamic changes in nucleus accumbens dopamine efflux during the Coolidge effect in male rats. J Neurosci 17:4849–4855
Fride E, Mechoulam R (1993) Pharmacological activity of the cannabinoid receptor agonist, anandamide, a brain constituent. Eur J Pharmacol 231:313–314
Gardner E (2005) Endocannabinoid signaling system and brain reward: emphasis on dopamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81:263–284
Garduño-Gutiérrez R, Guadarrama-Bazante L, León-Olea M, Rodríguez-Manzo G (2013) Endogenous opioids mediate the sexual inhibition, but not the drug hypersensitivity induced by sexual satiation in male rats. Behav Neurosci 127:458–464
Gorzalka B, Morrish A, Hill G (2008) Endocannabinoid modulation of male rat sexual behavior. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 198:479–486
Hernández-González M, Guevara MA, Morali G, Cervantes M (1997) Subcortical multiple unit activity changes during rat male sexual behavior. Physiol Behav 61:285–291
Johnson SW, North RA (1992) Opioids excite dopamine neurons by hyperpolarization of local interneurons. J Neurosci 12:483–488
Kelley A, Berridge K (2002) The neuroscience of natural rewards: relevance to addictive drugs. J Neurosci 22:3306–3311
Larsson K (1956) Conditioning and sexual behaviour in the male albino rat. Almqvist and Wiksell, Stockholm
Lobb CJ, Troyer TW, Wilson CJ, Paladini CA (2011) Disinhibition bursting of dopaminergic neurons. Front Syst Neurosci 5:1–8
Lupica C, Riegel A, Hoffman A (2004) Marijuana and cannabinoid regulation of brain reward circuits. Br J Pharmacol 143:227–234
Martínez-González D, Bonilla-Jaime H, Morales-Otal A, Henriksen SJ, Velázquez-Moctezuma J, Prospéro-García O (2004) Oleamide and anandamide effects on food intake and sexual behavior of rats. Neurosci Lett 364:1–6
Mas M, Gonzales-Mora JL, Louilot A, Solé C, Guadalupe T (1990) Increased dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens of copulating male rats as evidenced by in vivo voltammetry. Neurosci Lett 110:303–308
Merari A, Barak A, Plaves M (1973) Effects of 1(2)-tetrahydrocannabinol on copulation in the male rat. Psychopharmacologia 28:243–246
Micale V, Cristino L, Tamburella A, Petrosino S, Leggio GM, Drago F, Di Marzo V (2009) Anxiolytic effects in mice of a dual blocker of fatty acid amide hydrolase and transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1 channels. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:593–606
Murphy LL, Gher J, Steger RW, Bartke A (1994) Effects of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol on copulatory behavior and neuroendocrine responses of male rats to female conspecifics. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 48:1011–1017
Pfaus JG, Damsma G, Wenkstern DG, Blaha CD, Phillips AG, Fibiger HC (1990) Sexual behavior enhances central dopamine transmission in the rat. Brain Res 530:345–348
Pleim ET, Matochik JA, Barfield RJ, Auerbach SB (1990) Correlation of dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens with masculine sexual behavior in rats. Brain Res 524:160–163
Rodríguez-Manzo G, Fernández-Guasti A (1994) Reversal of sexual exhaustion by serotonergic and noradrenergic agents. Behav Brain Res 62:127–134
Rodríguez-Manzo G, Guadarrama-Bazante IL, Morales-Calderón A (2011) Recovery from sexual exhaustion-induced copulatory inhibition and drug hypersensitivity follow a same time course: two expressions of a same process? Behav Brain Res 217:253–260
Ross RA (2003) Anandamide and vanilloid TRPV1 receptors. Br J Pharmacol 140:790–801
Rubino T, Realini N, Castiglioni C, Guidali C, Vigano D, Marras E, Petrosino S, Perletti G, Maccarrone M, Di Marzo V, Parolaro D (2008) Role in anxiety behavior of the endocannabinoid system in the prefrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 18:1292–1301
Scherma M, Medalie J, Fratta W, Vadivel SK, Makriyannis A, Piomelli D, Mikics E, Haller J, Yasar S, Tanda G, Goldberg SR (2008) The endogenous cannabinoid anandamide has effects on motivation and anxiety that are revealed by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) inhibition. Neuropharmacology 54:129–140
Stewart J (1995) How does incentive motivational theory apply to sexual behaviour? In: Bancroft J (ed) The pharmacology of sexual function and dysfunction. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
Sulcova E, Mechoulam R, Fride E (1998) Biphasic effects of anandamide. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 59:347–352
Swanson LW (1982) The projections of the ventral tegmental area and adjacent regions: a combined fluorescent retrograde tracer and immunofluorescence study in the rat. Brain Res Bull 9:321–353
Szabo B, Siemes S, Wallmichrath I (2002) Inhibition of GABAergic neurotransmission in the ventral tegmental area by cannabinoids. Eur J Neurosci 15:2057–2061
Umathe SN, Manna SS, Jain NS (2012) Endocannabinoid analogues exacerbate marble-burying behavior in mice via TRPV1 receptor. Neuropharmacology 62:2024–2033
Wenkstern D, Pfaus JG, Fibiger HC (1993) Dopamine transmission increases in the nucleus accumbens of male rats during first exposure to sexually receptive female rats. Brain Res 618:41–46
Wu X, French ED (2000) Effects of chronic delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol on rat midbrain dopamine neurons: an electrophysiological assessment. Neuropharmacology 39:391–398
Acknowledgments
Authors wish to thank Miss Ángeles Ceja Gálvez for animal care. The data here reported are part of the MSc dissertation of Ana Canseco-Alba who received a scholarship from Conacyt (Nr. 232728)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Canseco-Alba, A., Rodríguez-Manzo, G. Low anandamide doses facilitate male rat sexual behaviour through the activation of CB1 receptors. Psychopharmacology 231, 4071–4080 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3547-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3547-9