Abstract
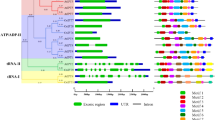
Several studies have shown that the plant 14-3-3 gene family plays an important role in plant growth and development, as well as its response to abiotic and biotic stresses. At present, the 14-3-3 gene family has been found successively in many plants; however, no detailed characterization and expression profiles of the 14-3-3 gene family are found in melon. Thus, the author performed genome-wide identification, characterization and expression pattern in different tissues and under various abiotic and biotic stresses by analyzing the published RNA-Seq raw data from NCBI database. Nine 14-3-3 genes in melon were identified and classified as non-epsilon and epsilon groups based on the orthologs of Arabidopsis 14-3-3 genes and dispersedly distributed on five chromosomes. The majority of melon 14-3-3 members contained 300 amino acids or less, which might localize in the nucleus. Members of the epsilon group commonly contained more exons or introns than those of the non-epsilon group. Gene duplication analysis indicated that segmental duplication was dominant in the expansion of the melon 14-3-3 family. Many cis-elements in response to different stresses and hormones were predicted by using the PlantCARE server. The published RNA-Seq showed that several 14-3-3 genes showed significant expression changes in different tissues, during fruit development and under salt, cold and pathogen stresses at a certain time point. These results provided a general introduction to melon 14-3-3 genes and a preliminary basis for later functional verification.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken A, Collinge DB, van Heusden BP, Isobe T, Roseboom PH, Rosenfeld G, Soll J (1992) 14-3-3 proteins: a highly conserved, widespread family of eukaryotic proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 17(12):498–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/0968-0004(92)90339-b
Bailey TL, Williams N, Misleh C, Li WW (2006) MEME: discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res 34:W369–W373. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl198
Barker MS, Baute GJ, Liu SL (2012) Duplications and turnover in plant genomes. Plant Genome Divers 1:155–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-1130-7_11
Chang L, Tong Z, Peng C, Wang D, Kong H, Yang Q, Luo M, Guo A, Xu B (2020) Genome-wide analysis and phosphorylation sites identification of the 14-3-3 gene family and functional characterization of MeGRF3 in cassava. Physiol Plant 169(2):244–257. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13070
Chen F, Li Q, Sun L, He Z (2006) The rice 14-3-3 gene family and its involvement in responses to biotic and abiotic stress. DNA Res 13(2):53–63. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsl001
Chen Y, Zhou X, Chang S, Chu Z, Wang H, Han S, Wang Y (2017) Calcium-dependent protein kinase 21 phosphorylates 14-3-3 proteins in response to ABA signaling and salt stress in rice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 493(4):1450–1456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.09.166
Cheng C, Wang Y, Chai F, Li S, Xin H, Liang Z (2018) Genome-wide identification and characterization of the 14–3-3 family in Vitis vinifera L. during berry development and cold- and heat-stress response. BMC Genomics 19(1):579. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4955-8
Chou KC, Shen HB (2010) A new method for predicting the subcellular localization of eukaryotic proteins with both single and multiple sites: Euk-mPLoc 2.0. PLoS One 5(4):e9931. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0009931
Crooks GE, Hon G, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE (2004) WebLogo: a sequence logo generator. Genome Res 14(6):1188–1190. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.849004
de Boer AH, van Kleeff PJ, Gao J (2013) Plant 14-3-3 proteins as spiders in a web of phosphorylation. Protoplasma 250(2):425–440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-012-0437-z
DeLille JM, Sehnke PC, Ferl RJ (2001) The arabidopsis 14-3-3 family of signaling regulators. Plant Physiol 126(1):35–38. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.126.1.35
Denison FC, Paul AL, Zupanska AK, Ferl RJ (2011) 14-3-3 proteins in plant physiology. Semin Cell Dev Biol 22(7):720–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.08.006
Dougherty MK, Morrison DK (2004) Unlocking the code of 14-3-3. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 10):1875–1884. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.01171
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39(4):783–791. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x
Garcia-Mas J, Benjak A, Sanseverino W, Bourgeois M, Mir G, González VM, Hénaff E, Câmara F, Cozzuto L, Lowy E, Alioto T, Capella-Gutiérrez S, Blanca J, Cañizares J, Ziarsolo P, Gonzalez-Ibeas D, Rodríguez-Moreno L, Droege M, Du L, Alvarez-Tejado M, Lorente-Galdos B, Melé M, Yang L, Weng Y, Navarro A, Marques-Bonet T, Aranda MA, Nuez F, Picó B, Gabaldón T, Roma G, Guigó R, Casacuberta JM, Arús P, Puigdomènech P (2012) The genome of melon (Cucumis melo L.). PNAS 109(29):11872–11877. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1205415109
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp 41:95–98
Hu B, Jin J, Guo AY, Zhang H, Luo J, Gao G (2015) GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 31(8):1296–1297. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu817
Huang C (2018) Transcriptome analysis of responding to low temperature in melon (Cucumis melo L.). Northeast Agricultural University (Master Thesis, In Chinese)
Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2015) HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods 12(4):357–360. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3317
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6):1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Latrasse D, Rodriguez-Granados NY, Veluchamy A, Mariappan KG, Bevilacqua C, Crapart N, Camps C, Sommard V, Raynaud C, Dogimont C, Boualem A, Benhamed M, Bendahmane A (2017) The quest for epigenetic regulation underlying unisexual flower development in Cucumis melo. Epigenetics Chromatin 10:22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13072-017-0132-6
Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouzé P, Rombauts S (2002) PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30(1):325–327. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/30.1.325
Letunic I, Bork P (2018) 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res 46(D1):D493–D496. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx922
Li MY, Xu BY, Liu JH, Yang XL, Zhang JB, Jia CH, Ren LC, Jin ZQ (2012) Identification and expression analysis of four 14–3-3 genes during fruit ripening in banana (Musa acuminata L. AAA group, cv. Brazilian). Plant Cell Rep 31(2):369–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1172-1
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2011) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15(12):550. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Lozano-Durán R, Robatzek S (2015) 14-3-3 proteins in plant-pathogen interactions. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 28(5):511–518. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-10-14-0322-CR
Meng X, Chen X, Wang Y, Xiao R, Liu H, Wang X, Ren J, Li Y, Niu H, Wang X, Yin J (2014) Characterization and subcellular localization of two 14-3-3 genes and their response to abiotic stress in wheat. Chin J Biotechnol 30(2):232–246. https://doi.org/10.13345/j.cjb.130232
Mistry J, Chuguransky S, Williams L, Qureshi M, Salazar GA, Sonnhammer ELL, Tosatto SCE, Paladin L, Raj S, Richardson LJ, Finn RD, Bateman A (2021) Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res 49(D1):D412–D419. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa913
Moore BW, Perez VJ (1967) Specific acidic proteins of the nervous system. Physiol Biochem Asp Nerv Integr. pp 343–359
Rittinger K, Budman J, Xu J, Volinia S, Cantley LC, Smerdon SJ, Gamblin SJ, Yaffe MB (1999) Structural analysis of 14-3-3 phosphopeptide complexes identifies a dual role for the nuclear export signal of 14-3-3 in ligand binding. Mol Cell 4(2):153–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80363-9
Robert X, Gouet P (2014) Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res 42:W320–W324. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku316
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Sang N, Liu H, Ma B, Huang X, Zhuo L, Sun Y (2021) Roles of the 14-3-3 gene family in cotton flowering. BMC Plant Biol 21(1):162. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-02923-9
Shao W, Chen W, Zhu X, Zhou X, Jin Y, Zhan C, Liu G, Liu X, Ma D, Qiao Y (2021) Genome-wide identification and characterization of wheat 14-3-3 genes unravels the role of TaGRF6-A in salt stress tolerance by binding MYB transcription factor. Int J Mol Sci 22(4):1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041904
Shin AY, Kim YM, Koo N, Lee SM, Nahm S, Kwon SY (2017) Transcriptome analysis of the oriental melon (Cucumis melo L. var. makuwa) during fruit development. PeerJ 5:e2834. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.2834
Silvia Sebastiani M, Bagnaresi P, Sestili S, Biselli C, Zechini A, Orrù L, Cattivelli L, Ficcadenti N (2017) Transcriptome analysis of the melon-fusarium oxysporum f. sp. melonis race 1.2 pathosystem in susceptible and resistant Plants. Front Plant Sci 8:362. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00362
Subramanian B, Gao S, Lercher MJ, Hu S, Chen WH (2019) Evolview v3: a webserver for visualization, annotation, and management of phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res 47(W1):W270–W275. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz357
Sun X, Luo X, Sun M, Chen C, Ding X, Wang X, Yang S, Yu Q, Jia B, Ji W, Cai H, Zhu Y (2014) A Glycine soja 14-3-3 protein GsGF14o participates in stomatal and root hair development and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 55(1):99–118. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pct161
Tian F, Wang T, Xie Y, Zhang J, Hu J (2015) Genome-wide identification, classification, and expression analysis of 14-3-3 gene family in Populus. PLoS One 10(4):e0123225. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0123225
Visconti S, D’Ambrosio C, Fiorillo A, Arena S, Muzi C, Zottini M, Aducci P, Marra M, Scaloni A, Camoni L (2019) Overexpression of 14-3-3 proteins enhances cold tolerance and increases levels of stress-responsive proteins of Arabidopsis plants. Plant Sci 289:110215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.110215
Walther D, Brunnemann R, Selbig J (2007) The regulatory code for transcriptional response diversity and its relation to genome structural properties in A. thaliana. PLoS Genet 3(2):e11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.0030011
Wang Y, Tang H, Debarry JD, Tan X, Li J, Wang X, Lee TH, Jin H, Marler B, Guo H, Kissinger JC, Paterson AH (2012) MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res 40(7):e49. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr1293
Wang LM, Zhang LD, Chen JB, Huang DF, Zhang YD (2016) Physiological analysis and transcriptome comparison of two muskmelon (Cucumis melo L.) cultivars in response to salt stress. Genet Mol Res. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr.15038738
Wang Y, Ling L, Jiang Z, Tan W, Liu Z, Wu L, Zhao Y, Xia S, Ma J, Wang G, Li W (2019) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the 14-3-3 gene family in soybean (Glycine max). PeerJ 7:e7950. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7950
Wang P, Wu H, Zhao G, He Y, Kong W, Zhang J, Liu S, Liu M, Hu K, Liu L, Xu Y, Xu Z (2020) Transcriptome analysis clarified genes involved in resistance to Phytophthora capsici in melon. PLoS One 15(2):e0227284. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0227284
Wu S, Yan HD, Zhang AL, Huang LK, Yin GH, Lee S (2016) Identification and characterization of the 14-3-3 gene family in switchgrass. Genet Mol Res. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr15048688
Xu WF, Shi WM (2006) Expression profiling of the 14-3-3 gene family in response to salt stress and potassium and iron deficiencies in young tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) roots: analysis by real-time RT-PCR. Ann Bot 98(5):965–974. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcl189
Xu M, Hu Z, Lai W, Liu S, Wu H, Zhou Y (2021) Comprehensive analysis of 14-3-3 family genes and their responses to cold and drought stress in cucumber. Funct Plant Biol 48(12):1264–1276. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP21022
Yang X, Lee WH, Sobott F, Papagrigoriou E, Robinson CV, Grossmann JG, Sundström M, Doyle DA, Elkins JM (2006) Structural basis for protein-protein interactions in the 14-3-3 protein family. PNAS 103(46):17237–17242. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0605779103
Yang ZP, Li HL, Guo D, Tang X, Peng SQ (2014) Identification and characterization of the 14-3-3 gene family in Hevea brasiliensis. Plant Physiol Biochem 80:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.03.034
Yang M, Derbyshire MK, Yamashita RA, Marchler-Bauer A (2020) NCBI’s conserved domain database and tools for protein domain analysis. Curr Protoc Bioinform 69(1):e90. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpbi.90
Yao Y, Du Y, Jiang L, Liu JY (2007) Molecular analysis and expression patterns of the 14-3-3 gene family from Oryza sativa. J Biochem Mol Biol 40(3):349–357. https://doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2007.40.3.349
Yashvardhini N, Bhattacharya S, Chaudhuri S, Sengupta DN (2018) Molecular characterization of the 14-3-3 gene family in rice and its expression studies under abiotic stress. Planta 247(1):229–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-017-2779-4
Zhang JZ (2003) Evolution by gene duplication: an update. Trends Ecol Evol 18:292–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-5347(03)00033-8
Zhang Z (2022) KaKs_calculator 3.0: calculating selective pressure on coding and non-coding sequences. Genomics Proteomics Bioinform. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2021.12.002
Zhang Y, Zhao H, Zhou S, He Y, Luo Q, Zhang F, Qiu D, Feng J, Wei Q, Chen L, Chen M, Chang J, Yang G, He G (2018) Expression of TaGF14b, a 14-3-3 adaptor protein gene from wheat, enhances drought and salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Planta 248(1):117–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-2887-9
Zhang ZB, Wang XK, Wang S, Guan Q, Zhang W, Feng ZG (2022) Expansion and diversification of the 14-3-3 gene family in Camellia sinensis. J Mol Evol 90(3–4):296–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-022-10060-6
Zhao Z, Dong Y, Wang J, Zhang G, Zhang Z, Zhang A, Wang Z, Ma P, Li Y, Zhang X, Ye C, Xie Z (2022) Comparative transcriptome analysis of melon (Cucumis melo L.) reveals candidate genes and pathways involved in powdery mildew resistance. Sci Rep 12(1):4936. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-08763-3
Acknowledgements
The author thanks Mr. Jiannong Zhang in Gansu Agricultural University for his providing melon inbreeding lines. The author also thanks Ms. Lilan Chen in Gansu Agricultural University for her help with manuscript revision.
Funding
This work was supported by Research Program Sponsored by State Key Laboratory of Aridland Crop Science, Gansu Agricultural University (GSCS-2020-09), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GYZ and BQW designed, conceived and performed the experiments. GYZ carried out the bioinformatics, edited the data, figures and tables, draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Cecile Segonzac.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G., Wei, B. Characterization of 14-3-3 gene family and their expression patterns under abiotic and biotic stresses in melon (Cucumis melo L.). Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 64, 1039–1054 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-023-00532-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-023-00532-z