Summary
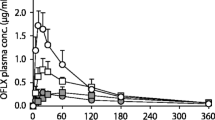
All tetracycline derivatives are bacteriostatics and their concentration in serum should not fall during the therapy below the generally accepted minimum therapeutic concentration of 0.5 to 1.5μg/ml.
Tetracyclines have a high affinity to form chelates with polyvalent metallic cations such as Fe+++, Fe++, At+++, Mg++ and Ca++. Many of these tetracyclinemetal complexes are either insoluble or otherwise poorly absorbable from the gastrointestinal tract. Milk and other dairy products, antacids containing polyvalent cations, as well as various iron salts ingested simultaneously with tetracycline derivatives, might interfere with their absorption by 50 to 90% or even more. The severity of interaction depends both on the nature of the tetracycline derivative and of the cation, on the doses used, on pharmaceutical factors, and on time schedules in dosing. An interval of 3 hours between the ingestion of tetracyclines and cations prevents the interaction.
The pharmacokinetic interactions in absorption of tetracyclines are likely to be clinically significant in cases where the infecting pathogens are moderately resistant to tetracyclines and relatively high serum concentrations are needed for proper bacteriostasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert, A.: Avidity of Terramycin and Aureomycin for metallic cations. Nature 172: 201 (1953)
Albert, A. and Rees, C.W.: Avidity of the tetracyclines for the cations of metals. Nature 177: 433–434 (1956)
Ball, A.P.; Gray, J.A. and Murdoch, J.McC: Antibacterial drugs today: I. Drugs 10: 1–55 (1975)
Barr, W.H.; Adir, J. and Garrettson, L.: Decrease of tetracycline absorption in man by sodium bicarbonate. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 12: 779–784 (1971)
Brise, H. and Hallberg, L.: Absorbability of different iron compounds. Acta Medica Scandinavica 171 (Suppl. 376): 23–37 (1962)
Brumfitt, W. and Hamilton-Miller, J.M.T.: The place of antibiotic prophylaxis in medicine. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1: 163–169 (1975)
Chin, T.-F. and Lach, J.L.: Drug diffusion and bioavailability: Tetracycline-metallic chelation. American Journal of Hospital Pharmacy 32: 625–629 (1975)
Edlund, A. and Gnarpe, H.: Interaktion mellan järn och två tetracyclinpreparat vid behandling av patienter med bronko-pulmonella infektioner. Läkartidningen 68 (Suppl. 3): 22–24 (1971)
Gothoni, G.: Neuvonen, P.J.; Mattila, M. and Hackman, R.: Iron-tetracycline interaction: Effect of time interval between the drugs. Acta Medica Scandinavica 191: 409–411(1972)
Gothoni, G.; Pentikäinen, P.; Vapaatalo, H.I.; Hackman, R. and Björksten, K.: Absorption of antibiotics: Influence of metoclopramide and atropine on serum levels of pivampicillin and tetracycline. Annals of Clinical Research 4: 228–232 (1972)
Greenberger, N.J.: Absorption of tetracyclines: Interference by iron. Annals of Internal Medicine 74: 792–793 (1971)
Greenberger, N.J.: Effects of antibiotics and other agents on the intestinal transport of iron. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 26: 104–112 (1973)
Greenberger, N.J.; Rubbert, R.D. and Cuppage, F.E.: Inhibition of intestinal iron transport induced by tetracycline. Gastroenterology 53: 590–597 (1967)
Harcourt, R.S. and Hamburger, M.: The effect of magnesium sulfate in lowering tetracycline blood levels. Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine 50: 464–468 (1957)
Heinrich, H.C. and Oppitz, K.H.: Tetracycline inhibits iron absorption in man. Die Naturwissenschaften 60: 524–525(1973)
Heinrich, H.C; Oppitz, K.H. and Gabbe, E.E.: Hemmung der Eisenabsorption beim Menschen durch Tetracyclin. Klinische Wochenschrift 52: 493–498 (1974)
Hägermark, Ö. and Höglund, S.: Iron metabolism in tetracycline-treated acne patients. Acta Dermato-Venereologica (Stockholm) 54: 45–48 (1974)
Jaffe, J.M.; Colaizzi, J.L.; Poust, R.J. and McDonald,Jr., R.H.: Effect of altered urinary pH on tetracycline and doxycycline excretion in humans. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 1: 267–282 (1973)
Kohn, K.W.: Mediation of divalent metal ions in the binding of tetracycline to macromolecules. Nature 191: 1156–1158(1961)
Kucers, A.: Tetracyclines; in The Use of Antibiotics, p.271–306 (William Heinemann, London 1972)
Mattila, M.J.; Neuvonen, P.J.; Gothoni, G. and Hackman, C.R.: Interference of iron preparations and milk with the absorption of tetracyclines; in Exerpta Medica International Congress Series No. 254: Toxicological Problems of Drug Combinations, p.128-133 (1972)
Neuvonen, P.J.; Gothoni, G.; Hackman, R. and Björksten, K.: Interference of iron with the absorption of tetracyclines in man. British Medical Journal 4: 532–534 (1970)
Neuvonen, P.J.; Pentikäinen, P.J. and Gothoni, G.: Inhibition of iron absorption by tetracycline. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2: 94–96 (1975)
Neuvonen, P.J. and Penttilä, O.: Interaction between doxycycline and barbiturates. British Medical Journal 1:535–536 (1974)
Neuvonen, P.J. and Penttilä, O.: Effect of oral ferrous sulphate on the half-life of doxycycline in man. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 7: 361 (1974)
Neuvonen, P.J. and Turakka, H.: Inhibitory effect of various iron salts on the absorption of tetracycline in man. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 7: 357–360 (1974)
Penttilä, O.; Neuvonen, P.J.; Aho, K. and Lehtovaara, R.: Interaction between doxycycline and some antiepileptic drugs. British Medical Journal 2: 470–472 (1974)
Rosenblatt, J.E.; Barrett, J.E.; Brodie, J.L. and Kirby, W.M.M.: Comparison of in vitro activity and clinical pharmacology of doxycydine with other tetracyclines; in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, p.134-141 (1966)
Schach von Wittenau, M.: Some pharmacokinetic aspects of doxycydine metabolism in man. Chemotherapy 13 (Suppl.): 41–50 (1968)
Scheiner, J. and Altemeier, W.A.: Experimental study of factors inhibiting absorption and effective therapeutic levels of declomycin. Surgery, Gynecology and Obstetrics 114: 9–14 (1962)
Steigbigel, N.H.; Reed, C.W. and Finland, M.: Susceptibility of common pathogenic bacteria to seven tetracydine antibiotics in vitro. American Journal of Medical Sciences 255: 179–195 (1968)
Sweeney, W.M.; Hardy, S.M.; Dornbush, A.C. and Ruegsegger, J.M.: Absorption of tetracydine in human beings as affected by certain exdpients. Antibiotic Medicine and Clinical Therapy 4: 642–656 (1957)
Waisbren, B.A. and Hueckel, J.S.: Reduced absorption of Aureomycin caused by aluminium hydroxide gel (Amphojel). Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine 73: 73–74 (1950)
Walter, A.M. and Heilmeyer, L.: Tetracycline; in Antibiotika Fibel, 3rd ed p.260–297 (Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 1969)
Weinberg, E.D.: The mutual effects of antimicrobial compounds and metallic cations. Bacteriological Reviews 21:46–68(1957)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neuvonen, P.J. Interactions with the Absorption of Tetracyclines. Drugs 11, 45–54 (1976). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-197611010-00004
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-197611010-00004