Abstract
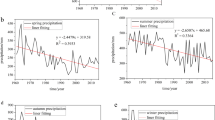
Based on the property of entropy, a new index Q was defined to measure the temporal concentration property of summertime daily rainfall in China, based on daily precipitation data collected at 553 observation stations in China during 1961–2010. Furthermore, changes in the temporal concentration property of summer precipitation in China were investigated. The results indicate that the regions with larger Q values were located in most parts of Northwest China and the north of the Yellow River, where daily precipitation tended to become temporally concentrated during the study period. On the contrary, smaller Q values were found in eastern Tibetan Plateau, southeastern Northwest China, and most parts of Southwest and South China. The most obvious increasing trend of Q index was found in South China and most parts of Southwest China, where precipitation showed a temporal concentration trend. However, a decreasing trend of Q index was found in Northwest China, the Tibetan Plateau, and the north of the Huaihe River. Variations of the Q index and the summer rainfall total during 1961–2010 in China both exhibited an increasing trend, implying larger temporal variability in rainfall attributes. It is illustrated that the summer precipitation in general became more temporally concentrated with more intense rainfall events and wetter days.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar, E., A. A. Barry, M. Brunet, et al., 2009: Changes in temperature and precipitation extremes in western central Africa, Guinea Conakry, and Zimbabwe, 1955–2006. J. Geophys. Res., 114(D2), D02115, doi: 10.1029/2008JD011010.
Bai, A. J., P. M. Zhai, and X. D. Liu, 2006: Climatology and trends of wet spells in China. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 88, 139–148, doi: 10.1007/s00704-006-0235-7.
Balling, R. C. Jr., and G. B. Goodrich, 2011: Spatial analysis of variations in precipitation intensity in the USA. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 104, 415–421, doi: 10.1007/s00704-010-0353-0.
Bates, B. C., Z. W. Kundzewicz, S. Wu, et al., 2008: Climate Change and Water. Technical Paper of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC Secretariat, Geneva, 16.
Brown, P. J., R. S. Bradley, and F. T. Keimig, 2010: Changes in extreme climate indices for northeastern United States, 1870–2005. J. Climate, 23, 6555–6572, doi: 10.1175/2010 JCLI3363.1.
Chen, Y., and P. M. Zhai, 2013: Persistent extreme precipitation events in China during 1951–2010. Climate Res., 57, 143–155, doi: 10.3354/cr01171.
Chen, Y., and P. M. Zhai, 2014: Changing structure of wet periods across Southwest China during 1961–2012. Climate Res., 61, 123–131, doi: 10.3354/cr01247.
Chen, Y., and P. M. Zhai, 2015: Synoptic-scale precursors of the East Asia/Pacific teleconnection pattern responsible for persistent extreme precipitation in the Yangtze River valley. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 141, 1389–1403, doi: 10.1002/qj.2448.
Deni, S. M., A. A. Jemain, and K. Ibrahim, 2008: The spatial distribution of wet and dry spells over Peninsular Malaysia. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 94, 163–173, doi: 10.1007/s00704-007-0355-8.
Endo, N., B. Ailikun, and T. Yasunari, 2005: Trends in precipitation amounts and the number of rainy days and heavy rainfall events during summer in China from 1961 to 2000. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 83, 621–631, doi: 10.2151/jmsj.83.621.
Forland, E. J., A. van Engelen, and J. Ashcroft, 1996: Change in “Normal” Precipitation in the North Atlantic Region. 2nd ed. DMNI Report 9/9 Klima, Norwegian Meteorological Institute, Oslo, 1–27.
Gemmer, M., T. Fischer, T. Jiang, et al., 2011: Trends in precipitation extremes in the Zhujiang River basin, South China. J. Climate, 24, 750–761, doi: 10.1175/2010JCLI3717.1.
Groisman, P. Y., T. R. Karl, D. R. Easterling, et al., 1999: Changes in the probability of heavy precipitation of heavy precipitation: Important indicators of climatic change. Climate Change, 42, 243–283, doi: 10.1023/A:1005432803188.
Hundecha, Y., and A. Bárdossy, 2005: Trends in daily precipitation and temperature extremes across western Germany in the second half of the 20th century. Int. J. Climatol., 25, 1189–1202, doi: 10.1002/joc.1182.
Karl, T. R., 1998: Regional trends and variations of temperature and precipitation. The Regional Impacts of Climate Change. An Assessment of Vulnerability. Watson, R. T., M. C. Zyinyowera, and R. H. Moss, Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 411–437.
Karl, T. R., and R. W. Knight, 1998: Secular trends of precipitation amount, frequency, and intensity in the United States. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 79, 231–241, doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1998)079<0231:STOPAF>2.0.CO;2.
Kunkel, K. E., 2003: North American trends in extreme precipitation. Natural Hazards, 29, 291–305, doi: 10.1023/A: 1023694115864.
Liu, Y. L., J. P. Yan, and M. Y. Cen, 2015: Comprehensive evaluation of precipitation heterogeneity in China. Acta Geographica Sinica, 70, 392–406, doi: 10.11821/dlxb201503004.
Liu, Y. L., J. P. Yan, and M. Y. Cen, 2016: The relationship between precipitation heterogeneity and meteorological drought/flood in China. J. Meteor. Res., 30, 758–770, doi: 10.1007/s13351-016-5993-2.
Peterson, T. C., M. A. Taylor, R. Demeritte, et al., 2002: Recent changes in climate extremes in the Caribbean region. J. Geophys. Res., 107(D21), ACL 16-1–ACL 16-9, doi: 10.1029/2002Jd002251.
Roy, S. S., and R. C. Jr. Balling, 2004: Trends in extreme daily precipitation indices in India. Int. J. Climatol., 24, 457–466, doi: 10.1002/joc.995.
Schmidli, J., and C. Frei, 2005: Trends of heavy precipitation and wet and dry spells in Switzerland during the 20th century. Int. J. Climatol., 25, 753–771, doi: 10.1002/joc.1179.
Schonwiese, C. D., and J. Rapp, 1997: Climate Trend Atlas of Europe Based on Observations 1891–1990. Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1–5.
Shannon, C. E., 1948: A mathematical theory of communication. The Bell System Technical Journal, 27, 379–423, doi: 10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb01338.x.
Tank, A. M. G. K., T. C. Peterson, D. A. Quadir, et al., 2006: Changes in daily temperature and precipitation extremes in central and South Asia. J. Geophys. Res., 111(D16), D16105, doi: 10.1029/2005JD006316.
Vincent, L. A., T. C. Peterson, V. R. Barros, et al., 2005: Observed trends in indices of daily temperature extremes in South America 1960–2000. J. Climate, 18, 5011–5023, doi: 10.1175/JCLI3589.1.
Yin, Z. Y., Y. L. Cai, X. Y. Zhao, et al., 2009: An analysis of the spatial pattern of summer persistent moderate-to-heavy rainfall regime in Guizhou Province of Southwest China and the control factors. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 97, 205–218, doi: 10.1007/s00704-008-0060-2.
Zhai, P. M., and X. H. Pan, 2003: Change in extreme temperature and precipitation over northern China during the second half of the 20th century. Acta Geographica Sinica, 58, 1–10. (in Chinese)
Zhai, P. M., A. J. Sun, F. M. Ren, et al., 1999: Changes of climate extremes in China. Climate Change, 42, 203–218, doi: 10.1023/A:1005428602279.
Zhai, P. M., X. B. Zhang, H. Wan, et al., 2005: Trends in total precipitation and frequency of daily precipitation extremes over China. J. Climate, 18, 1096–1108, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-3318.1.
Zhang, D. L., Y. H. Lin, P. Zhao, et al., 2013: The Beijing extreme rainfall of 21 July 2012: “Right results” but for wrong reasons. Geophys. Res. Lett., 40, 1426–1431, doi: 10.1002/grl.50304.
Zhang, L. J., and Y. F. Qian, 2003: Annual distribution features of precipitation in China and their interannual variations. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 17, 146–163.
Zhang, Q., C. Y. Xu, Z. X. Zhang, et al., 2010: Changes of atmospheric water vapor budget in the Pearl River basin and possible implications for hydrological cycle. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 102, 185–195, doi: 10.1007/s00704-010-0257-z.
Zhang, X. B., W. D. Hogg, and É. Mekis 2001: Spatial and temporal characteristics of heavy precipitation events over Canada. J. Climate, 14, 1923–1936, doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2001)014<1923:SATCOH>2.0.CO;2.
Ziegler, A. D., J. Sheffield, E. P. Maurer, et al., 2003: Detection of intensification in global-and continental-scale hydrological cycles: Temporal scale of evaluation. J. Climate, 16, 535–547, doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2003)016<0535:DOIIGA> 2.0.CO;2.
Zin, W. Z. W., and A. A. Jemain, 2010: Statistical distributions of extreme dry spell in Peninsular Malaysia. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 102, 253–264, doi: 10.1007/s00704-010-0254-2.
Zolina, O., C. Simmer, S. K. Gulev, et al., 2010: Changing structure of European precipitation: Longer wet periods leading to more abundant rainfalls. Geophys. Res. Lett., 37, L06704, doi: 10.1029/2010GL042468.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41575094 and 41275092), Project for Postgraduate Scientific Research and Innovation of Jiangsu Province (KYLX_0842 and CXZZ12-0485), and Innovation Program of the State Key Laboratory of Severe Weather, Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences (2015LASW-A03).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Zhai, P., Lu, E. et al. Changes in temporal concentration property of summer precipitation in China during 1961–2010 based on a new index. J Meteorol Res 31, 336–349 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-017-6020-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-017-6020-y