Abstract
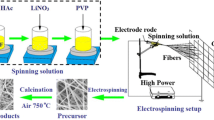
The morphology and electronic structure of a Li4Ti5O12 anode are known to determine its electrical and electrochemical properties in lithium rechargeable batteries. Ag-Li4Ti5O12 nanofibers have been rationally designed and synthesized by an electrospinning technique to meet the requirements of one-dimensional (1D) morphology and superior electrical conductivity. Herein, we have found that the 1D Ag-Li4Ti5O12 nanofibers show enhanced specific capacity, rate capability, and cycling stability compared to bare Li4Ti5O12 nanofibers, due to the Ag nanoparticles (<5 nm), which are mainly distributed at interfaces between Li4Ti5O12 primary particles. This structural morphology gives rise to 20% higher rate capability than bare Li4Ti5O12 nanofibers by facilitating the charge transfer kinetics. Our findings provide an effective way to improve the electrochemical performance of Li4Ti5O12 anodes for lithium rechargeable batteries.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jeong, G.; Kim, Y. U.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y. J.; Sohn, H. J. Prospective materials and applications for Li secondary batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1986–2002.
Deng, D.; Kim, M. G.; Lee, J. Y.; Cho, J. Green energy storage materials: Nanostructured TiO2 and Sn-based anodes for lithium-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 818–837.
Colbow, K. M.; Dahn J. R.; Haering, R. R. Structure and electrochemistry of the spinel oxides LiTi2O4 and Li4/3Ti5/3O4. J. Power Sources 1989, 26, 397–402.
Ferg, E.; Gummow, R. J.; de Kock, A.; Thackeray, M. M. Spinel anodes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1994, 141, L147–L150.
Ohzuku, T.; Ueda, A.; Yamamoto, N. Zero-strain insertion material of Li[Li1/3Ti5/3]O4 for rechargeable lithium cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 1431–1435.
Kavan, L.; Gratzel, M. Facile synthesis of nanocrystalline Li4Ti5O12(spinel) exhibiting fast Li insertion. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2002, 5, A39–A42.
Lu, X.; Zhao, L.; He, X.; Xiao, R.; Gu, L.; Hu, Y.-S.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Duan, X.; Chen, L. et al. Lithium storage in Li4Ti5O12 spinel: The full static picture from electron microscopy. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3233–3268.
Pan, H.; Zhao, L.; Hu, Y.-S.; Li, H.; Chen, L. Improved Li-storage performance of Li4Ti5O12 coated with C-N compounds derived from pyrolysis of urea through a low-temperature approach. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 526–529.
Pan, H.-L.; Hu, Y.-S.; Li, H.; Chen, L.-Q. Significant effect of electron transfer between current collector and active material on high rate performance of Li4Ti5O12. Chin. Phys. B 2011, 20, 118202.
Jansen, A. N.; Kahaian, A. J.; Kepler, K. D.; Nelson, P. A.; Amine, K.; Dees, D. W.; Vissers, D. R.; Thackeray, M. M. Development of a high-power lithium-ion battery. J. Power Sources 1999, 81–82, 902–905.
Ouyang, C. Y.; Zhong, Z. Y.; Lei, M. S. Ab initio studies of structural and electronic properties of Li4Ti5O12 spinel. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 1107–1112.
Wang, Y.-Q.; Gu, L.; Guo, Y.-G.; Li, H.; He, X.-Q.; Tsukimoto, S.; Ikuhara, Y.; Wan, L.-J. Rutile-TiO2 nanocoating for a high-rate Li4Ti5O12 anode of a lithium-ion battery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7874–7879.
Han, H.; Song, T.; Bae, J. Y.; Nazar, L. F.; Kim, H.; Paik, U. Nitridated TiO2 hollow nanofibers as an anode material for high power lithium ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 4532–4536.
Park, K. S.; Benayad, A.; Kang, D. J.; Doo, S. G. Nitridation-driven conductive Li4Ti5O12 for lithium ion batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14930–14931.
Seo, M. H.; Park, M.; Lee, K. T.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.; Cho, J. High performance Ge nanowire anode sheathed with carbon for lithium rechargeable batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 425–428.
Nugroho, A.; Chang, W.; Kim, S. J.; Chung, K. Y.; Kim, J. Superior high rate performance of core-shell Li4Ti5O12/carbon nanocomposite synthesized by a supercritical alcohol approach. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 10805–10808.
Lee, S.; Cho, Y.; Song, H.-K.; Lee, K. T.; Cho, J. Carbon-coated single-crystal LiMn2O4 nanoparticle clusters as cathode material for high-energy and high-power lithium-ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2012, 51, 8748–8752.
Cai, R.; Jiang, S. M.; Yu, X.; Zhao, B. T.; Wang, H. T.; Shao, Z. P. A novel method to enhance rate performance of an Al-doped Li4Ti5O12 electrode by post-synthesis treatment in liquid formaldehyde at room temperature. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 8013–8021.
Song, H.; Yun, S.-W.; Chun, H.-H.; Kim, M.-G.; Chung, K. Y.; Kim, H. S.; Cho, B.-W.; Kim, Y.-T. Anomalous decrease in structural disorder due to charge redistribution in Cr-doped Li4Ti5O12 negative-electrode materials for high-rate Li-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 9903–9913.
Gu, F.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z. Synthesis and electrochemical performances of Li4Ti4.95Zr0.05O12/C as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2012, 16, 375–382.
Nam, S. H.; Shim, H. S.; Kim, Y. S.; Dar, M. A.; Kim, J. G.; Kim, W. B. Ag or Au nanoparticle-embedded one-dimensional composite TiO2 nanofibers prepared via electrospinning for use in lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2010, 2, 2046–2052.
Du, G.; Sharma, N.; Peterson, V. K.; Kimpton, J. A.; Jia, D.; Guo, Z. Br-doped Li4Ti5O12 and composite TiO2 anodes for Li-ion batteries: Synchrotron X-ray and in situ neutron diffraction studies. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 3990–3997.
Guo, Y.-G.; Hu, Y.-S.; Sigle, W.; Maier, J. Superior electrode performance of nanostructured mesoporous TiO2 (anatase) through efficient hierarchical mixed conducting networks. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2087–2091.
Kim, J.-G.; Shi, D.; Kong, K.-J.; Heo, Y.-U.; Kim, J. H.; Jo, M. R.; Lee, Y. C.; Kang, Y.-M.; Dou, S. X. Structurally and electronically designed TiO2Nx nanofibers for lithium rechargeable batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 691–696.
Shim, H. W.; Lee, D. K.; Cho, I. S.; Hong, K. S.; Kim, D. W. Facile hydrothermal synthesis of porous TiO2 nanowire electrodes with high-rate capability for Li ion batteries. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 255706.
Xia, Y.; Yang, P.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Y.; Mayers, B.; Gates, B.; Yin, Y.; Kim, F.; Yan, H. One-dimentional Nanostructures: Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 353–389.
Lu, X.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y. One-dimensional composite nanomaterials: Synthesis by electrospinning and their applications. Small 2009, 5, 2349–2370.
Jo, M. R.; Jung, Y. S.; Kang, Y.-M. Tailored Li4Ti5O12 nanofibers with outstanding kinetics for lithium rechargeable batteries. Nanoscale, 2012, 4, 6870–6875
Li, D.; Xia, Y. Fabrication of titania nanofibers by electrospinning. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 555–560.
Li, D.; Xia, Y. Direct fabrication of composite and ceramic hollow nanofibers by electrospinning. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 933–938.
Yu, Y.; Gu, L.; Zhu, C.; Aken, P. A.; Maier, J. Tin nanoparticles encapsulated in porous multichannel carbon microtubes: Preparation by single-nozzle electrospinning and application as anode material for high-performance Li-based batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 15984–15985.
Cavaliere, S.; Subianto, S.; Savych, I.; Jones, D. J.; Roziere, J. Electrospinning: Designed architectures for energy conversion and storage devices. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 4761–4785.
Asokan, K.; Park, J. Y.; Choi, S.; Chang, C.; Kim, S. S. Stabilization of the anatase phase of Ti1−x SnxO2 (x < 0.5) nanofibers. Nano Res. 2010, 3, 256–263.
Kim, J.; Cho, J. Spinel Li4Ti5O12 nanowires for high-rate Li-ion intercalation electrode. Electrochen Solid-State Lett. 2007, 10, A81–A84.
Aldon, L.; Kubiak, P.; Womes, M.; Jumas, J. C.; Olivier-Fourcade, J.; Tirado, J. L.; Corredor, J. I.; Vicente, C. P. Chemical and electrochemical Li-insertion into the Li4Ti5O12 spinel. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 5721–5725.
Wan, Z.; Cai, R.; Jiang, S.; Shao, Z. Nitrogen- and TiN-modified Li4Ti5O12: One-step synthesis and electrochemical performance optimization. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 17773–17781.
Huang, S.; Wen, Z.; Zhu, X.; Gu, Z. Preparation and electrochemical performance of Ag doped Li4Ti5O12. Electrochem. Commun. 2004, 6, 1093–1097.
Liu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Z.; Sun, K. Highly dispersed Ag nanoparticles (<10 nm) deposited on nanocrystalline Li4Ti5O12 demonstrating high-rate charge/discharge capability for lithium-ion battery. J. Power Sources 2012, 205, 479–482.
Herle, P. S.; Ellis, B.; Coombs, N.; Nazar, L. F. Nano-network electronic conduction in iron and nickel olivine phosphates. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 147–152.
Suo, L.; Hu, Y.-S.; Li, H.; Armand, M.; Chen, L. A new class of solvent-in-salt electrolyte for high-energy rechargeable metallic lithium batteries. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1481.
Jo, M. R.; Nam, K. M.; Lee, Y.; Song, K.; Park, J. T.; Kang, Y.-M. Phosphidation of Li4Ti5O12 nanoparticles and their electrochemical and biocompatible superiority for lithium rechargeable batteries. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 11474–11476.
Zhao, L.; Hu, Y. S.; Li, H.; Wang, Z. X.; Chen, L. Q. Porous Li4Ti5O12 coated with N-doped carbon from ionic liquids for Li-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1385–1388.
Ma, Y.; Ji, G.; Ding, B.; Lee, J. Y. Facile solvothermal synthesis of anatase TiO2 microspheres with adjustable mesoporosity for the reversible storage of lithium ions. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24380–24385.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JG., Shi, D., Park, MS. et al. Controlled Ag-driven superior rate-capability of Li4Ti5O12 anodes for lithium rechargeable batteries. Nano Res. 6, 365–372 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-013-0313-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-013-0313-y