Abstract
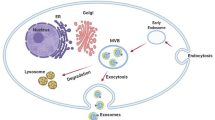
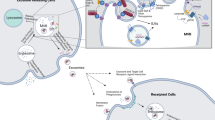
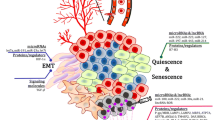
Exosomes are very small extracellular vesicles secreted by cells to local and distant tissues. These mini signal transporters elicit acute and chronic effects on recipient cells. Studies regarding exosomes and their relationship to disease, as well as healthy functions, are eliciting extraordinary excitement as data pours in from groups around the world. Reporting of exosome biogenesis, selective loading of cargo, directed release, and resulting changes in adjacent and distal cells are providing information that is changing the way we view cancer progression and treatment. As a result, the properties of exosomes are being exploited for diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic applications. First, by referring to the signaling molecules carried by exosomes, they are being tested as indicators of the presence of transformed cells in early stages of cancer. Secondly, the cargo of exosomes secreted from tumors have been linked to prognostic factors and metastatic properties. Thirdly, exosome-based therapies are being developed which utilize the inherent properties of these mini-transporters to affect and interfere with cancer. Exosome creation, loading, and release plays an important role in cancer formation, progression and organotropic metastasis. The developed and developing therapies should be considered with understanding of their advantages and pitfalls, as well as the various roles exosomes play in normal and pathogenic processes. The combination of previously discovered attributes of exosomes with new discoveries occurring daily provide valuable and additive relevant factors to be considered as we embark on the continued discovery of exosomes and their relationship to cancer diagnostics and therapeutics.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kucharzewska P, Belting M. Emerging roles of extracellular vesicles in the adaptive response of tumour cells to microenvironmental stress. J Extracell Vesicles. 2013. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v2i0.20304.
Meckes DG Jr. Exosomal communication goes viral. J Virol. 2015;89(10):5200–3. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02470-14.
Barteneva NS, Maltsev N, Vorobjev IA. Microvesicles and intercellular communication in the context of parasitism. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013;3:49. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2013.00049.
Baranyai T, Herczeg K, Onódi Z, Voszka I, Módos K, Marton N, et al. Isolation of exosomes from blood plasma: qualitative and quantitative comparison of ultracentrifugation and size exclusion chromatography methods. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0145686. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0145686.
Bard MP, Hegmans JP, Hemmes A, Luider TM, Willemsen R, Severijnen LA, et al. Proteomic analysis of exosomes isolated from human malignant pleural effusions. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2004;31(1):114–21. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2003-0238OC.
Andre F, Schartz NE, Movassagh M, Flament C, Pautier P, Morice P, et al. Malignant effusions and immunogenic tumour-derived exosomes. Lancet. 2002;360(9329):295–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(02)09552-1.
Keller S, Sanderson MP, Stoeck A, Altevogt P. Exosomes: from biogenesis and secretion to biological function. Immunol Lett. 2006;107(2):102–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2006.09.005.
Lawson C, Vicencio JM, Yellon DM, Davidson SM. Microvesicles and exosomes: new players in metabolic and cardiovascular disease. J Endocrinol. 2016;228(2):R57–71. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-15-0201.
Costa-Silva B, Aiello NM, Ocean AJ, Singh S, Zhang H, Thakur BK, et al. Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat Cell Biol. 2015;17(6):816–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3169.
Kahlert C, Kalluri R. Exosomes in tumor microenvironment influence cancer progression and metastasis. J Mol Med (Berl). 2013;91(4):431–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-013-1020-6.
Hornick NI, Huan J, Doron B, Goloviznina NA, Lapidus J, Chang BH, et al. Serum exosome MicroRNA as a minimally-invasive early biomarker of AML. Sci Rep. 2015;5:11295. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11295.
De Toro J, Herschlik L, Waldner C, Mongini C. Emerging roles of exosomes in normal and pathological conditions: new insights for diagnosis and therapeutic applications. Front Immunol. 2015;6:203. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00203.
Trams EG, Lauter CJ, Salem N Jr, Heine U. Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981;645(1):63–70.
Beach A, Zhang HG, Ratajczak MZ, Kakar SS. Exosomes: an overview of biogenesis, composition and role in ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res. 2014;7:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1757-2215-7-14.
Colombo M, Raposo G, Thery C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30:255–89. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101512-122326.
Kalra H, Drummen GP, Mathivanan S. Focus on extracellular vesicles: introducing the next small big thing. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(2):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020170.
Hanson PI, Shim S, Merrill SA. Cell biology of the ESCRT machinery. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21(4):568–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2009.06.002.
Mayers JR, Audhya A. Vesicle formation within endosomes: an ESCRT marks the spot. Commun Integr Biol. 2012;5(1):50–6.
Trajkovic K, Hsu C, Chiantia S, Rajendran L, Wenzel D, Wieland F, et al. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science. 2008;319(5867):1244–7. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1153124.
Stuffers S, Sem Wegner C, Stenmark H, Brech A. Multivesicular endosome biogenesis in the absence of ESCRTs. Traffic. 2009;10(7):925–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.00920.x.
Baietti MF, Zhang Z, Mortier E, Melchior A, Degeest G, Geeraerts A, et al. Syndecan-syntenin-ALIX regulates the biogenesis of exosomes. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14(7):677–85. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2502.
Roucourt B, Meeussen S, Bao J, Zimmermann P, David G. Heparanase activates the syndecan-syntenin-ALIX exosome pathway. Cell Res. 2015;25(4):412–28. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2015.29.
Zhang J, Li S, Li L, Li M, Guo C, Yao J, et al. Exosome and exosomal MicroRNA: trafficking, sorting, and function. Genom Proteom Bioinf. 2015;13(1):17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2015.02.001.
de Gassart A, Geminard C, Hoekstra D, Vidal M. Exosome secretion: the art of reutilizing nonrecycled proteins? Traffic. 2004;5(11):896–903. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2004.00223.x.
Raiborg C, Stenmark H. The ESCRT machinery in endosomal sorting of ubiquitylated membrane proteins. Nature. 2009;458(7237):445–52. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07961.
Tamai K, Tanaka N, Nakano T, Kakazu E, Kondo Y, Inoue J, et al. Exosome secretion of dendritic cells is regulated by Hrs, an ESCRT-0 protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;399(3):384–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.07.083.
Colombo M, Moita C, van Niel G, Kowal J, Vigneron J, Benaroch P, et al. Analysis of ESCRT functions in exosome biogenesis, composition and secretion highlights the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J Cell Sci. 2013;126(Pt 24):5553–65. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.128868.
Hurley JH, Odorizzi G. Get on the exosome bus with ALIX. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14(7):654–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2530.
Nabhan JF, Hu R, Oh RS, Cohen SN, Lu Q. Formation and release of arrestin domain-containing protein 1-mediated microvesicles (ARMMs) at plasma membrane by recruitment of TSG101 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109(11):4146–51. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1200448109.
Stahelin RV, Long F, Diraviyam K, Bruzik KS, Murray D, Cho W. Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate induces the membrane penetration of the FYVE domains of Vps27p and Hrs. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(29):26379–88. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M201106200.
Teo H, Gill DJ, Sun J, Perisic O, Veprintsev DB, Vallis Y, et al. ESCRT-I core and ESCRT-II GLUE domain structures reveal role for GLUE in linking to ESCRT-I and membranes. Cell. 2006;125(1):99–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.01.047.
Ghossoub R, Lembo F, Rubio A, Gaillard CB, Bouchet J, Vitale N, et al. Syntenin-ALIX exosome biogenesis and budding into multivesicular bodies are controlled by ARF6 and PLD2. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3477. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4477.
Perez-Hernandez D, Gutierrez-Vazquez C, Jorge I, Lopez-Martin S, Ursa A, Sanchez-Madrid F, et al. The intracellular interactome of tetraspanin-enriched microdomains reveals their function as sorting machineries toward exosomes. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(17):11649–61. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.445304.
Harding C, Heuser J, Stahl P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983;97(2):329–39.
Pan BT, Teng K, Wu C, Adam M, Johnstone RM. Electron microscopic evidence for externalization of the transferrin receptor in vesicular form in sheep reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1985;101(3):942–8.
Barr F, Lambright DG. Rab GEFs and GAPs. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010;22(4):461–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2010.04.007.
Stenmark H. Rab GTPases as coordinators of vesicle traffic. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10(8):513–25. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2728.
Ostrowski M, Carmo NB, Krumeich S, Fanget I, Raposo G, Savina A, et al. Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12(1):19–30. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2000.
Hoshino D, Kirkbride KC, Costello K, Clark ES, Sinha S, Grega-Larson N, et al. Exosome secretion is enhanced by invadopodia and drives invasive behavior. Cell Rep. 2013;5(5):1159–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2013.10.050.
Martin-Cofreces NB, Baixauli F, Sanchez-Madrid F. Immune synapse: conductor of orchestrated organelle movement. Trends Cell Biol. 2014;24(1):61–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2013.09.005.
Record M, Carayon K, Poirot M, Silvente-Poirot S. Exosomes as new vesicular lipid transporters involved in cell-cell communication and various pathophysiologies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1841(1):108–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.10.004.
Hsu C, Morohashi Y, Yoshimura S, Manrique-Hoyos N, Jung S, Lauterbach MA, et al. Regulation of exosome secretion by Rab35 and its GTPase-activating proteins TBC1D10A-C. J Cell Biol. 2010;189(2):223–32. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200911018.
Raposo G, Nijman HW, Stoorvogel W, Liejendekker R, Harding CV, Melief CJ, et al. B lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J Exp Med. 1996;183(3):1161–72.
Zitvogel L, Regnault A, Lozier A, Wolfers J, Flament C, Tenza D, et al. Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine: dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Nat Med. 1998;4(5):594–600.
van Niel G, Raposo G, Candalh C, Boussac M, Hershberg R, Cerf-Bensussan N, et al. Intestinal epithelial cells secrete exosome-like vesicles. Gastroenterology. 2001;121(2):337–49.
Wolfers J, Lozier A, Raposo G, Regnault A, Thery C, Masurier C, et al. Tumor-derived exosomes are a source of shared tumor rejection antigens for CTL cross-priming. Nat Med. 2001;7(3):297–303. https://doi.org/10.1038/85438.
Thery C, Zitvogel L, Amigorena S. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2(8):569–79. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri855.
Théry C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, Clayton A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Current protocols in cell biology. New York: Wiley; 2001.
Steinbichler TB, Dudas J, Riechelmann H, Skvortsova II. The role of exosomes in cancer metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2017;44:170–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.02.006.
Fitzner D, Schnaars M, van Rossum D, Krishnamoorthy G, Dibaj P, Bakhti M, et al. Selective transfer of exosomes from oligodendrocytes to microglia by macropinocytosis. J Cell Sci. 2011;124(Pt 3):447–58. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.074088.
Fruhbeis C, Frohlich D, Kuo WP, Kramer-Albers EM. Extracellular vesicles as mediators of neuron-glia communication. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013;7:182. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2013.00182.
Morelli AE, Larregina AT, Shufesky WJ, Sullivan ML, Stolz DB, Papworth GD, et al. Endocytosis, intracellular sorting, and processing of exosomes by dendritic cells. Blood. 2004;104(10):3257–66. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-03-0824.
Nazarenko I, Rana S, Baumann A, McAlear J, Hellwig A, Trendelenburg M, et al. Cell surface tetraspanin Tspan8 contributes to molecular pathways of exosome-induced endothelial cell activation. Cancer Res. 2010;70(4):1668–78. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2470.
Saunderson SC, Dunn AC, Crocker PR, McLellan AD. CD169 mediates the capture of exosomes in spleen and lymph node. Blood. 2014;123(2):208–16. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-03-489732.
Christianson HC, Svensson KJ, van Kuppevelt TH, Li JP, Belting M. Cancer cell exosomes depend on cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans for their internalization and functional activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(43):17380–5. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1304266110.
Palma J, Yaddanapudi SC, Pigati L, Havens MA, Jeong S, Weiner GA, et al. MicroRNAs are exported from malignant cells in customized particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(18):9125–38. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks656.
Sreekumar PG, Kannan R, Kitamura M, Spee C, Barron E, Ryan SJ, et al. alphaB crystallin is apically secreted within exosomes by polarized human retinal pigment epithelium and provides neuroprotection to adjacent cells. PLoS One. 2010;5(10):e12578. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0012578.
Tauro BJ, Greening DW, Mathias RA, Mathivanan S, Ji H, Simpson RJ. Two distinct populations of exosomes are released from LIM1863 colon carcinoma cell-derived organoids. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013;12(3):587–98. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M112.021303.
Gyorgy B, Szabo TG, Pasztoi M, Pal Z, Misjak P, Aradi B, et al. Membrane vesicles, current state-of-the-art: emerging role of extracellular vesicles. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011;68(16):2667–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0689-3.
Taylor DD, Shah S. Methods of isolating extracellular vesicles impact down-stream analyses of their cargoes. Methods. 2015;87:3–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.02.019.
Witwer KW, Buzas EI, Bemis LT, Bora A, Lasser C, Lotvall J, et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J Extracell Vesicles. 2013. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v2i0.20360.
Böing AN, van der Pol E, Grootemaat AE, Coumans FAW, Sturk A, Nieuwland R. Single-step isolation of extracellular vesicles by size-exclusion chromatography. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v3.23430.
Momen-Heravi F, Balaj L, Alian S, Trachtenberg AJ, Hochberg FH, Skog J, et al. Impact of biofluid viscosity on size and sedimentation efficiency of the isolated microvesicles. Fronti Physiol. 2012;3:162. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2012.00162.
Théry C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, Clayton A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;3:22. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471143030.cb0322s30.
Zarovni N, Corrado A, Guazzi P, Zocco D, Lari E, Radano G, et al. Integrated isolation and quantitative analysis of exosome shuttled proteins and nucleic acids using immunocapture approaches. Methods. 2015;87:46–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.05.028.
Gardiner C, Di Vizio D, Sahoo S, Théry C, Witwer KW, Wauben M, et al. Techniques used for the isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles: results of a worldwide survey. J Extracell Vesicles. 2016;5(1):32945. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v5.32945.
Li P, Kaslan M, Lee SH, Yao J, Gao Z. Progress in exosome isolation techniques. Theranostics. 2017;7(3):789–804. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.18133.
Rood IM, Deegens JK, Merchant ML, Tamboer WP, Wilkey DW, Wetzels JF, et al. Comparison of three methods for isolation of urinary microvesicles to identify biomarkers of nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int. 2010;78(8):810–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2010.262.
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, Lotvall JO. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1596.
Johnsen KB, Gudbergsson JM, Skov MN, Pilgaard L, Moos T, Duroux M. A comprehensive overview of exosomes as drug delivery vehicles—endogenous nanocarriers for targeted cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1846(1):75–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2014.04.005.
Alvarez ML, Khosroheidari M, Kanchi Ravi R, DiStefano JK. Comparison of protein, microRNA, and mRNA yields using different methods of urinary exosome isolation for the discovery of kidney disease biomarkers. Kidney Int. 2012;82(9):1024–32. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2012.256.
Li M, Zeringer E, Barta T, Schageman J, Cheng A, Vlassov AV. Analysis of the RNA content of the exosomes derived from blood serum and urine and its potential as biomarkers. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014;369(1652):20130502. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2013.0502.
Neurauter A, Kullmann A, Kierulf B, Oksvold MP, Pedersen KW. Magnetic beads for fast and reproducible isolation/characterization of exosomes based on surface protein expression. Institute for Cancer Research, Oslo University Hospital: Life Technologies; 2013. https://assets.thermofisher.com/TFS-Assets/CMD/posters/Exosome-poster-ISEV-2013-Boston.pdf. Accessed 15 Feb 2019.
Tauro BJ, Greening DW, Mathias RA, Ji H, Mathivanan S, Scott AM, et al. Comparison of ultracentrifugation, density gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods for isolating human colon cancer cell line LIM1863-derived exosomes. Methods. 2012;56(2):293–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.01.002.
Koliha N, Wiencek Y, Heider U, Jungst C, Kladt N, Krauthauser S, et al. A novel multiplex bead-based platform highlights the diversity of extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. 2016;5:29975. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v5.29975.
Chen C, Skog J, Hsu CH, Lessard RT, Balaj L, Wurdinger T, et al. Microfluidic isolation and transcriptome analysis of serum microvesicles. Lab Chip. 2010;10(4):505–11. https://doi.org/10.1039/b916199f.
Wu M, Ouyang Y, Wang Z, Zhang R, Huang P-H, Chen C, et al. Isolation of exosomes from whole blood by integrating acoustics and microfluidics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114(40):10584–9. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1709210114.
Enderle D, Spiel A, Coticchia CM, Berghoff E, Mueller R, Schlumpberger M, Sprenger-Haussels M, Shaffer JM, Lader E, Skog J, Noerholm M. Characterization of RNA from exosomes and other extracellular vesicles isolated by a novel spin column-based method. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0136133. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0136133.
Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200(4):373–83. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201211138.
Gámez-Valero A, Monguió-Tortajada M, Carreras-Planella L, Franquesa ML, Beyer K, Borràs FE. Size-exclusion chromatography-based isolation minimally alters extracellular vesicles’ characteristics compared to precipitating agents. Sci Rep. 2016;6:33641. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep33641.
Lobb RJ, Becker M, Wen SW, Wong CS, Wiegmans AP, Leimgruber A, et al. Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:27031. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v4.27031.
Muller L, Hong CS, Stolz DB, Watkins SC, Whiteside TL. Isolation of biologically-active exosomes from human plasma. J Immunol Methods. 2014;411:55–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2014.06.007.
Nordin JZ, Lee Y, Vader P, Mager I, Johansson HJ, Heusermann W, et al. Ultrafiltration with size-exclusion liquid chromatography for high yield isolation of extracellular vesicles preserving intact biophysical and functional properties. Nanomedicine. 2015;11(4):879–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2015.01.003.
Hagel LÖM, Andersson T. Apparent pore size distributions of chromatography media. J Chrom A. 1996;743:33–42.
Williams AHL. Column handbook for size exclusion chromatography. Philadelphia: Academic Press; 1999.
O’Brien JR. Cell membrane damage, platelet stickiness and some effects of aspirin. Br J Haematol. 1969;17(6):610–1.
Ogawa Y, Kanai-Azuma M, Akimoto Y, Kawakami H, Yanoshita R. Exosome-like vesicles with dipeptidyl peptidase IV in human saliva. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008;31(6):1059–62.
Sokolova V, Ludwig AK, Hornung S, Rotan O, Horn PA, Epple M, et al. Characterisation of exosomes derived from human cells by nanoparticle tracking analysis and scanning electron microscopy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2011;87(1):146–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.05.013.
Taylor DD, Chou IN, Black PH. Isolation of plasma membrane fragments from cultured murine melanoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983;113(2):470–6.
Taylor DD, Zacharias W, Gercel-Taylor C. Exosome isolation for proteomic analyses and RNA profiling. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;728:235–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-068-3_15.
Pietrowska M, Funk S, Gawin M, Marczak Ł, Abramowicz A, Widłak P, et al. Isolation of exosomes for the purpose of protein cargo analysis with the use of mass spectrometry. In: Kaufmann M, Klinger C, Savelsbergh A, editors. Functional genomics: methods and protocols. New York: Springer; 2017. p. 291–307.
Worst TS, von Hardenberg J, Gross JC, Erben P, Schnölzer M, Hausser I, et al. Database-augmented mass spectrometry analysis of exosomes identifies claudin 3 as a putative prostate cancer biomarker. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017;16(6):998–1008. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M117.068577.
Haraszti RA, Didiot M-C, Sapp E, Leszyk J, Shaffer SA, Rockwell HE, et al. High-resolution proteomic and lipidomic analysis of exosomes and microvesicles from different cell sources. J Extracell Vesicles. 2016;5:32570. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v5.32570.
Yang J, Hagen J, Guntur KV, Allette K, Schuyler S, Ranjan J, et al. A next generation sequencing based approach to identify extracellular vesicle mediated mRNA transfers between cells. BMC Genomics. 2017;18(1):987. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-4359-1.
Ogawa Y, Tsujimoto M, Yanoshita R. Next-generation sequencing of protein-coding and long non-protein-coding RNAs in two types of exosomes derived from human whole saliva. Biol Pharm Bull. 2016;39(9):1496–507. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b16-00297.
Jenjaroenpun P, Kremenska Y, Nair VM, Kremenskoy M, Joseph B, Kurochkin IV. Characterization of RNA in exosomes secreted by human breast cancer cell lines using next-generation sequencing. PeerJ. 2013;1:e201. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.201.
Vong S, Kalluri R. The role of stromal myofibroblast and extracellular matrix in tumor angiogenesis. Genes Cancer. 2011;2(12):1139–45. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947601911423940.
Webber JP, Spary LK, Sanders AJ, Chowdhury R, Jiang WG, Steadman R, et al. Differentiation of tumour-promoting stromal myofibroblasts by cancer exosomes. Oncogene. 2015;34(3):290–302. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.560.
Orimo A, Gupta PB, Sgroi DC, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Delaunay T, Naeem R, et al. Stromal fibroblasts present in invasive human breast carcinomas promote tumor growth and angiogenesis through elevated SDF-1/CXCL12 secretion. Cell. 2005;121(3):335–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.02.034.
Skog J, Wurdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer DH, Gainche L, Curry WT, et al. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(12):1470–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1800.
Brentnall TA, Lai LA, Coleman J, Bronner MP, Pan S, Chen R. Arousal of cancer-associated stroma: overexpression of palladin activates fibroblasts to promote tumor invasion. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30219. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030219.
Webber J, Steadman R, Mason MD, Tabi Z, Clayton A. Cancer exosomes trigger fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation. Cancer Res. 2010;70(23):9621–30. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1722.
Luga V, Wrana JL. Tumor-stroma interaction: revealing fibroblast-secreted exosomes as potent regulators of Wnt-planar cell polarity signaling in cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 2013;73(23):6843–7. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1791.
Park JE, Tan HS, Datta A, Lai RC, Zhang H, Meng W, et al. Hypoxic tumor cell modulates its microenvironment to enhance angiogenic and metastatic potential by secretion of proteins and exosomes. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010;9(6):1085–99. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M900381-MCP200.
Min L, Shen J, Tu C, Hornicek F, Duan Z. The roles and implications of exosomes in sarcoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016;35(3):377–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-016-9630-4.
You Y, Shan Y, Chen J, Yue H, You B, Shi S, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 13-containing exosomes promote nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis. Cancer Sci. 2015;106(12):1669–77. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.12818.
Borsig L, Wong R, Feramisco J, Nadeau DR, Varki NM, Varki A. Heparin and cancer revisited: mechanistic connections involving platelets, P-selectin, carcinoma mucins, and tumor metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98(6):3352–7. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.061615598.
Nieswandt B, Hafner M, Echtenacher B, Mannel DN. Lysis of tumor cells by natural killer cells in mice is impeded by platelets. Cancer Res. 1999;59(6):1295–300.
Labelle M, Begum S, Hynes RO. Direct signaling between platelets and cancer cells induces an epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and promotes metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2011;20(5):576–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2011.09.009.
Karpatkin S, Pearlstein E, Ambrogio C, Coller BS. Role of adhesive proteins in platelet tumor interaction in vitro and metastasis formation in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1988;81(4):1012–9. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI113411.
Sierko E, Wojtukiewicz MZ. Inhibition of platelet function: does it offer a chance of better cancer progression control? Semin Thromb Hemost. 2007;33(7):712–21. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-991540.
Dean WL, Lee MJ, Cummins TD, Schultz DJ, Powell DW. Proteomic and functional characterisation of platelet microparticle size classes. Thromb Haemost. 2009;102(4):711–8. https://doi.org/10.1160/TH09-04-243.
Dovizio M, Alberti S, Sacco A, Guillem-Llobat P, Schiavone S, Maier TJ, et al. Novel insights into the regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by platelet-cancer cell cross-talk. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015;43(4):707–14. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20140322.
Gay LJ, Felding-Habermann B. Platelets alter tumor cell attributes to propel metastasis: programming in transit. Cancer Cell. 2011;20(5):553–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2011.11.001.
Matsumoto Y, Kano M, Akutsu Y, Hanari N, Hoshino I, Murakami K, et al. Quantification of plasma exosome is a potential prognostic marker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2016;36(5):2535–43. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2016.5066.
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105(30):10513–8. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804549105.
Silva J, Garcia V, Rodriguez M, Compte M, Cisneros E, Veguillas P, et al. Analysis of exosome release and its prognostic value in human colorectal cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2012;51(4):409–18.
Logozzi M, De Milito A, Lugini L, Borghi M, Calabro L, Spada M, et al. High levels of exosomes expressing CD63 and caveolin-1 in plasma of melanoma patients. PLoS One. 2009;4(4):e5219. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0005219.
King HW, Michael MZ, Gleadle JM. Hypoxic enhancement of exosome release by breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:421. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-12-421.
Ban JJ, Lee M, Im W, Kim M. Low pH increases the yield of exosome isolation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;461(1):76–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.03.172.
Parolini I, Federici C, Raggi C, Lugini L, Palleschi S, De Milito A, et al. Microenvironmental pH is a key factor for exosome traffic in tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(49):34211–22. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.041152.
Gutierrez-Vazquez C, Villarroya-Beltri C, Mittelbrunn M, Sanchez-Madrid F. Transfer of extracellular vesicles during immune cell-cell interactions. Immunol Rev. 2013;251(1):125–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12013.
Qian BZ, Pollard JW. Macrophage diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell. 2010;141(1):39–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.014.
Kang Y. Dissecting tumor-stromal interactions in breast cancer bone metastasis. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2016;31(2):206–12. https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.2.206.
Subramanian A, Gupta V, Sarkar S, Maity G, Banerjee S, Ghosh A, et al. Exosomes in carcinogenesis: molecular palkis carry signals for the regulation of cancer progression and metastasis. J Cell Commun Signal. 2016;10(3):241–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-016-0338-6.
Ojalvo LS, Whittaker CA, Condeelis JS, Pollard JW. Gene expression analysis of macrophages that facilitate tumor invasion supports a role for Wnt-signaling in mediating their activity in primary mammary tumors. J Immunol. 2010;184(2):702–12. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0902360.
Chow A, Zhou W, Liu L, Fong MY, Champer J, Van Haute D, et al. Macrophage immunomodulation by breast cancer-derived exosomes requires Toll-like receptor 2-mediated activation of NF-kappaB. Sci Rep. 2014;4:5750. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep05750.
de Jong OG, Verhaar MC, Chen Y, Vader P, Gremmels H, Posthuma G, et al. Cellular stress conditions are reflected in the protein and RNA content of endothelial cell-derived exosomes. J Extracell Vesicles. 2012. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v1i0.18396.
Fais S, Venturi G, Gatenby B. Microenvironmental acidosis in carcinogenesis and metastases: new strategies in prevention and therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014;33(4):1095–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-014-9531-3.
Spugnini E, Fais S. Proton pump inhibition and cancer therapeutics: a specific tumor targeting or it is a phenomenon secondary to a systemic buffering? Semin Cancer Biol. 2017;43:111–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.01.003.
Logozzi M, Angelini DF, Iessi E, Mizzoni D, Di Raimo R, Federici C, et al. Increased PSA expression on prostate cancer exosomes in in vitro condition and in cancer patients. Cancer Lett. 2017;403:318–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.06.036.
Logozzi M, Mizzoni D, Angelini DF, Di Raimo R, Falchi M, Battistini L, et al. Microenvironmental pH and exosome levels interplay in human cancer cell lines of different histotypes. Cancers (Basel). 2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10100370.
Hedlund M, Nagaeva O, Kargl D, Baranov V, Mincheva-Nilsson L. Thermal- and oxidative stress causes enhanced release of NKG2D ligand-bearing immunosuppressive exosomes in leukemia/lymphoma T and B cells. PLoS One. 2011;6(2):e16899. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0016899.
Salomon C, Ryan J, Sobrevia L, Kobayashi M, Ashman K, Mitchell M, et al. Exosomal signaling during hypoxia mediates microvascular endothelial cell migration and vasculogenesis. PLoS One. 2013;8(7):e68451. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068451.
Kucharzewska P, Christianson HC, Welch JE, Svensson KJ, Fredlund E, Ringner M, et al. Exosomes reflect the hypoxic status of glioma cells and mediate hypoxia-dependent activation of vascular cells during tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(18):7312–7. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1220998110.
Berchem G, Noman MZ, Bosseler M, Paggetti J, Baconnais S, Le Cam E, et al. Hypoxic tumor-derived microvesicles negatively regulate NK cell function by a mechanism involving TGF-beta and miR23a transfer. Oncoimmunology. 2016;5(4):e1062968. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2015.1062968.
Chen L, Wang Y, Pan Y, Zhang L, Shen C, Qin G, et al. Cardiac progenitor-derived exosomes protect ischemic myocardium from acute ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;431(3):566–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.01.015.
Arslan F, Lai RC, Smeets MB, Akeroyd L, Choo A, Aguor EN, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes increase ATP levels, decrease oxidative stress and activate PI3K/Akt pathway to enhance myocardial viability and prevent adverse remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2013;10(3):301–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scr.2013.01.002.
Sinha A, Alfaro J, Kislinger T. Characterization of protein content present in exosomes isolated from conditioned media and urine. Curr Protoc Protein Sci. 2017;87(1):24–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpps.23.
ExoCarta: exosome protein, RNA and lipid database [database on the Internet]. http://www.exocarta.org/. Accessed 19 Dec 2018.
Wubbolts R, Leckie RS, Veenhuizen PT, Schwarzmann G, Mobius W, Hoernschemeyer J, et al. Proteomic and biochemical analyses of human B cell-derived exosomes. Potential implications for their function and multivesicular body formation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(13):10963–72. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M207550200.
Øverbye A, Skotland T, Koehler CJ, Thiede B, Seierstad T, Berge V, et al. Identification of prostate cancer biomarkers in urinary exosomes. Oncotarget. 2015;6(30):30357–76.
Melo SA, Luecke LB, Kahlert C, Fernandez AF, Gammon ST, Kaye J, et al. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2015;523(7559):177–82. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14581.
Hu J, Sheng Y, Kwak KJ, Shi J, Yu B, Lee LJ. A signal-amplifiable biochip quantifies extracellular vesicle-associated RNAs for early cancer detection. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):1683. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01942-1.
Yang KS, Im H, Hong S, Pergolini I, Del Castillo AF, Wang R, et al. Multiparametric plasma EV profiling facilitates diagnosis of pancreatic malignancy. Sci Transl Med. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3226.
Lai X, Wang M, McElyea SD, Sherman S, House M, Korc M. A microRNA signature in circulating exosomes is superior to exosomal glypican-1 levels for diagnosing pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017;393:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.02.019.
Chaudhary SC, Khalid S, Smethurst V, Monier D, Mobley J, Huet A, et al. Proteomic profiling of extracellular vesicles released from vascular smooth muscle cells during initiation of phosphate-induced mineralization. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(sup1):55–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/03008207.2018.1444759.
Poliakov A, Spilman M, Dokland T, Amling CL, Mobley JA. Structural heterogeneity and protein composition of exosome-like vesicles (prostasomes) in human semen. Prostate. 2009;69(2):159–67. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.20860.
Hong CS, Muller L, Boyiadzis M, Whiteside TL. Isolation and characterization of CD34+ blast-derived exosomes in acute myeloid leukemia. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e103310. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0103310.
Al-Nedawi K, Meehan B, Rak J. Microvesicles: messengers and mediators of tumor progression. Cell Cycle. 2009;8(13):2014–8. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.8.13.8988.
Liu Q, Yu Z, Yuan S, Xie W, Li C, Hu Z, et al. Circulating exosomal microRNAs as prognostic biomarkers for non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(8):13048–58. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14369.
Wang M, Ji S, Shao G, Zhang J, Zhao K, Wang Z, et al. Effect of exosome biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of breast cancer patients. Clin Transl Oncol. 2018;20(7):906–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-017-1805-0.
Sun Y, Zheng W, Guo Z, Ju Q, Zhu L, Gao J, et al. A novel TP53 pathway influences the HGS-mediated exosome formation in colorectal cancer. Sci Rep. 2016;6:28083. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28083.
McCready J, Sims JD, Chan D, Jay DG. Secretion of extracellular hsp90alpha via exosomes increases cancer cell motility: a role for plasminogen activation. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:294. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-10-294.
Hoshino A, Costa-Silva B, Shen TL, Rodrigues G, Hashimoto A, Tesic Mark M, et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature. 2015;527(7578):329–35. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15756.
Lea J, Sharma R, Yang F, Zhu H, Ward ES, Schroit AJ. Detection of phosphatidylserine-positive exosomes as a diagnostic marker for ovarian malignancies: a proof of concept study. Oncotarget. 2017;8(9):14395–407. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14795.
Yang J, Liu W, Lu X, Fu Y, Li L, Luo Y. High expression of small GTPase Rab3D promotes cancer progression and metastasis. Oncotarget. 2015;6(13):11125–38. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.3575.
Hong CS, Muller L, Whiteside TL, Boyiadzis M. Plasma exosomes as markers of therapeutic response in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Front Immunol. 2014;5:160. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00160.
Ko H, Jeon H, Lee D, Choi HK, Kang KS, Choi KC. Sanguiin H6 suppresses TGF-beta induction of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and inhibits migration and invasion in A549 lung cancer. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015;25(23):5508–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.10.067.
Wang T, Ning K, Lu TX, Sun X, Jin L, Qi X, et al. Increasing circulating exosomes-carrying TRPC5 predicts chemoresistance in metastatic breast cancer patients. Cancer Sci. 2017;108(3):448–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13150.
Guescini M, Guidolin D, Vallorani L, Casadei L, Gioacchini AM, Tibollo P, et al. C2C12 myoblasts release micro-vesicles containing mtDNA and proteins involved in signal transduction. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316(12):1977–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.04.006.
Balaj L, Lessard R, Dai L, Cho YJ, Pomeroy SL, Breakefield XO, et al. Tumour microvesicles contain retrotransposon elements and amplified oncogene sequences. Nat Commun. 2011;2:180. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1180.
Kahlert C, Melo SA, Protopopov A, Tang J, Seth S, Koch M, et al. Identification of double-stranded genomic DNA spanning all chromosomes with mutated KRAS and p53 DNA in the serum exosomes of patients with pancreatic cancer. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(7):3869–75. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C113.532267.
Ratajczak J, Miekus K, Kucia M, Zhang J, Reca R, Dvorak P, et al. Embryonic stem cell-derived microvesicles reprogram hematopoietic progenitors: evidence for horizontal transfer of mRNA and protein delivery. Leukemia. 2006;20(5):847–56. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404132.
Deregibus MC, Cantaluppi V, Calogero R, Lo Iacono M, Tetta C, Biancone L, et al. Endothelial progenitor cell derived microvesicles activate an angiogenic program in endothelial cells by a horizontal transfer of mRNA. Blood. 2007;110(7):2440–8. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-03-078709.
Kislauskis EH, Zhu X, Singer RH. Sequences responsible for intracellular localization of beta-actin messenger RNA also affect cell phenotype. J Cell Biol. 1994;127(2):441–51.
Batagov AO, Kuznetsov VA, Kurochkin IV. Identification of nucleotide patterns enriched in secreted RNAs as putative cis-acting elements targeting them to exosome nano-vesicles. BMC Genomics. 2011;12(Suppl 3):S18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-S3-S18.
Batagov AO, Kurochkin IV. Exosomes secreted by human cells transport largely mRNA fragments that are enriched in the 3’-untranslated regions. Biol Direct. 2013;8:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6150-8-12.
Andreassi C, Riccio A. To localize or not to localize: mRNA fate is in 3’UTR ends. Trends Cell Biol. 2009;19(9):465–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2009.06.001.
Zhou W, Fong MY, Min Y, Somlo G, Liu L, Palomares MR, et al. Cancer-secreted miR-105 destroys vascular endothelial barriers to promote metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2014;25(4):501–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2014.03.007.
Melo SA, Sugimoto H, O’Connell JT, Kato N, Villanueva A, Vidal A, et al. Cancer exosomes perform cell-independent microRNA biogenesis and promote tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2014;26(5):707–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2014.09.005.
Kawahara Y, Zinshteyn B, Sethupathy P, Iizasa H, Hatzigeorgiou AG, Nishikura K. Redirection of silencing targets by adenosine-to-inosine editing of miRNAs. Science. 2007;315(5815):1137–40. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1138050.
Velazquez-Torres G, Shoshan E, Ivan C, Huang L, Fuentes-Mattei E, Paret H, et al. A-to-I miR-378a-3p editing can prevent melanoma progression via regulation of PARVA expression. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):461. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-02851-7.
Paul D, Sinha AN, Ray A, Lal M, Nayak S, Sharma A, et al. A-to-I editing in human miRNAs is enriched in seed sequence, influenced by sequence contexts and significantly hypoedited in glioblastoma multiforme. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):2466. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-02397-6.
Wang Y, Xu X, Yu S, Jeong KJ, Zhou Z, Han L, et al. Systematic characterization of A-to-I RNA editing hotspots in microRNAs across human cancers. Genome Res. 2017;27(7):1112–25. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.219741.116.
Pinto Y, Buchumenski I, Levanon EY, Eisenberg E. Human cancer tissues exhibit reduced A-to-I editing of miRNAs coupled with elevated editing of their targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(1):71–82. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1176.
Nigita G, Distefano R, Veneziano D, Romano G, Rahman M, Wang K, et al. Tissue and exosomal miRNA editing in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):10222. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-28528-1.
Shen J, Hruby GW, McKiernan JM, Gurvich I, Lipsky MJ, Benson MC, et al. Dysregulation of circulating microRNAs and prediction of aggressive prostate cancer. Prostate. 2012;72(13):1469–77. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.22499.
Manier S, Liu CJ, Avet-Loiseau H, Park J, Shi J, Campigotto F, et al. Prognostic role of circulating exosomal miRNAs in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2017;129(17):2429–36. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-09-742296.
Sanchez CA, Andahur EI, Valenzuela R, Castellon EA, Fulla JA, Ramos CG, et al. Exosomes from bulk and stem cells from human prostate cancer have a differential microRNA content that contributes cooperatively over local and pre-metastatic niche. Oncotarget. 2016;7(4):3993–4008. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6540.
Muntion S, Ramos TL, Diez-Campelo M, Roson B, Sanchez-Abarca LI, Misiewicz-Krzeminska I, et al. Microvesicles from mesenchymal stromal cells are involved in HPC-microenvironment crosstalk in myelodysplastic patients. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0146722. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146722.
Huang Z, Zhu D, Wu L, He M, Zhou X, Zhang L, et al. Six serum-based miRNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers for gastric cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2017;26(2):188–96. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-16-0607.
Fong MY, Zhou W, Liu L, Alontaga AY, Chandra M, Ashby J, et al. Breast-cancer-secreted miR-122 reprograms glucose metabolism in premetastatic niche to promote metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 2015;17(2):183–94. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3094.
Hannafon BN, Trigoso YD, Calloway CL, Zhao YD, Lum DH, Welm AL, et al. Plasma exosome microRNAs are indicative of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2016;18(1):90. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-016-0753-x.
Madhavan B, Yue S, Galli U, Rana S, Gross W, Muller M, et al. Combined evaluation of a panel of protein and miRNA serum-exosome biomarkers for pancreatic cancer diagnosis increases sensitivity and specificity. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(11):2616–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29324.
Liu W, Hu J, Zhou K, Chen F, Wang Z, Liao B, et al. Serum exosomal miR-125b is a novel prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2017;10:3843–51. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S140062.
Rodriguez M, Silva J, Lopez-Alfonso A, Lopez-Muniz MB, Pena C, Dominguez G, et al. Different exosome cargo from plasma/bronchoalveolar lavage in non-small-cell lung cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2014;53(9):713–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.22181.
Li Z, Ma YY, Wang J, Zeng XF, Li R, Kang W, et al. Exosomal microRNA-141 is upregulated in the serum of prostate cancer patients. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:139–48. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s95565.
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C. MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;110(1):13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.04.033.
Fernandez-Mercado M, Manterola L, Lawrie CH. MicroRNAs in lymphoma: regulatory role and biomarker potential. Curr Genomics. 2015;16(5):349–58. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389202916666150707160147.
Que R, Ding G, Chen J, Cao L. Analysis of serum exosomal microRNAs and clinicopathologic features of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 2013;11:219. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7819-11-219.
Umezu T, Ohyashiki K, Kuroda M, Ohyashiki JH. Leukemia cell to endothelial cell communication via exosomal miRNAs. Oncogene. 2013;32(22):2747–55. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.295.
Matsumura T, Sugimachi K, Iinuma H, Takahashi Y, Kurashige J, Sawada G, et al. Exosomal microRNA in serum is a novel biomarker of recurrence in human colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2015;113(2):275–81. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2015.201.
Zhu HT, Liu RB, Liang YY, Hasan AME, Wang HY, Shao Q, et al. Serum microRNA profiles as diagnostic biomarkers for HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2017;37(6):888–96. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.13356.
Zhu M, Huang Z, Zhu D, Zhou X, Shan X, Qi LW, et al. A panel of microRNA signature in serum for colorectal cancer diagnosis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(10):17081–91. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15059.
Le MT, Hamar P, Guo C, Basar E, Perdigao-Henriques R, Balaj L, et al. miR-200-containing extracellular vesicles promote breast cancer cell metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(12):5109–28. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI75695.
Cappellesso R, Tinazzi A, Giurici T, Simonato F, Guzzardo V, Ventura L, et al. Programmed cell death 4 and microRNA 21 inverse expression is maintained in cells and exosomes from ovarian serous carcinoma effusions. Cancer Cytopathol. 2014;122(9):685–93. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncy.21442.
Liu W, Chen S, Liu B. Diagnostic and prognostic values of serum exosomal microRNA-21 in children with hepatoblastoma: a Chinese population-based study. Pediatr Surg Int. 2016;32(11):1059–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-016-3960-8.
Zhou X, Wen W, Shan X, Zhu W, Xu J, Guo R, et al. A six-microRNA panel in plasma was identified as a potential biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma diagnosis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(4):6513–25. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14311.
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST, Patel T. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology. 2007;133(2):647–58. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2007.05.022.
Wang H, Hou L, Li A, Duan Y, Gao H, Song X. Expression of serum exosomal microRNA-21 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:864894. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/864894.
Li L, Li C, Wang S, Wang Z, Jiang J, Wang W, et al. Exosomes derived from hypoxic oral squamous cell carcinoma cells deliver miR-21 to normoxic cells to elicit a prometastatic phenotype. Cancer Res. 2016;76(7):1770–80. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1625.
Masoudi MS, Mehrabian E, Mirzaei H. MiR-21: a key player in glioblastoma pathogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(2):1285–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26300.
Liu Y, Luo F, Wang B, Li H, Xu Y, Liu X, et al. STAT3-regulated exosomal miR-21 promotes angiogenesis and is involved in neoplastic processes of transformed human bronchial epithelial cells. Cancer Lett. 2016;370(1):125–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.10.011.
Cui H, Seubert B, Stahl E, Dietz H, Reuning U, Moreno-Leon L, et al. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 induces a pro-tumourigenic increase of miR-210 in lung adenocarcinoma cells and their exosomes. Oncogene. 2015;34(28):3640–50. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.300.
Huang Y, Zhu J, Li W, Zhang Z, Xiong P, Wang H, et al. Serum microRNA panel excavated by machine learning as a potential biomarker for the detection of gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 2018;39(3):1338–46. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.6163.
Sohn W, Kim J, Kang SH, Yang SR, Cho JY, Cho HC, et al. Serum exosomal microRNAs as novel biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp Mol Med. 2015;47:e184. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2015.68.
Ye SB, Zhang H, Cai TT, Liu YN, Ni JJ, He J, et al. Exosomal miR-24-3p impedes T-cell function by targeting FGF11 and serves as a potential prognostic biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Pathol. 2016;240(3):329–40. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4781.
Jiao C, Jiao X, Zhu A, Ge J, Xu X. Exosomal miR-34s panel as potential novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in patients with hepatoblastoma. J Pediatr Surg. 2017;52(4):618–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2016.09.070.
Corcoran C, Rani S, O’Driscoll L. miR-34a is an intracellular and exosomal predictive biomarker for response to docetaxel with clinical relevance to prostate cancer progression. Prostate. 2014;74(13):1320–34. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.22848.
Guduric-Fuchs J, O’Connor A, Camp B, O’Neill CL, Medina RJ, Simpson DA. Selective extracellular vesicle-mediated export of an overlapping set of microRNAs from multiple cell types. BMC Genomics. 2012;13:357. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-357.
Pigati L, Yaddanapudi SC, Iyengar R, Kim DJ, Hearn SA, Danforth D, et al. Selective release of microRNA species from normal and malignant mammary epithelial cells. PLoS One. 2010;5(10):e13515. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0013515.
Liu C, Eng C, Shen J, Lu Y, Takata Y, Mehdizadeh A, et al. Serum exosomal miR-4772-3p is a predictor of tumor recurrence in stage II and III colon cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(46):76250–60. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12841.
Sugimachi K, Matsumura T, Hirata H, Uchi R, Ueda M, Ueo H, et al. Identification of a bona fide microRNA biomarker in serum exosomes that predicts hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after liver transplantation. Br J Cancer. 2015;112(3):532–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.621.
Wu H, Zhou J, Mei S, Wu D, Mu Z, Chen B, et al. Circulating exosomal microRNA-96 promotes cell proliferation, migration and drug resistance by targeting LMO7. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(6):1228–36. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13056.
Akers JC, Hua W, Li H, Ramakrishnan V, Yang Z, Quan K, et al. A cerebrospinal fluid microRNA signature as biomarker for glioblastoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8(40):68769–79. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.18332.
Conigliaro A, Costa V, Lo Dico A, Saieva L, Buccheri S, Dieli F, et al. CD90+ liver cancer cells modulate endothelial cell phenotype through the release of exosomes containing H19 lncRNA. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:155. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-015-0426-x.
Isin M, Uysaler E, Ozgur E, Koseoglu H, Sanli O, Yucel OB, et al. Exosomal lncRNA-p21 levels may help to distinguish prostate cancer from benign disease. Front Genet. 2015;6:168. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2015.00168.
Liu T, Zhang X, Gao S, Jing F, Yang Y, Du L, et al. Exosomal long noncoding RNA CRNDE-h as a novel serum-based biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(51):85551–63. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13465.
Wilusz JE, Sunwoo H, Spector DL. Long noncoding RNAs: functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev. 2009;23(13):1494–504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1800909.
Diepenbruck M, Christofori G. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis: yes, no, maybe? Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2016;43:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2016.06.002.
Hood JL. Melanoma exosome induction of endothelial cell GM-CSF in pre-metastatic lymph nodes may result in different M1 and M2 macrophage mediated angiogenic processes. Med Hypotheses. 2016;94:118–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2016.07.009.
Franzen CA, Blackwell RH, Todorovic V, Greco KA, Foreman KE, Flanigan RC, et al. Urothelial cells undergo epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition after exposure to muscle invasive bladder cancer exosomes. Oncogenesis. 2015;4:e163. https://doi.org/10.1038/oncsis.2015.21.
Vella LJ. The emerging role of exosomes in epithelial-mesenchymal-transition in cancer. Front Oncol. 2014;4:361. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2014.00361.
Liu Y, Gu Y, Han Y, Zhang Q, Jiang Z, Zhang X, et al. Tumor exosomal RNAs promote lung pre-metastatic niche formation by activating alveolar epithelial TLR3 to recruit neutrophils. Cancer Cell. 2016;30(2):243–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2016.06.021.
Rahman MA, Barger JF, Lovat F, Gao M, Otterson GA, Nana-Sinkam P. Lung cancer exosomes as drivers of epithelial mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget. 2016;7(34):54852–66. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10243.
Cao M, Seike M, Soeno C, Mizutani H, Kitamura K, Minegishi Y, et al. MiR-23a regulates TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting E-cadherin in lung cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2012;41(3):869–75. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2012.1535.
Kim J, Kim TY, Lee MS, Mun JY, Ihm C, Kim SA. Exosome cargo reflects TGF-beta1-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) status in A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;478(2):643–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.07.124.
Ohshima K, Inoue K, Fujiwara A, Hatakeyama K, Kanto K, Watanabe Y, et al. Let-7 microRNA family is selectively secreted into the extracellular environment via exosomes in a metastatic gastric cancer cell line. PLoS One. 2010;5(10):e13247. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0013247.
Tanaka S, Hosokawa M, Yonezawa T, Hayashi W, Ueda K, Iwakawa S. Induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and down-regulation of miR-200c and miR-141 in oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 2015;38(3):435–40. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b14-00695.
Xiao D, Barry S, Kmetz D, Egger M, Pan J, Rai SN, et al. Melanoma cell-derived exosomes promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in primary melanocytes through paracrine/autocrine signaling in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Lett. 2016;376(2):318–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.03.050.
Liao J, Liu R, Shi YJ, Yin LH, Pu YP. Exosome-shuttling microRNA-21 promotes cell migration and invasion-targeting PDCD4 in esophageal cancer. Int J Oncol. 2016;48(6):2567–79. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2016.3453.
Lu X, Kang Y. Organotropism of breast cancer metastasis. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007;12(2–3):153–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-007-9047-3.
Fidler IJ. Selection of successive tumour lines for metastasis. Nat New Biol. 1973;242(118):148–9.
Paget S. The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. 1889. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1989;8(2):98–101.
Hood JL, San RS, Wickline SA. Exosomes released by melanoma cells prepare sentinel lymph nodes for tumor metastasis. Cancer Res. 2011;71(11):3792–801. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4455.
Javle M, Li Y, Tan D, Dong X, Chang P, Kar S, et al. Biomarkers of TGF-beta signaling pathway and prognosis of pancreatic cancer. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e85942. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085942.
Ellermeier J, Wei J, Duewell P, Hoves S, Stieg MR, Adunka T, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of bifunctional siRNA combining TGF-beta1 silencing with RIG-I activation in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2013;73(6):1709–20. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3850.
Lugini L, Valtieri M, Federici C, Cecchetti S, Meschini S, Condello M, et al. Exosomes from human colorectal cancer induce a tumor-like behavior in colonic mesenchymal stromal cells. Oncotarget. 2016;7(31):50086–98. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10574.
Peinado H, Aleckovic M, Lavotshkin S, Matei I, Costa-Silva B, Moreno-Bueno G, et al. Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat Med. 2012;18(6):883–91. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2753.
Abusamra AJ, Zhong Z, Zheng X, Li M, Ichim TE, Chin JL, et al. Tumor exosomes expressing Fas ligand mediate CD8+ T-cell apoptosis. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2005;35(2):169–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcmd.2005.07.001.
Wieckowski EU, Visus C, Szajnik M, Szczepanski MJ, Storkus WJ, Whiteside TL. Tumor-derived microvesicles promote regulatory T cell expansion and induce apoptosis in tumor-reactive activated CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 2009;183(6):3720–30. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0900970.
Szajnik M, Czystowska M, Szczepanski MJ, Mandapathil M, Whiteside TL. Tumor-derived microvesicles induce, expand and up-regulate biological activities of human regulatory T cells (Treg). PLoS One. 2010;5(7):e11469. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0011469.
Whiteside TL. Immune modulation of T-cell and NK (natural killer) cell activities by TEXs (tumour-derived exosomes). Biochem Soc Trans. 2013;41(1):245–51. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20120265.
Chalmin F, Ladoire S, Mignot G, Vincent J, Bruchard M, Remy-Martin JP, et al. Membrane-associated Hsp72 from tumor-derived exosomes mediates STAT3-dependent immunosuppressive function of mouse and human myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Clin Invest. 2010;120(2):457–71. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI40483.
Nagaraj S, Nelson A, Youn JI, Cheng P, Quiceno D, Gabrilovich DI. Antigen-specific CD4(+) T cells regulate function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer via retrograde MHC class II signaling. Cancer Res. 2012;72(4):928–38. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2863.
Lv LH, Wan YL, Lin Y, Zhang W, Yang M, Li GL, et al. Anticancer drugs cause release of exosomes with heat shock proteins from human hepatocellular carcinoma cells that elicit effective natural killer cell antitumor responses in vitro. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(19):15874–85. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.340588.
Goler-Baron V, Assaraf YG. Structure and function of ABCG2-rich extracellular vesicles mediating multidrug resistance. PLoS One. 2011;6(1):e16007. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0016007.
Bebawy M, Combes V, Lee E, Jaiswal R, Gong J, Bonhoure A, et al. Membrane microparticles mediate transfer of P-glycoprotein to drug sensitive cancer cells. Leukemia. 2009;23(9):1643–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.76.
Corcoran C, Rani S, O’Brien K, O’Neill A, Prencipe M, Sheikh R, et al. Docetaxel-resistance in prostate cancer: evaluating associated phenotypic changes and potential for resistance transfer via exosomes. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50999. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0050999.
Safaei R, Larson BJ, Cheng TC, Gibson MA, Otani S, Naerdemann W, et al. Abnormal lysosomal trafficking and enhanced exosomal export of cisplatin in drug-resistant human ovarian carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4(10):1595–604. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0102.
Lehmann BD, Paine MS, Brooks AM, McCubrey JA, Renegar RH, Wang R, et al. Senescence-associated exosome release from human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008;68(19):7864–71. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6538.
Khan S, Jutzy JM, Aspe JR, McGregor DW, Neidigh JW, Wall NR. Survivin is released from cancer cells via exosomes. Apoptosis. 2011;16(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0534-4.
Jaiswal R, Luk F, Gong J, Mathys JM, Grau GE, Bebawy M. Microparticle conferred microRNA profiles–implications in the transfer and dominance of cancer traits. Mol Cancer. 2012;11:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-11-37.
Hergenreider E, Heydt S, Treguer K, Boettger T, Horrevoets AJ, Zeiher AM, et al. Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14(3):249–56. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2441.
Clynes RA, Towers TL, Presta LG, Ravetch JV. Inhibitory Fc receptors modulate in vivo cytotoxicity against tumor targets. Nat Med. 2000;6(4):443–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/74704.
Aung T, Chapuy B, Vogel D, Wenzel D, Oppermann M, Lahmann M, et al. Exosomal evasion of humoral immunotherapy in aggressive B-cell lymphoma modulated by ATP-binding cassette transporter A3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(37):15336–41. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1102855108.
Battke C, Ruiss R, Welsch U, Wimberger P, Lang S, Jochum S, et al. Tumour exosomes inhibit binding of tumour-reactive antibodies to tumour cells and reduce ADCC. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011;60(5):639–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-011-0979-5.
Kosaka N, Iguchi H, Yoshioka Y, Takeshita F, Matsuki Y, Ochiya T. Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(23):17442–52. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.107821.
Cho DY, Lin SZ, Yang WK, Hsu DM, Lee HC, Lee WY, et al. Recent advances of dendritic cells (DCs)-based immunotherapy for malignant gliomas. Cell Transplant. 2009;18(9):977–83. https://doi.org/10.3727/096368909X12483162196962.
Cho JA, Yeo DJ, Son HY, Kim HW, Jung DS, Ko JK, et al. Exosomes: a new delivery system for tumor antigens in cancer immunotherapy. Int J Cancer. 2005;114(4):613–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.20757.
Elsner L, Muppala V, Gehrmann M, Lozano J, Malzahn D, Bickeboller H, et al. The heat shock protein HSP70 promotes mouse NK cell activity against tumors that express inducible NKG2D ligands. J Immunol. 2007;179(8):5523–33.
Escudier B, Dorval T, Chaput N, Andre F, Caby MP, Novault S, et al. Vaccination of metastatic melanoma patients with autologous dendritic cell (DC) derived-exosomes: results of thefirst phase I clinical trial. J Transl Med. 2005;3(1):10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-3-10.
Morse MA, Garst J, Osada T, Khan S, Hobeika A, Clay TM, et al. A phase I study of dexosome immunotherapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Transl Med. 2005;3(1):9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-3-9.
de la Fuente A, Alonso-Alconada L, Costa C, Cueva J, Garcia-Caballero T, Lopez-Lopez R, et al. M-Trap: exosome-based capture of tumor cells as a new technology in peritoneal metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015;107(9):djv184. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djv184.
Kim MS, Haney MJ, Zhao Y, Mahajan V, Deygen I, Klyachko NL, et al. Development of exosome-encapsulated paclitaxel to overcome MDR in cancer cells. Nanomedicine. 2016;12(3):655–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2015.10.012.
Kooijmans SA, Vader P, van Dommelen SM, van Solinge WW, Schiffelers RM. Exosome mimetics: a novel class of drug delivery systems. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:1525–41. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S29661.
Zhang W, Li C, Shen C, Liu Y, Zhao X, Liu Y, et al. Prodrug-based nano-drug delivery system for co-encapsulate paclitaxel and carboplatin for lung cancer treatment. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(7):2575–80. https://doi.org/10.3109/10717544.2015.1035466.
Airoldi M, Amadori D, Barni S, Cinieri S, De Placido S, Di Leo A, et al. Clinical activity and cardiac tolerability of non-pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in breast cancer: a synthetic review. Tumori. 2011;97(6):690–2. https://doi.org/10.1700/1018.11082.
Swenson CE, Perkins WR, Roberts P, Janoff AS. Liposome technology and the development of Myocet™ (liposomal doxorubicin citrate). The Breast. 2001;10:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-9776(01)80001-1.
Doxorubicin (Myocet) 50 mg powder, dispersion and solvent for concentrate for dispersion for infusion. Teva Pharma B.V., Electronic Medicines Compendium. 2015. https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/5378/smpc#companyDetails. Accessed 4 Jan 2019.
Trivedi M, Talekar M, Shah P, Ouyang Q, Amiji M. Modification of tumor cell exosome content by transfection with wt-p53 and microRNA-125b expressing plasmid DNA and its effect on macrophage polarization. Oncogenesis. 2016;5(8):e250. https://doi.org/10.1038/oncsis.2016.52.
Federici C, Petrucci F, Caimi S, Cesolini A, Logozzi M, Borghi M, D'Ilio S, Lugini L, Violante N, Azzarito T, Majorani C, Brambilla D, Fais S. Exosome release and low pH belong to a framework of resistance of human melanoma cells to cisplatin. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e88193. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0088193.
Iessi E, Logozzi M, Lugini L, Azzarito T, Federici C, Spugnini EP, et al. Acridine Orange/exosomes increase the delivery and the effectiveness of acridine orange in human melanoma cells: a new prototype for theranostics of tumors. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2017;32(1):648–57. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2017.1292263.
Kusuzaki K, Hosogi S, Ashihara E, Matsubara T, Satonaka H, Nakamura T, et al. Translational research of photodynamic therapy with acridine orange which targets cancer acidity. Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(10):1414–20.
Blakely CM, Watkins TBK, Wu W, Gini B, Chabon JJ, McCoach CE, McGranahan N, Wilson GA, Birkbak NJ, Olivas VR, Rotow J, Maynard A, Wang V, Gubens MA, Banks KC, Lanman RB, Caulin AF, St John J, Cordero AR, Giannikopoulos P, Simmons AD, Mack PC, Gandara DR, Husain H, Doebele RC, Riess JW, Diehn M, Swanton C, Bivona TG. Evolution and clinical impact of co-occurring genetic alterations in advanced-stage EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Nat. Genet. 2017;49(12):1693–1704.
Zocco D, Ferruzzi P, Cappello F, Kuo WP, Fais S. Extracellular vesicles as shuttles of tumor biomarkers and anti-tumor drugs. Front Oncol. 2014;4:267. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2014.00267.
Lener T, Gimona M, Aigner L, Borger V, Buzas E, Camussi G, et al. Applying extracellular vesicles based therapeutics in clinical trials - an ISEV position paper. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:30087. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v4.30087.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WWW: conception and planning, manuscript writing, and final approval of manuscript. TG: conception and planning, manuscript writing, and final approval of manuscript. HTT: conception and planning, manuscript editing, and final approval of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for the preparation of this review.
Conflict of Interest
Wendy W. Weston, Timothy Ganey, and H. Thomas Temple have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weston, W.W., Ganey, T. & Temple, H.T. The Relationship between Exosomes and Cancer: Implications for Diagnostics and Therapeutics. BioDrugs 33, 137–158 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40259-019-00338-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40259-019-00338-5