Abstract
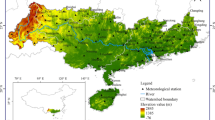
In this study, we investigated the spatial and temporal characteristics of precipitation heterogeneity and meteorological drought/flood in China based on the precipitation-concentration degree (PCD) and the integrated meteorological drought index. We also studied the corresponding relationship between precipitation heterogeneity and meteorological drought/flood in China by using Spearman correlation analysis and canonical correlation analysis. The results show that: (1) The severity of meteorological drought/flood exhibited a spatial pattern of gradual change from Northwest to Southeast China. (2) With a higher PCD and a delayed precipitation-concentration period (PCP), the drought severity was higher but the flood severity was lower. In contrast, with a lower PCD and an early PCP, the drought severity was lower and the flood severity was higher. (3) The correlation between meteorological drought/flood and PCD was significant. The higher the PCD, the longer the duration of drought and more frequently, the droughts occurred, and vice versa. It is concluded that PCD and PCP were significantly correlated with meteorological drought/flood in China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, L.-V., X. B. Zhang, T. C. Peterson, et al., 2006: Global observed changes in daily climate extremes of temperature and precipitation. J. Geophys. Res., 111, D05109, doi: 10.1029/2005jd006290.
Busuioc, A., D. L. Chen, and C. HellstrÄom, 2001: 8. Int. J. Climatol., 21, 557–578, doi: 10.1002/joc.624.
Chen, J., F. D. Bushman, J. D. Lewis, et al., 2013: Structure-constrained sparse canonical correlation analysis with an application to microbiome data analysis. Biostatistics, 14, 244–258, doi: 10.1093/biostatistics/kxs038.
Chen, Y., and P. M. Zhai, 2014: Changing structure of wet periods across Southwest China during 1961–2012. Climate Research, 61, 123–131, doi: 10.3354/cr01247.
CMA, 2006: GB/T 20481-2006 Classification of Meteorological Drought Category. Standards Press of China, Beijing, 3–13. (in Chinese)
Dos Santos, S.-F., and H. S. Brandi, 2014: A canonical correlation analysis of the relationship between sustainability and competitiveness. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 16, 1735–1746, doi: 10.1007/s10098-014-0755-2.
Dong, Q., X. Chen, and T. X. Chen, 2011: Characteristics and changes of extreme precipitation in the Yellow–Huaihe and Yangtze–Huaihe River basins, China. J. Climate, 24, 3781–3795, doi: 10.1175/2010jcli3653.1.
Glann, H. R., 1968: Canonical correlation and its relationship to discriminant analysis and multiple regression. J. Atmos. Sci., 25, 23–31, doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1968)025<0023:ccairt>2.0.CO;2.
Hotelling, H., 1936: Relations between two sets of variates. Biometrika, 28, 321–377, doi: 10.2307/2333955.
Jackson, D.-J.-R., J. A. Stillman, and P. Englert, 2010: Task-based assessment centers: Empirical support for a systems model. International Journal of Selection and Assessment, 18, 141–154, doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2389.2010.00496.x.
Li, X.-M., F. Q. Jiang, L. H. Li, et al., 2011: Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation concentration index, concentration degree, and concentration period in Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Climatol., 31, 1679–1693, doi: 10.1002/joc.2181.
Liu Yonglin, Yan Junping, and Cen Minyi, 2015: Comprehensive evaluation of precipitation heterogeneity in China. Acta Geographica Sinica, 70, 392–406. (in Chinese)
Naylor, M.-G., X. H. Lin, S. T. Weiss, et al., 2010: Using canonical correlation analysis to discover genetic regulatory variants. PLoS One, 5, e10395, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010395.
Qin, W.-J., Y. Q. Wang, and Z. N. Qin, 2010: Study on the variation characteristics of precipitation concentration degree in Guangxi under the background of global climate becoming warm. Meteor. Environ. Res., 1, 17–21.
Ran, Q.-H., Z. N. Shi, and Y. P. Xu, 2013: Canonical correlation analysis of hydrological response and soil erosion under moving rainfall. Journal of Zhejiang University Science (A), 14, 353–361, doi: 10.1631/jzus.a1200306.
Singh, A., M. A. Kulkarni, U. C. Mohanty, et al., 2012: Prediction of Indian summer monsoon rainfall (ISMR) using canonical correlation analysis of global circulation model products. Meteor. Appl., 19, 179–188, doi: 10.1002/met.1333.
Soneson, C., H. LilljebjÄorn, T. Fioretos, et al., 2010: Integrative analysis of Gene expression and copy number alterations using canonical correlation analysis. BMC Bioinformatics, 11, 191, doi: 10.1186/14712105-11-191.
Tang Qicheng and Yang Xiuyun, 1982: Calculation and discussion of non-uniformity coe±cients of annual river run-off distribution. Resources Science, 4, 59–65. (in Chinese)
Wang Chunlin, Guo Jing, Xue Lifang, et al., 2011: An improved comprehensive meteorological drought index CInew and its applicability analysis. Chinese J. Agrometeor., 32, 621–626, 631. (in Chinese)
Wang Huan, Lu Er, Zhao Wei, et al., 2015: A new method to reflect the intra-seasonal heterogeneity of the precipitation in China. J. Trop. Meteor., 31, 655–663. (in Chinese)
Ye, R.-Z., and A. L. Wright, 2010: Multivariate analysis of chemical and microbial properties in histosols as influenced by land-use types. Soil and Tillage Research, 110, 94–100, doi: 10.1016/j.still.2010.06.013.
Zhang Lujin and Qian Yongfu, 2003: Annual distribution features of precipitation in China and their interannual variations. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 17, 146–163.
Zhang Lujun and Qian Yongfu, 2004: A study on the feature of precipitation concentration and its relation to flood-producing in the Yangtze River valley of China. Chinese J. Geophysics, 47, 622–630. (in Chinese)
Zhang, X.-B., G. Hegerl, F. W. Zwiers, et al., 2005: Avoiding inhomogeneity in percentile-based indices of temperature extremes. J. Climate, 18, 1641–1651, doi: 10.1175/jcli3366.1.
Zhang, X.-B., J. F. Wang, F. W. Zwiers, et al., 2010: The influence of large-scale climate variability on winter maximum daily precipitation over North America. J. Climate, 23, 2902–2915, doi: 10.1175/2010jcli3249.1.
Zhao Haiyan, Gao Ge, Zhang Peiqun, et al., 2011: The modification of meteorological drought composite index and its application in Southwest China. J. Appl. Meteor. Sci., 22, 698–705. (in Chinese)
Zolina, O., C. Simmer, S. K. Gulev, et al., 2010: Changing structure of European precipitation: Longer wet periods leading to more abundant rainfalls. Geophys. Res. Lett., 37, L06704, doi: 10.1029/2010gl042468.
Zou Xukai, Ren Guoyu, and Zhang Qiang, 2010: Drought variations in China based on a compound index of meteorological drought. Climatic Environ. Res., 15, 371–378. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (41171090) and National Social Science Foundation of China (14AZD094 and 14XSK019).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Yan, J. & Cen, M. The relationship between precipitation heterogeneity and meteorological drought/flood in China. J Meteorol Res 30, 758–770 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-016-5993-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-016-5993-2