Abstract
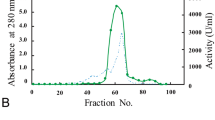
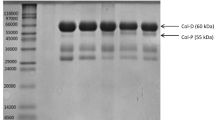
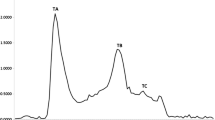
Skin and bone gelatins of pangasius catfish (Pangasius sutchi) were hydrolyzed with alcalase to isolate Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides. Samples with the highest degree of hydrolysis (DH) were separated into different fractions with molecular weight cut-off (MWCO) sizes of 10, 3 and 1 kDa, respectively and assayed for ACE inhibitory activity. Skin and bone gelatins had highest DH of 64.87 and 68.48 % after 2 and 1 h incubation, respectively. Results from this study indicated that by decreasing the molecular weight of fractions, ACE inhibitory activity was increased. Therefore, F3 permeates (MWCO < 1 kDa) of skin (IC50 = 3.2 μg/ml) and bone (IC50 = 1.3 μg/ml) gelatins possessed higher ACE inhibitory activity compared to their untreated gelatins and corresponding hydrolyzed fractions. In this study, the major amino acids were Glycine followed by Proline with an increased amount of hydrophobic amino acid content in F3 permeates of skin (4.01 %) and bone (5.79 %) gelatin. Digestion stability against gastrointestinal proteases did not show any remarkable change on ACE inhibition potency of these permeates. It was concluded that alcalase hydrolysis of P. sutchi by-products could be utilized as a part of functional food or ingredients of a formulated drug in order to control high blood pressure.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaiz M, Navarro JL, Girón J, Vioque E (1992) Amino acid analysis by high-performance liquid chromatography after derivatization with diethyl ethoxymethylenemalonate. J Chromatogr 591:181–186
Alemán A, Giménez B, Pérez-Santín E, Gómez-Guillén MC, Montero P (2011) Contribution of Leu and Hyp residues to antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory activities of peptides sequences isolated from squid gelatin hydrolysate. Food Chem 125:334–341
Alfaro AT, Costa CS, Fonseca GG, Prentice C (2009) Effect of extraction parameters on the properties of gelatin from King weakfish (Macrodon ancylodon) bones. Food Sci Tech Int 15:553–562
AOAC (2005) Official methods of the association of official agricultural Chemist’s International, 17th edn. Gaithersburg, AOAC International
Benjakul S, Morrissey MT (1997) Protein hydrolysates from pacific whiting solid wastes. J Agric Food Chem 45:3423–3430
Bougatef A, Nedjar-Arroume N, Ravallec-Plé R, Leroy Y, Guillochon D, Barkia A, Nasri M (2008) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activities of sardinelle (Sardinella aurita) by-products protein hydrolysates obtained by treatment with microbial and visceral fish serine proteases. Food Chem 111:350–356
Byun HG, Kim SK (2001) Purification and characterization of angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from Alaska pollack (Theragra chalcogramma) skin. Process Biochem 36:1155–1162
Chen HM, Muramoto K, Yamauchi F (1995) Structural analysis of antioxidative peptides from soybean β-conglycinin. J Agric Food Chem 43:574–578
Church FC, Swaisgood HE, Porter DH, Catignani GL (1983) Spectrophotometric assay using o-phthaldialdehyde for determination of proteolysis in milk and isolated milk proteins. J Dairy Sci 66:1219–1227
Cohen SA, Meys M, Tarvin TL (1988) The PicoTag Method. A manual of advanced techniques for amino acid analysis. Waters Chromatography Division, Millipore Corp, Milford, MA
Diniz FM, Martin AM (1996) Use of response surface methodology to describe the combined effects of pH, temperature and E/S ratio on the hydrolysis of dogfish (Squalus acanthias) muscle. Int J Food Sci Tech 31:419–426
Fahmi A, Morimura S, Guo HC, Shigematsu T, Kida K, Uemura Y (2004) Production of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from sea bream scales. Process Biochem 39:1195–1200
Fujita H, Yokoyama K, Yoshikawa M (2000) Classification and antihypertensive activity of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from food protein. J Food Sci 65:564–569
Ghassem M, Siau Fern S, Said M, Mohd Ali Z, Ibrahim S, Salam Babji A (2011a) Kinetic characterization of Channa striatus muscle sarcoplasmic and myofibrillar protein hydrolysates. J Food Sci Technol. doi:10.1007/s13197-011-0526-6
Ghassem M, Arihara K, Babji AS, Said M, Ibrahim S (2011b) Purification and identification of ACE inhibitory peptides from Haruan (Channa striatus) myofibrillar protein hydrolysate using HPLC–ESI-TOF MS/MS. Food Chem 129:1770–1777
Giménez B, Alemán A, Montero P, Gómez-Guillén MC (2009) Antioxidant and functional properties of gelatin hydrolysates obtained from skin of sole and squid. Food Chem 114:976–983
Gómez-Guillén MC, Giménez B, López-Caballero ME, Montero MP (2011) Functional and bioactive properties of collagen and gelatin from alternative sources: a review. Food Hydrocoll 25:1813–1827
Gómez-Ruiz JÁ, Ramos M, Recio I (2004) Identification and formation of angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides in Manchego cheese by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1054:269–277
Guérard F, Guimas L, Binet A (2002) Production of tuna waste hydrolysates by a commercial neutral protease preparation. J Mol Catal B: Enzym 19:489–498
Harnedy PA, Fitzgerald RJ (2012) Bioactive peptides from marine processing waste and shellfish: a review. J Funct Foods 4:6–24
Hernández-Ledesma B, Del Mar CM, Recio I (2011) Antihypertensive peptides: production, bioavailability and incorporation into foods. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 165:23–35
Hoyle NT, Merritt JH (1994) Quality of fish protein hydrolysate from Herring (Clupea harengus). J Food Sci 59:76–79
Ichimura T, Yamanaka A, Otsuka T, Yamashita E, Maruyama S (2009) Antihypertensive effect of enzymatic hydrolysate of collagen and Gly-Pro in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:2317–2319
Jeon Y, Byun H, Kim S (1999) Improvement of functional properties of cod frame protein hydrolysates using ultrafiltration membranes. Process Biochem 35:471–478
Jimsheena VK, Gowda LR (2011) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides derived from arachin by simulated gastric digestion. Food Chem 125:561–569
Karim A, Bhat R (2009) Fish gelatin: properties, challenges, and prospects as an alternative to mammalian gelatins. Food Hydrocoll 23:563–576
Kim SK, Byun HG, Park PJ, Shahidi F (2001) Angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides purified from bovine skin gelatin hydrolysate. J Agric Food Chem 49:2992–2997
Kim SY, Je JY, Kim SK (2007) Purification and characterization of antioxidant peptide from hoki (Johnius belengerii) frame protein by gastrointestinal digestion. J Nutr Biochem 18:31–38
Klompong V, Benjakul S, Kantachote D, Shahidi F (2007) Antioxidative activity and functional properties of protein hydrolysate of yellow stripe trevally (Selaroides leptolepis) as influenced by the degree of hydrolysis and enzyme type. Food Chem 102:1317–1327
Korhonen H, Pihlanto A (2003) Food-derived bioactive peptides-opportunities for designing future foods. Curr Pharm Des 9:1297–1308
Kristinsson HG, Rasco BA (2000a) Biochemical and functional properties of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) muscle hydrolyzed with various alkaline proteases. J Agric Food Chem 48:657–666
Kristinsson HG, Rasco BA (2000b) Fish protein hydrolysates: production, biochemical and functional properties. Food Sci Nutr 40:43–81
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 277:680–685
Lee JK, Hong S, Jeon JK, Kim SK, Byun HG (2009) Purification and characterization of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from the rotifer, Brachionus rotundiformis. Bioresour Technol 100:5255–5259
Lee JK, Jeon JK, Byun HG (2011) Effect of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide purified from skate skin hydrolysate. Food Chem 125:495–499
Li H, Aluko RE (2010) Identification and inhibitory properties of multifunctional peptides from pea protein hydrolysate. J Agric Food Chem 58:11471–11476
Lin L, Li BF (2006) Radical scavenging properties of protein hydrolysates from jumbo flying squid (Dosidicus eschrichitii steenstrup) skin gelatin. J Sci Food Agric 86:2290–2295
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biolog Chem 193:265–275
Majumder K, Wu J (2011) Purification and characterisation of angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides derived from enzymatic hydrolysate of ovotransferrin. Food Chem 126:1614–1619
Meisel H (2005) Biochemical properties of peptides encrypted in bovine milk proteins. Curr Med Chem 12:1905–1919
Mendis E, Rajapakse N, Byun H, Kim S (2005) Investigation of jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) skin gelatin peptides for their in vitro antioxidant effects. Life Sci 77:2166–2178
Montero P, Gómez-Guillén MC (2000) Extracting conditions for megrim (Lepidorhombus boscii) skin collagen affect functional properties of the resulting gelatin. J Food Sci 65:434–438
Mullally MM, Meisel H, FitzGerald RJ (1997) Identification of novel angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide corresponding to tryptic fragment of bovine beta lactoglobulin. FEBS Lett 402:99–101
Nagai T, Nagashima T, Abe A, Suzuki N (2006) Antioxidative activities and angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibition of extracts prepared from chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) cartilage and skin. Int J Food Prop 9:813–822
Nam KA, You SG, Kim SM (2008) Molecular and physical characteristics of squid (Toradores pacificus) skin collagens and biological properties of their enzymatic hydrolysates. J Food Sci 73:249–255
Pan D, Cao J, Guo H, Zhao B (2012) Studies on purification and the molecular mechanism of a novel ACE inhibitory peptide from whey protein hydrolysate. Food Chem 130:121–126
Park P, Jung W, Nam K, Shahidi F, Kim S (2001) Purification and characterization of antioxidative peptides from protein hydrolysate of lecithin-free egg yolk. JAOCS, J Am Oil Chem Soc 78:651–656
Park CH, Kim HJ, Kang KT, Park JW, Kim JS (2009) Fractionation and angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity of gelatin hydrolysates from by-products of Alaska pollock surimi. Fish Aquat Sci 12:79–85
Phelan M, Aherne A, Fitzgerald RJ, O’Brien NM (2009) Casein-derived bioactive peptides: biological effects, industrial uses, safety aspects and regulatory status. Int Dairy J 19:643–654
Picot L, Ravallec R, Fouchereau-Peron M, Vandanjon L, Jaouen P, Chaplain-Derouiniot M, Guérard F, Chabeaud A, Legal Y, Martinez Alvarez O, Berge JP, Piot JM, Batista I, Pires C, Thorkelsson G, Delannoy C, Jakobsen G, Johansson I, Bourseau P (2010) Impact of ultrafiltration and nanofiltration of an industrial fish protein hydrolysate on its bioactive properties. J Sci Food Agric 90:1819–1826
Radha C, Ramesh Kumar P, Prakash V (2008) Preparation and characterization of a protein hydrolysate from an oilseed flour mixture. Food Chem 106:1166–1174
Schagger H, von Jagow G (1987) Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfatepolyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem 166:368–379
See SF, Hong PK, Ng KL, Wan Aida WM, Babji AS (2010) Physicochemical properties of gelatins extracted from skins of different freshwater fish species. Int Food Research J 17:809–816
Segura-Campos MR, Chel-Guerrero LA, Betancur-Ancona DA (2011) Purification of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from a cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) enzymatic hydrolysate. Process Biochem 46:864–872
Thiansilakul Y, Benjakul S, Shahidi F (2007) Compositions, functional properties and antioxidative activity of protein hydrolysates prepared from round scad (Decapterus maruadsi). Food Chem 103:1385–1394
Tsai JS, Chen JL, Pan BS (2008) ACE-inhibitory peptides identified from the muscle protein hydrolysate of hard clam (Meretrix lusoria). Process Biochem 43:743–747
Wijesekara I, Qian ZJ, Ryu B, Ngo DH, Kim SK (2011) Purification and identification of antihypertensive peptides from seaweed pipefish (Syngnathus schlegeli) muscle protein hydrolysate. Food Res Int 44:703–707
Wu J, Aluko RE (2007) Quantitative structure–activity relationship study of bitter di-and tri-peptides including relationship with angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity. J Pept Sci 13:63–69
Wu J, Ding X (2002) Characterization of inhibition and stability of soy protein derived angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. Food Res Int 35:367–375
Wu J, Aluko RE, Muir AD (2002) Improved method for direct high performance liquid chromatography assay of angiotensin-converting enzyme catalysed reactions. J Chromatogr A 950:125–130
Wu HC, Chen HM, Shiau CY (2003) Free amino acids and peptides as related to antioxidant properties in protein hydrolysates of mackerel (Scomber austriasicus). Food Res Int 36:949–957
Wu H, He HL, Chen XL, Sun CY, Zhang YZ, Zhou BC (2008) Purification and identification of novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from shark meat hydrolysate. Process Biochem 43:457–461
Xu W, Kong BH, Zhao XH (2011) Optimization of some conditions of Neutrase-catalyzed plastein reaction to mediate ACE-inhibitory activity in vitro of casein hydrolysate prepared by Neutrase. J Food Sci Technol. doi:10.1007/s13197-011-0503-0
Yang JI, Ho HY, Chu YJ, Chow CJ (2008) Characteristic and antioxidant activity of retorted gelatin hydrolysates from cobia (Rachycentron canadum) skin. Food Chem 110:128–136
Zhao Y, Li B, Liu Z, Dong S, Zhao X, Zeng M (2007) Antihypertensive effect and purification of an ACE inhibitory peptide from sea cucumber gelatin hydrolysate. Process Biochem 42:1586–1591
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to express their sincere thanks to the National University of Malaysia (UKM) for the financial support under the grant, STGL-009-2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoodani, F., Ghassem, M., Babji, A.S. et al. ACE inhibitory activity of pangasius catfish (Pangasius sutchi) skin and bone gelatin hydrolysate. J Food Sci Technol 51, 1847–1856 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-012-0742-8
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-012-0742-8