Abstract
Background
Soft tissue augmentation using autologous materials usually is associated with high resorption rates. To obtain more durable soft tissue filler, acellular dermal matrix (ADM) was seeded with adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) in this study.
Methods
For ADM preparation, split-thickness skin was obtained from the dorsum of two Fischer rats. Harvested skin was acellularized to obtain ADM and subsequently seeded in vitro with ASCs isolated from the same rats. Subcutaneous soft tissue augmentation was carried out in the dorsal area of 20 Fischer rats. The implant materials were ADM (group 1), ADM with ASCs (group 2), collagen type 1 gel (group 3), and collagen type 1 gel with ASCs (group 4). Each specimen was harvested after 8 weeks for quantitative evaluation of thickness, vascular density, and collagen content.
Results
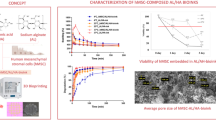
Histologic analysis showed that ASCs were successfully seeded onto ADM. The thickness of the implanted material and the vascular density were highest 8 weeks postoperatively in group 2. The subpanniculus layer became significantly thicker in group 3 than in group 4. The collagen content was significantly higher in group 2 than in the other groups.
Conclusion
These findings suggest that ADM seeded with ASCs forms the best implant material in terms of volume maintenance, vascular density, and collagen content.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman AM, Chiu ES, Bai X, Yan Y, Song YH, Newsome RE et al (2008) Human adipose-derived stem cells adhere to acellular dermal matrix. Aesthetic Plast Surg 32:698–699
Altman AM, Matthias N, Yan Y, Song YH, Bai X, Chiu ES, Slakey DP, Alt EU (2008) Dermal matrix as a carrier for in vivo delivery of human adipose-derived stem cells. Biomaterials 29:1431–1442
Altman AM, Abdul Khalek FJ, Alt EU, Butler CE (2010) Adipose tissue-derived stem cells enhance bioprosthetic mesh repair of ventral hernias. Plast Reconstr Surg 126:845–854
Barry FP, Murphy JM (2004) Mesenchymal stem cells: clinical applications and biological characterization. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:568–584
Buck DW II, Alam M, Kim JY (2009) Injectable fillers for facial rejuvenation: a review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 62:11–18
Glasberg SB, D’Amico RA (2006) Use of regenerative human acellular tissue (AlloDerm) to reconstruct the abdominal wall following pedicle TRAM flap breast reconstruction surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 118:8–15
Itoi Y, Takatori M, Hyakusoku H, Mizuno H (2010) Comparison of readily available scaffolds for adipose tissue engineering using adipose-derived stem cells. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63:858–864
Jones FR, Schwartz BM, Silverstein P (1996) Use of a nonimmunogenic acellular dermal allograft for soft tissue augmentation: a preliminary report. Aesthetic Surg J 16:196–201
Kern S, Eichler H, Stoeve J, Klüter H, Bieback K (2006) Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, or adipose tissue. Stem Cells 24:1294–1301
Kim WS, Park BS, Sung JH, Yang JM, Park SB, Kwak SJ et al (2007) Wound-healing effect of adipose-derived stem cells: a critical role of secretory factors on human dermal fibroblasts. J Dermatol Sci 48:15–24
Kim WS, Park BS, Sung JH (2009) Protective role of adipose-derived stem cells and their soluble factors in photoaging. Arch Dermatol Res 301:329–336
Kim WS, Park BS, Park SH, Kim HK, Sung JH (2009) Antiwrinkle effect of adipose-derived stem cell: activation of dermal fibroblast by secretory factors. J Dermatol Sci 53:96–102
Kirschner RE, Cabiling DS, Slemp AE, Siddiqi F, LaRossa DD, Losee JE (2006) Repair of oronasal fistulae with acellular dermal matrices. Plast Reconstr Surg 118:1431–1440
Klinger M, Marazzi M, Vigo D, Torre M (2008) Fat injection for cases of severe burn outcomes: a new perspective of scar remodeling and reduction. Aesthetic Plast Surg 32:465–469
Liu S, Zhang H, Zhang X, Lu W, Huang X, Xie H, Zhou J, Wang W, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Deng Z, Jin Y: Synergistic angiogenesis-promoting effects of extracellular matrix scaffolds and adipose-derived stem cells during wound repair. Tissue Eng Part A
Livesey SA, Herndon DN, Hollyoak MA, Atkinson YH, Nag A (1995) Transplanted acellular allograft dermal matrix: potential as a template for the reconstruction of viable dermis. Transplantation 60:1–9
Mojallal A, Lequeux C, Shipkov C, Breton P, Foyatier JL, Braye F, Damour O (2009) Improvement of skin quality after fat grafting: clinical observation and an animal study. Plast Reconstr Surg 124:765–774
Namnoum JD (2009) Expander/implant reconstruction with AlloDerm: recent experience. Plast Reconstr Surg 124:387–394
Nasir S, Aydin MA, Altuntas S, Sonmez E, Safak T (2008) Soft tissue augmentation for restoration of facial contour deformities using the free SCIA/SIEA flap. Microsurgery 28:333–338
Nie C, Yang D, Morris SF (2009) Local delivery of adipose-derived stem cells via acellular dermal matrix as a scaffold: a new promising strategy to accelerate wound healing. Med Hypotheses 72:679–682
Ogawa R, Mizuno H, Watanabe A, Migita M, Shimada T, Hyakusoku H (2004) Osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation by adipose-derived stem cells harvested from GFP transgenic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 313:871–877
Okabe K, Yamada Y, Ito K, Kohgo T, Yoshimi R, Ueda M (2009) Injectable soft-tissue augmentation by tissue engineering and regenerative medicine with human mesenchymal stromal cells, platelet-rich plasma, and hyaluronic acid scaffolds. Cytotherapy 11:307–316
Park BS, Jang KA, Sung JH et al (2008) Adipose-derived stem cells and their secretory factors as a promising therapy for skin aging. Dermatol Surg 34:1323–1326
Rehman J, Traktuev D, Li J, Merfeld-Clauss S, Temm-Grove CJ, Bovenkerk JE et al (2004) Secretion of angiogenic and antiapoptotic factors by human adipose stromal cells. Circulation 109:1292–1298
Rigotti G, Marchi A, Galie M, Baroni G, Benati D, Krampera M et al (2007) Clinical treatment of radiotherapy tissue damage by lipoaspirate transplant: a healing process mediated by adipose-derived adult stem cells. Plast Reconstr Surg 119:1409–1422 (discussion 1423–1404)
Rohrich RJ, Monheit G, Nguyen AT, Brown SA, Fagien S (2010) Soft-tissue filler complications: the important role of biofilms. Plast Reconstr Surg 125:1250–1256
Rohrich RJ, Reagan BJ, Adams WP Jr, Kenkel JM, Beran SJ (2000) Early results of vermilion lip augmentation using acellular allogeneic dermis: an adjunct in facial rejuvenation. Plast Reconstr Surg 105:409–416 (discussion 417–418)
Sclafani AP, Romo T III, Jacono AA, McCormick S, Cocker R, Parker A (2000) Evaluation of acellular dermal graft in sheet (AlloDerm) and injectable (micronized AlloDerm) forms for soft tissue augmentation: clinical observations and histological analysis. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2:130–136
Takami Y, Matsuda T, Yoshitake M, Hanumadass M, Walter RJ (1996) Dispase/detergent treated dermal matrix as a dermal substitute. Burns 22:182–190
Wainwright DJ (1995) Use of an acellular allograft dermal matrix (AlloDerm) in the management of full-thickness burns. Burns 21:243–248
Wainwright D, Madden M, Luterman A, Hunt J, Monafo W, Heimbach D et al (1996) Clinical evaluation of an acellular allograft dermal matrix in full-thickness burns. J Burn Care Rehabil 17:124–136
Wise JB, Cabiling D, Yan D, Mirza N, Kirschner RE (2007) Submucosal injection of micronized acellular dermal matrix: analysis of biocompatibility and durability. Plast Reconstr Surg 120:1156–1160
Yoo G, Lim JS (2009) Tissue engineering of injectable soft tissue filler: using adipose stem cells and micronized acellular dermal matrix. J Korean Med Sci 24:104–109
Yoshimura K, Suga H, Eto H (2009) Adipose-derived stem/progenitor cells: roles in adipose tissue remodeling and potential use for soft tissue augmentation. Regen Med 4:265–273
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, De Ugarte DA, Huang JI, Mizuno H (2002) Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell 13:4279–4295
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (c)-22592005 from the Ministry of Education, Japan.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orbay, H., Takami, Y., Hyakusoku, H. et al. Acellular Dermal Matrix Seeded with Adipose-Derived Stem Cells as a Subcutaneous Implant. Aesth Plast Surg 35, 756–763 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-011-9683-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-011-9683-2