Abstract
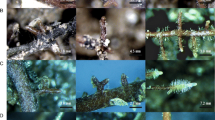
The effectiveness of 16 fungal isolates in forming ectomycorrhizas and increasing the growth and phosphorus uptake of Eucalyptus globulus Labill. and E. diversicolor F. Muell. seedlings was examined in the glasshouse. Seedlings were grown in yellow sand at 2 phosphorus levels (4 and 12 mg P kg-1 sand). At the time of harvest (100 days), the non-inoculated seedlings and seedlings inoculated with Paxillus muelleri (Berk.) Sacc. and Cortinarius globuliformis Bougher had a low level of contamination from an unknown mycorrhizal fungi. Seedlings inoculated with Thaxterogaster sp. nov. and Hysterangium inflatum Rodway had developed mycorrhizas of the superficial type whereas Hydnangium carneum Wallr. in Dietr., Hymenogaster viscidus Massee & Rodway, Hymenogaster zeylanicus Petch, Setchelliogaster sp. nov., Laccaria laccata (Scop. ex. Fr.) Berk., Scleroderma verrucosum (Vaillant) Pers., Amanita xanthocephala (Berk.) Reid & Hilton, Descolea maculata Bougher and Malajczuk and Pisolithus tinctorius (Pers.) Coker & Couch formed typical pyramidal ectomycorrhizas. The dry weight of non-inoculated and inoculated E. globulus seedlings at 12 mg P kg-1 sand did not differ, whereas several isolates caused growth depression of E. diversicolor. By contrast, at 4 mg P kg-1 sand growth increases ranged from 0–13 times above that of non-inoculated seedlings. P. tinctorius produced the largest growth increase on both eucalypt species. In general, isolates which developed more extensive mycorrhizas on roots produced the largest growth responses to inoculation. Isolates which increased plant growth also increased phosphorus uptake by the plant. Seedlings inoculated with L. laccata and S. verrucosum retained more phosphorus in their roots than plants inoculated with the other fungal isolates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott L K and Robson A D 1984 Formation of external hyphae in soil by four species of versicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 99, 245–255.
Bethlenfalvay G J, Bayne H G and Pacovsky R S 1983 Parasitic and mutualistic associations between mycorrhizal fungus and soybean: The effect of phosphorus on host plant-endophyte interactions. Physiol. Plant. 57, 543–548.
Bougher N L, Grove T S and Malajczuk N 1990 Growth and phosphorus acquisition of karri (Eucalyptus diversicolor) seedlings inoculated with ectomycorrhizal fungi in relation to soil phosphorus supply. New Phytol. 114, 77–85.
Chilvers G A 1973 Host range of some eucalypt mycorrhizal fungi. Aust. J. Bot. 21, 103–111.
Daughteridge A T, Pallardy S G, Garrett H G and Sanders I L 1986 Growth analysis of mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal black oak (Quercus velutina Lam) seedlings. New Phytol. 103, 473–480.
Duncan D B 1955 Multiple range and multiple F-tests. Biometrics 11, 1–24.
Ford V L, Torbert J L, Burger J A and Miller O K 1985 Comparative effects of four mycorrhizal fungi on Loblolly pine seedlings growing in a greenhouse in Piedmont soil. Plant and Soil 83, 215–221.
Harley J E and Smith S E 1983 Mycorrhizal Symbiosis. Academic Press, London. 483 p.
Heinrich P A and Patrick J W 1986 Phosphorus accumulation in the soil-root system of Eucalyptus pilularis Sm. seedlings. II. The effect of ectomycorrhizas on the pattern of phosphorus acquisition. Aust. J. Bot. 34, 445–454.
Heinrich P A, Mulligan D R and Patrick J W 1988 The effect of ectomycorrhizas on the phosphorus and dry weight acquisition of Eucalyptus seedlings. Plant and Soil 109, 147–149.
Lapeyrie F F, Chilvers G A and Douglas P A 1984 Formation of metachromatic granules following phosphorus uptake by mycelial hyphae of an ectomycorrhizal fungus. New Phytol. 98, 345–360.
Malajczuk N, McComb A J and Loneragan J F 1975 Phosphorus uptake and growth of mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal seedlings of Eucalyptus calophylla R. Br. Aust. J. Bot. 23, 231–238.
Malajczuk N, Dell B and Bougher N L 1987 Ectomycorrhizal formation in Eucalyptus. III. Superficial ectomycorrhizas initiated by Hysterangium and Cortinarius species. New Phytol. 105, 421–428.
Martin F, Marchal J P, Timiniska A and Carnet D 1985 The metabolism and physical state of polyphosphates in ectomycorrhizal fungi: A 31P nuclear magnetic resonance study. New Phytol. 101, 275–290.
Marx D H 1969 The influence of ectotrophic mycorrhizal fungi on the resistance of pine roots to pathogenic infection. I. Antagonism of mycorrhizal fungi to root pathogenic fungi and soil bacteria. Phytopathology 59, 153–163.
Mulligan D R and Patrick J W 1985 Growth and phosphorus partitioning in Eucalyptus pilularis Smith seedlings raised in phosphorus deficient soil. Aust. J. Bot. 33, 245–259.
Newman E I 1966 A method for estimating the total root length in a sample. J. Appl. Ecol. 3, 139–145.
Rousseau J V D and Reid C P P 1990 Effects of phosphorus and ectomycorrhizas on the carbon balance of Loblolly pine seedling. For. Sci. 36, 101–112.
Thomson B D, Robson A D and Abbott L K 1986 Effects of phosphorus on the formation of mycorrhizas by Gigaspora calospora and Glomus fasciculatum in relation to root carbohydrates. New. Phytol. 103, 751–765.
Wild A. (1957) The phosphate content of Australian soils. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 9, 194–204.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burgess, T.I., Malajczuk, N. & Grove, T.S. The ability of 16 ectomycorrhizal fungi to increase growth and phosphorus uptake of Eucalyptus globulus Labill. and E. diversicolor F. Muell.. Plant Soil 153, 155–164 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00012988
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00012988