Abstract
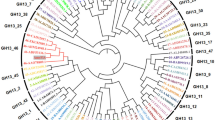
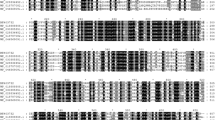
In this study, an alpha-amylase enzyme from a locally isolated Aspergillus flavus NSH9 was purified and characterized. The extracellular α-amylase was purified by ammonium sulfate precipitation and anion-exchange chromatography at a final yield of 2.55-fold and recovery of 11.73%. The molecular mass of the purified α-amylase was estimated to be 54 kDa using SDS-PAGE and the enzyme exhibited optimal catalytic activity at pH 5.0 and temperature of 50 °C. The enzyme was also thermally stable at 50 °C, with 87% residual activity after 60 min. As a metalloenzymes containing calcium, the purified α-amylase showed significantly increased enzyme activity in the presence of Ca2+ ions. Further gene isolation and characterization shows that the α-amylase gene of A. flavus NSH9 contained eight introns and an open reading frame that encodes for 499 amino acids with the first 21 amino acids presumed to be a signal peptide. Analysis of the deduced peptide sequence showed the presence of three conserved catalytic residues of α-amylase, two Ca2+-binding sites, seven conserved peptide sequences, and several other properties that indicates the protein belongs to glycosyl hydrolase family 13 capable of acting on α-1,4-bonds only. Based on sequence similarity, the deduced peptide sequence of A. flavus NSH9 α-amylase was also found to carry two potential surface/secondary-binding site (SBS) residues (Trp 237 and Tyr 409) that might be playing crucial roles in both the enzyme activity and also the binding of starch granules.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Zeid AM (1996) Production, purification and characterization of an extracellular alpha-amylase enzyme isolated from Aspergillus flavus. Microbios 89(358):55–66
Aguilar G, Morlon-Guyot J, Trejo-Aguilar B, Guyot JP (2000) Purification and characterization of an extracellular α-amylase produced by Lactobacillus manihotivorans LMG 18010 T, an amylolytic lactic acid bacterium. Enzyme Microb Technol 27(6):406–413
Bhanja T, Rout S, Banerjee R, Bhattacharya BC (2007) Comparative profiles of α-amylase production in conventional tray reactor and GROWTEK bioreactor. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 30:369–376
Bhardwaj S, Vedamurthy AB, Bhattacharya S, Das A (2012) Effect of inorganic salts and surfactants on the production of [alpha]-amylase by a mangrove isolate of Aspergillus flavus using solid-state fermentation. J Chem Biol Phys Sci (JCBPS) 2(3):1390
Bhattacharya S, Bhardwaj S, Das A, Anand S (2011) Utilization of sugarcane bagasse for solid-state fermentation and characterization of α-amylase from Aspergillus flavus isolated from Muthupettai Mangrove, Tamil Nadu, India. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 5(12):1012–1022
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the determination of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chakraborty K, Bhattacharyya BK, Sen SK (2000) Purification and characterization of a thermostable α-amylase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Folia Microbiologica (Praha) 45(3):207–210
Chen J, Li DC, Zhang YQ, Zhou QX (2005) Purification and characterization of a thermostable glucoamylase from Chaetomium thermophilum. J Gen Appl Microbiol 51:175–181
Cockburn D, Svensson B (2013) Surface binding sites in carbohydrate active enzymes: an emerging picture of structural and functional diversity. Carbohydr Chem 39:204–221
Cockburn D, Nielsen MM, Christiansen C, Andersen JM, Rannes JB, Blennow A, Svensson B (2015) Surface binding sites in amylase have distinct roles in recognition of starch structure motifs and degradation. Int J Biol Macromol 75:338–345
Couto SR, Sanromán MA (2006) Application of solid-state fermentation to food industry—a review. J Food Eng 76:291–302
Cubero OF, Crespo A, Fatehi J, Bridge PD (1999) DNA extraction and PCR amplification method suitable for fresh, herbarium-stored, lichenized and other fungi. Plant Syst Evol 216:243–249
Da Lage JL, Binder M, Hua-Van A, Janeck S, Casanel D (2013) Gene make-up: rapid and massive intron gains after horizontal transfer of a bacterial α-amylase gene to Basidiomycetes. BMC Evol Biol 13:40
El-Abyad MS, Fawzeya A, El-Sayed A, Hafez M (1992) Effects of culture conditions on amylase production by some soil fungi. Zentralblatt fur Mikrobiologie 147:23–34
El-Safey EM, Ammar MS (2004) Purification and characterization of α-amylase isolated from Aspergillus falvus var. columnaris. Assiut Univ Bull Environ Res 7(1):93–100
Fadahunsi IF, Garuba OE (2012) Amylase production by Aspergillus flavus associated with the bio-deterioration of starch-based fermented foods. NY Sci J 5(1):13–18
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Goyal N, Gupta JK, Soni SK (2005) A novel raw starch digesting thermostable α-amylase from Bacillus sp. I-3 and its use in the direct hydrolysis of raw potato starch. Enzyme Microb Technol 37(7):723–734
Gupta R, Gigras P, Mohapatra H, Goswami VK, Chauhan B (2003) Microbial α-amylases: a biotechnological perspective. Process Biochem 38:1599–1616
Gurr SJ, Unkles SE, Kinghorn JR (1987) The structure and organization of nuclear genes of filamentous fungi. In: Kinghorn JR (ed) Gene structure in eukaryotic microbes. IRL, Oxford, pp 93–139
Henrissat B (1991) A classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem J 280(2):309–316
Hostinová E, Janeček Š, Gašperík J (2010) Gene sequence, bioinformatics and enzymatic characterization of α-amylase from Saccharomycopsis fibuligera KZ. Protein J 29(5):355–364
Imperiali B, O’Connor SE (1999) Effect of N-linked glycosylation on glycopeptide and glycoprotein structure. Curr Opin Chem Biol 3(6):643–649
Janecek S (1997) α-Amylase family: molecular biology and evolution. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 67(1):67–97
Janecek S (2002) How many conserved sequence regions are there in the α-amylase family? Biologia Bratislava 57(Suppl. 11):29–41
Jones DT, Taylor WR, Thornton JM (1992) The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Comput Appl Biosci CABIOS 8(3):275–282
Karim KMR, Husaini A, Hossain M, Sing NN, Mohd Sinang F, Hussain MHM, Roslan HA (2016) Heterologous, expression, and characterization of thermostable glucoamylase derived from Aspergillus flavus NSH9 in Pichia pastoris. BioMed Res Int 2016:5962028. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5962028
Karim KMR, Husaini A, Tasnim T (2017) Production and characterization of crude glucoamylase from newly isolated Aspergillus flavus NSH9 in liquid culture. Am J Biochem Mol Biol 7:118–126
Kariya M, Shigemi Y, Yano M, Konno H, Takii YJ (2003) Purification and properties of alpha-amylase from Aspergillus oryzae MIBA316. J Biol Macromol 2:57–60
Khoo SL, Amirul AA, Kamaruzaman M, Nazalan N, Azizan MN (1994) Purification and characterization of alpha amylase from Aspergillus. Folia Microbiol 39:392–398
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
MacGregor EA (2005) An overview of clan GH-H and distantly related families. Biologia 60(Suppl 16):5–12
MacGregor EA, Janeček Š, Svensson B (2001) Relationship of sequence and structure to specificity in the α-amylase family of enzymes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Protein Struct Mol Enzymol 1546(1):1–20
Madihah MS, Ariff AB, Khalil MS, Suraini AA, Karim MIA (2000) Partial purification and some properties of alpha amylase and glucoamylase obtained as by-product from direct fermentation of sago starch to solvent by Clostridium acetobutylicum. Pak J Biol Sci 5:744–749
Marchler-Bauer A, Bo Y, Han L, He J, Lanczycki CJ, Lu S, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, Geer RC, Gonzales NR, Gwadz M (2017) CDD/SPARCLE: functional classification of proteins via subfamily domain architectures. Nucleic Acids Res 45(D1):D200–D203
Matsubara T, Ammar YB, Anindyawati T, Yamamoto S, Ito K, Iizuka M, Minamiura N (2004) Molecular cloning and determination of the nucleotide sequence of raw starch digesting α-Amylase from Aspergillus awamori KT-11. J Biochem Mol Biol 37(4):429–438
Matsuura A, Ishii Y, Yuasa H, Narita H, Kon S, Takami T, Kikuchi K (1984) Rat T lymphocyte antigens comparable with mouse Lyt-1 and Lyt-2, 3 antigenic systems: characterization by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol 132(1):316–322
Nakajima R, Imanaka T, Aiba S (1986) Comparison of amino acid sequences of eleven different α-amylases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 23:355–360
Negi S, Banerjee R (2009) Characterization of amylase and protease produced by Aspergillus awamori in a single bioreactor. Food Res Int 42(4):443–448
Nguyen QD, Rezessy-Szabo JM, Claeyssens M, Stals I, Hoschke A (2002) Purification and characterization of amylolytic enzymes from thermophilic fungus Thermomyces lanuginosus strain ATCC 34626. Enzyme Microb Technol 31:345–352
Nielsen MM, Bozonnet S, Seo ES, Mótyán JA, Andersen JM, Dilokpimol A, Abou Hachem M, Gyémánt G, Næsted H, Kandra L, Sigurskjold BW (2009) Two secondary carbohydrate binding sites on the surface of barley α-amylase 1 have distinct functions and display synergy in hydrolysis of starch granules. Biochemistry 48(32):7686–7697
Nielsen JW, Kramhøft B, Bozonnet S, Hachem MA, Stipp SLS, Svensson B, Willemoës M (2012) Degradation of the starch components amylopectin and amylose by barley α-amylase 1: role of surface binding site 2. Arch Biochem Biophys 528(1):1–6
Ragunath C, Manuel SG, Venkataraman V, Sait HB, Kasinathan C, Ramasubbu N (2008) Probing the role of aromatic residues at the secondary saccharide-binding sites of human salivary α-amylase in substrate hydrolysis and bacterial binding. J Mol Biol 384(5):1232–1248
Reddy NS, Nimmagadda A, Rao KS (2003) An overview of the microbial α-amylase family. Afr J Biotechnol 2(12):645–648
Sanghvi GV, Koyani RD, Rajput KS (2011) Isolation, optimization and partial purification of amylase from Chrysosporium asperatum by submerged fermentation. J Microbiol Biotechnol 21(5):470–476
Saranraj P, Stella D (2013) Fungal amylase—a review. Int J Microbiol Res 4(2):203–211
Saxena L, Iyer BK, Ananthanarayan L (2010) Purification of a bifunctional amylase/protease inhibitor from ragi (Eleusine coracana) by chromatography and its use as an affinity ligand. J Chromatogr B 878(19):1549–1554
Schumann U, Smith NA, Wang MB (2013) A fast and efficient method for preparation of high-quality RNA from fungal mycelia. BMC Res Notes 6:71
Shaw JF, Lin FP, Chen SC, Chen HC (1995) Purification and properties of an extracellular α-amylase from Thermus sp. Bot Bull Acad Sinica 36:195–200
Souza PMD (2010) Application of microbial α-amylase in industry—a review. Braz J Microbiol 41(4):850–861
Stam MR, Danchin EGJ, Rancurel C, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B (2006) Dividing the large glycoside hydrolase family 13 into subfamilies: towards improved functional annotations of alpha-amylase-related proteins. Protein Eng Des Sel 19:555–562
Sundarram A, Murthy TPK (2014) α-Amylase production and applications: a review. J Appl Environ Microbiol 2(4):166–175
Takase K, Matsumoto T, Mizuno H, Yamane K (1992) Site-directed mutagenesis of active site residues in Bacillus subtilis α-amylase. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Protein Struct Mol Enzymol 1120(3):281–288
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Valk V, Van Der Kaaij RM, Dijkhuizen L (2016) Characterization of the starch-acting MaAmyB enzyme from Microbacterium aurum B8. A representing the novel subfamily GH13_42 with an unusual, multi-domain organization. Sci Rep 6:36100–36111
van der Kaaij RM, Janecek S, van der Maarel MJEC, Dijkhuizen L (2007) Phylogenetic and biochemical characterization of a novel cluster of intracellular fungal alpha-amylase enzymes. Microbiology 153:4003–4015
van der Maarel MJEC, van der Veen B, Uitdehaag JCM, Leemhuis H, Dijkhuizen L (2002) Properties and applications of starch-converting enzymes of the alpha-amylase family. J Biotechnol 94(2):137–155
Vihinen M, Ollikka P, Niskanen J, Meyer P, Suominen I, Karp M, Holm L, Knowles J, Mäntsälä P (1990) Site-directed mutagenesis of a thermostable α-amylase from Bacillus stearothermophilus: putative role of three conserved residues. J Biochem 107(2):267–272
Xiao Z, Storms R, Tsang A (2006) A quantitative starch-iodine method for measuring alpha-amylase and glucoamylase activities. Anal Biochem 351:146–148
Zhang X, Caner S, Kwan E, Li C, Brayer GD, Withers SG (2016) Evaluation of the significance of starch surface binding sites on human pancreatic α-amylase. Biochemistry 55(43):6000–6009
Zhang Q, Han Y, Xiao H (2017) Microbial α-amylase: a biomolecular overview. Process Biochem 53:88–101
Acknowledgements
This research project was financially supported by the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia (MoHE) under the Research Acculturation Grant Scheme (RAGS) RAGS/b(9)/931/2012(32).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karim, K.M.R., Husaini, A., Sing, N.N. et al. Purification of an alpha amylase from Aspergillus flavus NSH9 and molecular characterization of its nucleotide gene sequence. 3 Biotech 8, 204 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1225-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1225-z