Abstract
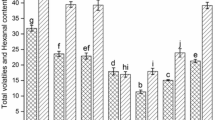
Effects of pulsed electric fields (PEF) on quality characteristics and microbial inactivation of soymilk were studied with different PEF parameters. PEF did not affect significantly the values of pH, “a” (an indicator of redness ranging from “−a” to “+a”, −a = green, +a = red) and electric conductivity. The values of “L” (white if “L” = 100, black if “L” = 0) increased slightly, whereas values of viscosity and “b” (an indicator of yellowness ranging from “−b” to “+b”, −b = blue, +b = yellow) decreased slightly as PEF time increased from 0 to 547 μs. Cysteine, tyrosine, phenylalanine, and serine reduced with the increase of PEF time. The relative activities of soybean lipoxygenase (SLOX) decreased with PEF time increasing from 0 to 1,036 μs. When PEF time and strength increased, the inactivation of Escherichia coli and Staphylococus aureus increased significantly (p < 0.05), achieving a maximum of 5.20 and 3.51 log10 cycles reduction at PEF time 547 μs and pulsed electric strength 40 kV/cm, respectively. The inactivation of E. coli, S. aureus, and SLOX as a function PEF time followed Weibull distribution. This study demonstrated that PEF could inactivate efficiently E. coli, S. aureus, and SLOX without affecting the quality characteristics of soymilk. Thus, this technique could be an advantageous alternative to heat treatment for pasteurization of soymilk.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akdemir, E. G., Jina, Z. T., Ruhlmana, K. T., Qiua, X., Zhanga, Q. H., & Richterb, E. R. (2000). Microbial safety and shelf-life of apple juice and cider processed by bench and pilot scale PEF systems. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 1, 77–86.
Akoum, O., Richfield, D., Jaffrin, M. Y., Ding, L. H., & Swart, P. (2006). Recovery of trypsin inhibitor and soy milk protein concentration by dynamic filtration. Journal of Membrane Science, 279, 291–300.
Altuntas, J., Evrendilek, G. A., Sangun, M. K., & Zhang, H. Q. (2010). Effects of pulsed electric field processing on the quality and microbial inactivation of sour cherry juice. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 45, 899–905.
Amiali, M., Ngadi, M. O., Raghavan, V. G. S., & Smith, J. P. (2004). Inactivation of Escherichia coli O157 H7 in liquid dialyzed egg using pulsed electric fields. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 82, 151–156.
Antoine, F., Wei, C., Littell, R., Quinn, B., Hogle, A., & Marshall, M. (2001). Free amino acids in dark- and white-muscle fish as determined by o-phthaldialdehyde precolumn derivatization. Journal of Food Science, 66, 72–74.
Aronsson, K., Lindgren, M., Johansson, B. R., & Ronner, U. (2001). Inactivation of microorganisms using pulsed electric fields: the influence of process parameters on Escherichia coli, Listeria innocua, Leuconostoc mesenteroides and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 2, 41–54.
Arroyo, C., Cebrián, G., Pagán, R., & Condón, S. (2010). Resistance of enterobacter sakazakii to pulsed electric fields. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 11, 314–321.
Barsotti, L., Dumay, E., Mu, T. H., Diaz, M. D. F., & Cheftel, J. C. (2002). Effects of high voltage electric pulses on protein-based food constituents and structures. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 12, 136–144.
Baur, C., Groch, W., Wieser, H., & Jugel, H. (1977). Enzymatic oxidation of linoleic acid: formation of bittertasting fatty acids. Zeitschrift für Lebensmittel-Untersuchung und -Forschung, 164, 171–176.
Bazhal, M. I., Ngadi, M. O., Raghavan, G. S. V., & Smith, J. P. (2006). Inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in liquid whole egg using combined pulsed electric field and thermal treatments. LWT- Food Science and Technology, 39, 419–425.
Carroll, K. K., & Kurowska, E. M. (1995). Soy consumption and cholesterol reduction: review of animal and human studies. Journal of Nutrition, 125, 594S–597S.
Cortés, C., Esteve, M. J., Frίgola, A., & Torregrosa, F. (2005). Quality characteristics of horchata (a Spanish vegetable beverage) treated with pulsed electric fields during shelf-life. Food Chemistry, 91, 319–325.
Cruz, A. G. D., Faria, J. D. A. F., Saad, S. M. I., Bolini, H. M. A., Ana, A. S. S., & Cristianini, M. (2010). High pressure processing and pulsed electric fields: potential use in probiotic dairy foods processing. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 21, 483–493.
D’Alessandro, T., Prasain, J., Benton, M. R., Botting, N., Moore, R., Darley-Usmar, V., Patel, R., & Barnes, S. (2003). Polyphenol, inflammatory response, and cancer prevention: chlorination of isoflavones by human neutrophils. Journal of Nutrition, 133, 3773S–3777S.
Dutreux, N., Notermans, S., Wijtzes, T., Gongora-Nieto, M. M., Barbosa-Canovas, G. V., & Swanson, B. G. (2000). Pulsed electric fields inactivation of attached and free-living Escherichia coli and Listeria innocua under several conditions. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 54, 91–98.
Elez-Martίnez, P., & Martίn-Belloso, O. (2007). Effects of high intensity pulsed electric field processing conditions on vitamin C and antioxidant capacity of orange juice and gazpacho, a cold vegetable soup. Food Chemistry, 102, 201–209.
Elez-Martίnez, P., Aguilό-Aguayo, I., & Martίn-Belloso, O. (2006). Inactivation of orange juice peroxidase by high-intensity pulsed electric fields as influenced by process parameters. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 86, 71–81.
Eskin, N. A. M., Grossman, S., & Pinsky, A. (1977). Biochemistry of lipoxygenase in relation to food quality. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 4, 1–40.
Evrendilek, G. A., Jin, Z. T., Ruhlman, K. T., Qiu, X., Zhang, Q. H., & Richter, E. R. (2000). Microbial safety and shelf-life of apple juice and cider processed by bench and pilot scale PEF systems. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 1, 77–86.
Evrendilek, G. A., Zhang, Q. H., & Richter, E. R. (2004). Application of pulsed electric fields to skim milk inoculated with Staphylococcus aureus. Biosystems Engineering, 87, 137–144.
Fernandez-Diaz, M. D., Barsotti, L., Dumay, E., & Cheftel, J. C. (2000). Effects of pulsed electric fields on ovalbumin solutions and dialyzed egg white. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 48, 2332–2339.
Gachovska, T. K., Kumar, S., Thippareddi, H., Subbiah, J., & Williams, F. (2008). Ultraviolet and pulsed electric field treatments have additive effect on inactivation of E. coli in apple juice. Journal of Food Science, 73, M412–M417.
García, D., Somolinos, M., Hassani, M., Alvarez, I., & Pagán, R. (2009). Modeling the inactivation kinetics of Escherichia coli O157:H7 during the storage under refrigeration of apple juice treated by pulsed electric fields. Journal of Food Safety, 29, 546–563.
Geeraerd, A. H., Valdramidis, V. P., & Van Impe, J. F. (2005). GInaFiT, a freeware tool to assess non-log-linear microbial survivor curves. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 102, 95–105.
Girigowda, K., & Mulimani, V. H. (2006). Hydrolysis of galacto-oligosaccharides in soymilk by κ-carrageenan-entrapped α-galactosidase from Aspergillus oryzae. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 22, 437–442.
Heinz, V., Álvarez, I., Angersbach, A., & Knorr, D. (2001). Preservation of liquid foods by high intensity pulsed electric fields-basic concepts for process design. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 12, 103–111.
Heinz, V., Toepfl, S., & Knorr, D. (2003). Impact of temperature on lethality and energy efficiency of apple juice pasteurization by pulsed electric fields treatment. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 4, 167–175.
Huang, K., & Wang, J. (2009). Designs of pulsed electric fields treatment chambers for liquid foods pasteurization process: a review. Journal of Food Engineering, 95, 227–239.
Jaeger, H., Meneses, N., Moritz, J., & Knorr, D. (2010). Model for the differentiation of temperature and electric field effects during thermal assisted PEF processing. Journal of Food Engineering, 100, 109–118.
Kumara, V., Rania, A., Tindwanib, C., & Jainb, M. (2003). Lipoxygenase isozymes and trypsin inhibitor activities in soybean as influenced by growing location. Food Chemistry, 83, 79–83.
Li, S. Q., & Zhang, Q. H. (2004). Inactivation of E. coli 8739 in enriched soymilk using pulsed electric fields. Journal of Food Science, 69, M169–M174.
Li, S. Q., Zhang, Q. H., Lee, Y. Z., & Pham, T. V. (2003). Effects of pulsed electric fields and thermal processing on the stability of bovine immunoglobulin G (IgG) in enriched soymilk. Journal of Food Science, 68, 1201–1207.
Li, Y., Chen, Z., & Mo, H. (2007). Effects of pulsed electric fields on physicochemical properties of soybean protein isolates. LWT- Food Science and Technology, 40, 1167–1175.
Li, Y. Q., Chen, Q., Liu, X. H., & Chen, Z. X. (2008). Inactivation of soybean lipoxygenase in soymilk by pulsed electric fields. Food Chemistry, 109, 408–414.
Min, S., Jin, Z. T., & Zhang, Q. H. (2003). Commercial scale pulsed electric field processing of tomato juice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 51, 3338–3344.
Monfort, S., Gayán, E., Raso, J., Condón, S., & Álvarez, I. (2010a). Evaluation of pulsed electric fields technology for liquid whole egg pasteurization. Food Microbiology, 27, 845–852.
Monfort, S., Gayán, E., Saldaña, G., Puértolas, E., Condón, S., Raso, J., & Álvarez, I. (2010b). Inactivation of Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus by pulsed electric fields in liquid whole egg. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 11, 306–313.
Mosqueda-Melgar, J., Raybaudi-Massilia, R. M., & Martín-Belloso, O. (2008). Nonthermal pasteurization of fruit juices by combining high-intensity pulsed electric fields with natural antimicrobials. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 9, 328–340.
Mukhopadhyay, S., & Ramaswamy, R. (2011). Application of emerging technologies to control Salmonella in foods: a review. Food Research International. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2011.05.016.
Nagata, Y., Ishiwaki, M., & Sugano, M. (1982). Studies on the mechanism of antihypercholesterolemic action of soy protein-type amino acid mixtures in relation to the casein counterpart in rats. Journal of Nutrition, 112, 1614–1625.
Olsena, N. V., Grunertb, K. G., & Sonne, A. M. (2010). Consumer acceptance of high pressure processing and pulsed-electric field: a review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 21, 464–472.
Pereira, R. N., & Vicente, A. A. (2010). Environmental impact of novel thermal and non-thermal technologies in food processing. Food Research International, 43, 1936–1943.
Pothakamury, U. R., Monsalve-González, A., Barbosa-Cánovas, G. V., & Swanson, B. G. (1995). Inactivation of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus in model foods by pulsed electric field technology. Food Research International, 28, 167–171.
Pothakamury, U. R., Barbosa-Cánovas, G. V., Swanson, B. G., & Spence, K. D. (1997). Ultrastructural changes in Staphylococcus aureus treated with pulsed electric fields. Food Science and Technology, 3, 113–121.
Quitão-Teixeira, L. J., Aguiló-Aguayo, I., Ramos, A. M., & Martín-Belloso, O. (2008). Inactivation of oxidative enzymes by high-intensity pulsed electric field for retention of color in carrot juice. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1, 364–373.
Rawson, A., Patras, A., Tiwari, B. K., Noci, F., Koutchma, T., & Brunton, N. (2011). Effect of thermal and non thermal processing technologies on the bioactive content of exotic fruits and their products: review of recent advances. Food Research International, 44, 1875–1887.
Riener, J., Noci, F., Cronin, D. A., Morgan, D. J., & Lyng, J. G. (2008). Combined effect of temperature and pulsed electric fields on soya milk lipoxygenase inactivation. European Food Research and Technology, 227, 1461–1465.
Rios-Iriarte, B. J., & Barnes, R. H. (1996). The effect of overheating on certain nutritional properties of the proteins of soybean. Food Technology, 32, 836–839.
Rodrigo, D., Barbosa-Canovas, G. V., Martınez, A., & Rodrigo, M. (2003). Pectin methyl esterase and natural microflora of fresh mixed orange and carrot juice treated with pulsed electric fields. Journal of Food Protection, 66, 2336–2342.
Rodríguez-Calleja, J. M., Cebrián, G., Condón, S., & Mañas, P. (2006). Variation in resistance of natural isolates of Staphylococcus aureus to heat, pulsed electric fields and ultrasound under pressure. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 100, 1054–1062.
Saldaña, G., Puértolas, E., López, N., García, D., Álvarez, I., & Raso, J. (2009). Comparing the PEF resistance and occurrence of sublethal injury on different strains of Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus in media of pH 4 and 7. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 10, 160–165.
Saldaña, G., Puértolas, E., Condón, S., Álvarez, I., & Raso, J. (2010). Modeling inactivation kinetics and occurrence of sublethal injury of a pulsed electric field-resistant strain of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium in media of different pH. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 11, 290–298.
Sobrino-Lopez, A., Raybaudi-Massilia, R., & Martin-Belloso, O. (2006). High-Intensity pulsed electric field variables affecting Staphylococcus aureus inoculated in milk. Journal of Dairy Science, 89, 3739–3748.
Sorgentini, D. A., Wagner, J. R., & Anon, M. C. (1995). Effects of thermal treatment soy protein isolate on the characteristics and structure–function relationship of soluble and insoluble fractions. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 43, 2471–2479.
Toepfl, S., Heinz, V., & Knorr, D. (2007). High intensity pulsed electric fields applied for food preservation. Chemical Engineering and Processing, 46, 537–546.
Van Loey, A., Verachtert, B., & Hendrickx, M. (2002). Effects of high electric field pulses on enzymes. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 12, 94–102.
Walkling-Ribeiro, M., Noci, F., Riener, J., Cronin, D. A., Lyng, J. G., & Morgan, D. J. (2009). The impact of thermosonication and pulsed electric fields on Staphylococcus aureus inactivation and selected quality parameters in orange juice. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2, 422–430.
Wei, H., Saladi, R., Lu, Y., Wang, Y., Palep, S. R., Moore, J., Phelps, R., Shyong, E., & Lebwohl, M. G. (2003). Isoflavone genistein: photoprotection and clinical implications in dermatology. Journal of Nutrition, 133, 3811S–3819S.
Wouters, P. C., Alvarez, I., & Raso, J. (2001). Critical factors determining inactivation kinetics by pulsed electric field food processing. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 12, 112–121.
Xiang, B. Y., Ngadi, M. O., Ochoa-Martinez, L. A., & Simpson, M. V. (2010). Pulsed electric field-induced structural modification of whey protein isolate. Food and Bioprocess Technology. doi:10.1007/s11947-009-0266-z.
Yu, L. J., Ngadi, M., & Raghavan, V. (2010). Proteolysis of cheese slurry made from pulsed electric field-treated milk. Food and Bioprocess Technology. doi:10.1007/s11947-010-0341-5.
Zhang, Q., Chang, F. J., Barbosa-Cánovas, G. V., & Swanson, B. G. (1994). Inactivation of microorganisms in semisolid foods using high voltage pulsed electric fields. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 19, 103–118.
Zhao, W., & Yang, R. (2010). Pulsed electric field induced aggregation of food proteins: ovalbumin and bovine serum albumin. Food and Bioprocess Technology. doi:10.1007/s11947-010-0464-8.
Zhao, W., Yang, R., Lu, R., Wang, M., Qian, P., & Yang, W. (2008). Effect of PEF on microbial inactivation and physical-chemical properties of green tea extracts. LWT- Food Science and Technology, 41, 425–431.
Zimmermann, U., Pilwat, G., & Riemann, F. (1974). Dielectric breakdown of cell membranes. Biophysics of Journal, 14, 881–899.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Development Planning of Shandong Province (2010GNC10917 and 2011GGH22110) and Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2011CM039), Jinan, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, YQ., Tian, WL., Mo, HZ. et al. Effects of Pulsed Electric Field Processing on Quality Characteristics and Microbial Inactivation of Soymilk. Food Bioprocess Technol 6, 1907–1916 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-0868-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-0868-8