Abstract
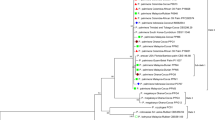
A total of 15 endophytic Bacillus thuringiensis isolates were obtained from root nodules of six legumes (soybean, ricebean, gahat, frenchbean, lentil and pea). All of these isolates were characterized by the presence of one of two different types of crystalline inclusions (spherical and bipyramidal) and tolerance to a wide pH range (4–10; optimum 7.0) and NaCl concentrations up to 8%. Genetic diversity among the B. thuringiensis isolates was determined by repetitive extragenic palindromic PCR assays (rep-PCR) using the Bacillus cereus-repetitive extragenic palindromic, BOX, enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus sequence and (GTG)5 primers. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis proteogram of the B. thuringiensis isolates revealed the presence of two major polypeptides (24.4 and 131.0 kDa). Maximum crystal protein profile was observed in the B. thuringiensis isolates producing the spherical crystal, while those isolates producing the bipyramidal crystal protein showed four four major polypeptides (24.4, 33.8, 81.2 and 131.0 kDa). The purified crystal protein profile of the B. thuringiensis isolates revealed the presence of only one major protein of 130 kDa mass. Isolates VRB1 and VLG15 possessing the cry1 and cry2 family genes demonstrated 100% mortality against first-instar larvae of the Bihar hairy caterpillar (lepidopteran pest). Our study of the ecological and molecular diversity among newly identified B. thuringiensis isolates suggests that these could be useful in planning new strategies for integrated pest management in sustainable agricultural systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allwin L, Kennedy JS, Radhakrishnan V (2007) Characterization of different geographical strains of Bacillus thuringiensis from Tamil Nadu. Res J Agri Biol Sci 3:362–366
Andrup L, Jensen GB, Wilcks A, Smidt L, Hoflack L, Mahillon J (2003) The patchwork nature of rolling–circle plasmids: comparison of six plasmids from two distinct Bacillus thuringiensis serotypes. Plasmid 49:205–232
Aronson AI, Beckman W, Dunn Ρ (1986) Bacillus thuringiensis and related insect pathogens. In: Microbiol Rev Ingraham JL (ed) Washington DC, American Society for Microbiology, pp 1–24
Arturo RR, Ibarra JE (2005) Fingerprinting of Bacillus thuringiensis type strains and isolates by using Bacillus cereus group specific repetitive extragenic palindromic sequence based PCR analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1346–1355
Arturo RR, Ibarra JE (2008) Plasmid patterns of Bacillus thuringiensis type strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:125–129
Attathom T, Chongrattanameteekul W, Chanpaisang J, Siriyan R (1995) Morphological diversity and toxicity of delta-endotoxin produced by various strains of Bacillus thuringiensis. Bull Entomol Res 85:167–173
Bai Y, D’Aoust F, Smith DL, Driscoll BT (2002) Isolation of plant-growth-promoting Bacillus strains from soybean root nodules. Can J Microbiol 48:230–238
Beatrix T (1997) The difference between conventional Bacillus thuringiensis strains and transgenic insect resistant plants: Possible reasons for rapid resistance development and susceptibility of non target organisms. Prepared for the 3rd Meeting of the Open-ended Working Group on Biosafety, Oct 13–17, Montreal, Canada, pp 1–6
Bizzarri MF, Bishop AH (2008) The ecology of Bacillus thuringiensis on the Phylloplane: colonization from soil, plasmid transfer, and interaction with larvae of Pieris brassicae. Microb Ecol 56:133–139
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of micro-gram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–25
Bravo A, Sarabia S, Lopez L, Ontiveros H, Abarca C, Ortiz A, Ortiz M, Lina L, Villalobos FJ, Pena G, Valdez MN, Soberon M, Quintero R (1998) Characterization of cry genes in a Mexican Bacillus thuringiensis strain collection. Appl Envion Microbiol 64:4965–4972
Burges HD, Hurst JA (1977) Ecology of Bacillus thuringiensis in storage moths. J Invertebr Pathol 30:131–139
Burges HD, Jarrett P (1990) Preparation of strains of Bacillus thuringiensis having an improved activity against certain lepidopterous pest and novel strain produced thereby. US Patent Number 4:935353. United States Patent and Trademark Office, Alexandria
Carozzi NB, Kramer VC, Warren GW, Evola S, Koziel MG (1991) Prediction of insecticidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis strains by polymerase chain reaction product profiles. Appl Envion Microbiol 57:3057–3061
Chatterjee SN, Bhattacharya TK, Chandra G (2007) Ecology and diversity of Bacillus thuringiensis in soil environment. Afr J Biotechnol 6:1587–1591
Collins CH, Lyne PM (1980) Microbiological methods. Butterworth and Co., London
da Silva RB, Valicente FH (2013) Molecular characterization of Bacillus thuringiensis using rep-PCR. SpringerPlus 2:641. doi:10.1186/2193-1801-2-641
Dangar TK, Babu YK, Das J (2010) Population dynamics of soil microbes and diversity of Bacillus thuringiensis in agricultural and botanic garden soils of India. Afr J Biotechnol 9:496–501
Dean DH (1984) Biochemical genetics of the bacterial insect-control agent Bacillus thuringiensis: basic principles and prospects of genetic engineering. Biotechnol Gen Eng Rev 2:543–525
De Brujin FJ (1992) Use of repetitive (repetitive extragenic palindromic and enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus) sequences and the polymerase chain reaction to fingerprint the genomes of Rhizobium isolates and other soil bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2180–2187
Dulmage HT, Correa JA, Martinez AJ (1970) Co-precipitation with lactose as a means of recovering the spore-crystal complex of Bacillus thuringiensis. J Invertebr Pathol 15:15–20
Ferrandis MD, Juarez-Pe’rez VM, Frutos R, Bel Y, Ferre J (1999) Distribution of cryI, cryII and cryV genes within Bacillus thuringiensis isolates from Spain. Syst Appl Microbiol 22:179–185
Gonzalez JM, Brown BJ, Carlton BC (1982) Transfer of Bacillus thuringiensis plasmid coding for β-endotoxin among strains of Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus cereus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:6951–6955
Harwood CR, Cutting SM (1990) Molecular biology methods for Bacillus. Techniques in microbial genetics, practical manual, vol 56. Department of Entomology, University of Maryland, College Park, pp 1314–1321
Hastowo S, Lay BW, Ohba M (1992) Naturally occurring Bacillus thuringiensis in Indonesia. J Appl Bacteriol 73:108–113
Holt JG, Kreig NR, Sneath PHA, Stanley JT, Williams ST (1994) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 9th edn. The Williams & Wilkins Co, Baltimore
Iriarte J, Porcar M, Lecadet MM, Caballero P (2000) Isolation and characterization of Bacillus thuringiensis strains from aquatic environments in Spain. Curr Micobiol 40:402–408
Jaccard P (1908) Nouvelles recherches sur la distribution florale. Bull Soc Vaud Sci Nat 4:223–270
Jarrett P, Stephenson M (1990) Plasmid transfer between strains of Bacillus thuringiensis infecting Galleria mellonella and Spodoptera littoalis. Appl Environ Microbiol 31:346–352
Kan FL, Chen ZY, Wang ET, Tian CF, Sui XH, Chen WX (2007) Characterization of symbiotic and endophytic bacteria isolated from root nodules of herbaceous legumes grown in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and in other zones of China. Arch Microbiol 188:103–115
Krattiger AF (1997) Insect resistance crops: A case study of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) and its transfer to developing countries. ISAAA Briefs No 2. ISAAA, Ithaca, p 42
Kronstad JW, Schnepf HF, Whiteley HR (1983) Diversity of locations for Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein genes. J Bacteriol 154:419–428
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Li JH, Wang ET, Chen WF, Chen WX (2008) Genetic diversity and potential for promotion of plant growth detected in nodule endophytic bacteria of soybean grown in Heilongjiang province of China. Soil Biol Biochem 40:238–246
Lupski JR, Weinstock GM (1992) Short interspersed repetitive DNA sequences in prokaryotic genomes. J Bacteriol 174:4525–4529
Manuel P, Victor J-P (2003) PCR-based identification of Bacillus thuringiensis pesticidal crystal genes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26(2003):419–432
Martin BO, Humbert M, Camara E, Guenci J, Walker T, Mitchell P, Andrew M, Prudhomme G, Alloing R, Hukenbeck DA, Morrison GJ, Boulnois JP, Claverys (1992) A highly conserved repeated DNA element located in the chromosome of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Nucleic Acids Res 20:3479–3483
Masson L, Erlandson M, Pulstai-Carey M, Brosseau R, Juarez- Perez VM, Frutos R (1998) A holistic approach for determining the entomopathogenic potencial of Bacillus thuringiensis strains. Appl Envion Microbiol 64:4782–4788
Ramalakshmi A, Udayasuriyan V (2010) Diversity of Bacillus thuringiensis isolated from Western Ghats of Tamil Nadu State, India. Curr Micriobiol 61:13–18
Rohlf FJ (1998) NTSYSpc numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Version 2.02i. Exeter Software, Setauket, New York
Sanchis V, Lereclus D, Menou G, Chaufaux J, Lecadet MM (1988) Multiplicity of delta-endotoxin genes with different specificities in Bacillus thuringiensis aizawai. Mol Microbiol 2:393–404
Schnepf E, Crickmors N, Rie JV, Lereclus D, Baum J, Feitelson J, Zeigler DR, Dean DH (1998) Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:775–806
Seifinejad A, Jouzani SGR, Hosseinzadeh A, Abdmishani C (2008) Characterization of Lepidoptera-active cry and vip genes in Iranian Bacillus thuringiensis strain collection. Biol Control 44:216–226
Shishir A, Roy A, Islam N, Rahman A, Khan SN, Hoq MM (2014) Abundance and diversity of Bacillus thuringiensis in Bangladesh and their cry genes profile. Front Environ Sci 2:20. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2014.00020
Siliciano SD, Fortein N, Mihoc A, Wisse G, Labelle S, Beaumier D, Ouellette D, Roy R, Whyte LG, Banks MK, Schwab P, Lee K, Greer CW (2001) Selection of specific endophytic bacterial genotypes by plants in response to soil contamination. Appl Envion Microbiol 67:2469–2475
Smith RA, Couche GA (1991) The phylloplane as a source of Bacillus thuringiensis variants. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:311–315
Travers RS, Martin AW, Reichelderfer CF (1987) Selective process for efficient isolation of soil Bacillus spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:1263–1266
Uribe D, Martinez W, Ceron J (2003) Distribution and diversity of cry genes in native strains of Bacillus thuringiensis obtained from different ecosystems from Colombia. J Invertebr Pathol 82:119–127
Valicente FH, Lana UGP (2008) Molecular Characterization of the Bacillus thuringiensis (Berliner) Strains 344 and 1644, Efficient Against Fall Armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith). Revista Brasileira de Milho e Sorgo 7(3):195–209
Versalovic J, Schneider M, De-Bruijn FJ, Lupski JR (1994) Genomic fingerprinting of bacteria using repetitive sequence-based polymerase chain reaction. Methods Mol Cell Biol 5:25–40
Wadman M (1997) Dispute over insect resistance to crops. Nature 388:817
Xue J, Liang GM, Crickmore N, Li HT, He KL, Song FP, Feng X, Huang DF, Zhang J (2008) Cloning and characterization of a novel Cry1A toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis with high toxicity to the Asian corn borer and other lepidopteran insect. FEMS Microbiol Lett 280:95–101
Zhang YZ, Chen WF, Li M, Sui XH, Liu HC, Zhang XX, Chen WX (2012) Bacillus endoradicis sp. nov., an endophytic bacterium isolated from soybean root. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:359–363
Acknowledgements
The facilities provided by the Director, ICAR–Vivekananda Institute of Hill Agriculture, Almora-263601, Uttarakhand, India to carry out this study are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, P.K., Bisht, S.C., Ruwari, P. et al. Genetic diversity and functional characterization of endophytic Bacillus thuringiensis isolates from the North Western Indian Himalayas. Ann Microbiol 67, 143–155 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-016-1244-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-016-1244-0