Summary
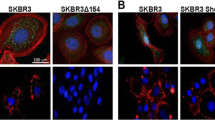
MCF-7 human breast cancer cells express E-cadherin and show, at least in some circumstances, E-cadherin-dependent cell-cell adhesion (Bracke et al., 1993). The MCF-7/AZ variant spontaneously displays E-cadherin-dependent fast aggregation; in the MCF-7/6 variant, E-cadherin appeared not to be spontaneously functional in the conditions of the fast aggregation assay, but function could be induced by incubation of the suspended cells in the presence of insulinlike growth factor I (IGF-I) (Bracke et al., 1993).
E-cadherin from MCF-7 cells was shown to contain sialic acid. Treatment with neuraminidase was shown to remove this sialic acid, as well as most of the sialic acid present at the cell surface. Applied to MCF-7/AZ, and MCF-7/6 cells, pretreatment with neuraminidase abolished spontaneous as well as IGF-I induced, E-cadherin-dependent fast cell-cell adhesion of cells in suspension, as measured in the fast aggregation assay. Treatment with neuraminidase did not, however, inhibit the possibly different, but equally E-cadherin-mediated, process of cell-cell adhesion of MCF-7 cells on a flat plastic substrate as assessed by determining the percentage of cells remaining isolated (without contact with other cells) 24 h after plating.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acheson, A.; Sunshine, J. L.; Rutishauser, U. NCAM polysialic acid can regulate both cell-cell and cell-substrate interactions. J. Cell Biol. 114:143–153; 1991.
Becker, J. W.; Erickson, H. P.; Toffman, S., et al. Topology of cell adhesion molecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:1088–1092; 1989.
Bell, G.; Dembo, M.; Bongrand, P. Cell adhesion: competition between nonspecific repulsion and specific bonding. Biophys. J. 45:1051–1064; 1984.
Blaschuk, O. W.; Sullivan, R.; David, S., et al. Identification of a cadherin cell adhesion recognition sequence. Dev. Biol. 139:227–229; 1990.
Bracke, M. E.; Van Larebeke, N. A.; Vyncke, B. M. et al. Retinoic acid modulates both invasion and plasma membrane ruffling of MCF-7 human mammary carcinoma cells in vitro. Br. J. Cancer 63:867–872; 1991.
Bracke, M. E.; Vyncke, B. M.; Bruyneel, E. A., et al. Insulinlike growth factor I activates the invasion suppressor function of E-Cadherin in MCF-7 human mammary carcinoma cells in vitro. Br. J. Cancer 68: 282–289; 1993.
Bradford, M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248–254; 1976.
Cunningham, B. A.; Leutzinger, Y.; Gallin, W. J., et al. Linear organization of the liver cell adhesion molecule L-CAM. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:5787–5791; 1984.
Deman, J.; Mareel, M.; Bruyneel, E. Effects of calcium and bound sialic acid on the viscosity of mucin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 297:486–490; 1973.
Deman, J. J.; Bruyneel, E. A.; Mareel M. M. A study on the mechanism of intercellular adhesion: Effects of neuraminidase, calcium and trypsin on the aggregation of suspended HeLa cells. J. Cell Biol. 60:641–652; 1974.
Gamallo, C.; Palacios, J.; Suarez, A., et al. Correlation of E-cadherin expression with differentiation grade and histological type in breast carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 142:987–993; 1993.
Lasky, L. A. Selectins: interpreters of cell-specific carbohydrate information during inflammation. Science 258:964–968; 1992.
Ligtenberg, M. J. L.; Buijs, F.; Vos, H. L., et al. Suppression of cellular aggregation by high levels of episialin. Cancer Res. 52:2318–2324; 1992.
Mareel, M.; Bracke, M.; Van Roy, F. Invasion promoter versus invasion suppressor molecules: the paradigm of E-cadherin. Mol. Biol. Rep. 19:45–67; 1994.
Peyrieras, N.; Louvard, D.; Jacob, F. Characterization of antigens recognized by monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies directed against uvomorulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:8067–8071; 1985.
Phillips, M. L.; Nudelman, E.; Gaeta, F. C. A., et al. ELAM-1 mediates cell adhesion by recognition of a carbohydrate ligand Sialyl-Lex. Science 250:1130–1132; 1990.
Plessers, L.; Bosmans, E.; Cox, A., et al. Specific monoclonal antibodies reacting with human breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 6:885–888; 1986.
Ringwald, M.; Schuh, R.; Vestweber, D., et al. The structure of cell adhesion molecule uvomorulin. Insights into the molecular mechanism of Ca2+-dependent cell adhesion. EMBO J. 6:3647–3653; 1987.
Rutishauser, U.; Acheson, A.; Hall, A. K., et al. The neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) as a regulator of cell-cell interactions. Science 240:53–57; 1988.
Shirayoshi, Y.; Nose, A.; Iwasaki, K., et al. N-linked oligosaccharides are not involved in the function on a cell-cell binding glycoprotein E-cadherin. Cell Struct. Funct. 11:245–252; 1986.
Simon, N.; Noel, A.; Foidart, J. M. Evaluation of in vitro reconstituted basement assay to assess the invasiveness of tumor cells. Invasion & Metastasis 12:156–167; 1992.
Springer, T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature 346:425–434; 1990.
Takeichi, M. The cadherins: cell-cell adhesion molecules controlling animal morphogenesis. Development 102:639–655; 1988.
Walz, G.; Aruffo, A.; Kolanus, W., et al. Recognition by ELAM-1 of the Sialyl-Lex determinant on myeloid and tumor cells. Science 250:1132–1135; 1990.
Warren, L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J. Biol. Chem. 234:1971–1975; 1959.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deman, J.J., van Larebeke, N.A., Bruyneel, E.A. et al. Removal of sialic acid from the surface of human MCF-7 mammary cancer cells abolishes E-cadherin-dependent cell-cell adhesion in an aggregation assay. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Animal 31, 633–639 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02634317
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02634317