Abstract
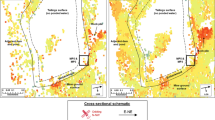
An effective microwave Differential Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (D-InSAR) technique was used to rapidly assess the potential land subsidence with high precision by exploiting the phase difference of two temporally separated SAR data in the region of Kolkata city, India. The objective of this study is to assess land subsidence using D-InSAR technique and to delineate the regions of land subsidence caused by over exploitation of groundwater by minimising the errors by applying topographic and atmospheric corrections. The study area forms a part of Indo-Gangetic plain. Three ENVISAT Advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar (ASAR) images of the years 2003, 2007 and 2010 were acquired to study the temporal evolution of land subsidence in the study area. The phase changes due to topography in the interferograms were removed by using Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) degital elevation model data. Medium Spectral Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MERIS) data were applied to remove the atmospheric noise in the interferogram. The deformation fringes were observed in the northern and central part of the study area where the land subsidence was 12 and 18 mm during the years of 2003–2007 and 2007–2010. The regional variation in the piezometric head compares well with the fringes of the interferogram. This confirms over extraction of groundwater is the main cause for land subsidence in this region. Hence, it is necessary to reduce groundwater pumping and to augment rainfall recharge in northern part of the study area.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baek J, Sang-Wan K, Park HJ, Jung HS, Kim KD, Kim JW (2008) Analysis of ground subsidence in coal mining area using SAR interferometry. Geosci J 12:277–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-008-0028-3
Bhattacharya AK (2011) Land subsidence in Kolkata due to groundwater depletion. EJGE 16:1415–1428
Calderhead AI, Martel R, Rivera A, Garfias J, Alasset PJ (2009) C-band D-INSAR and field data for calibrating a groundwater flow and land subsidence model. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium 149–152
Calderhead AI, Therrien R, Rivera A, Martel R, Garfias J (2011) Simulating pumping-induced regional land subsidence with the use of InSAR and field data in the Toluca valley, Mexico. Adv Water Resour 34:83–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2010.09.017
Chang CP, Chang TY, Wang CT, Kuo CH, Chen KS (2004) Land-surface deformation corresponding to seasonal ground-water fluctuation, determining by SAR interferometry in the SW Taiwan. Math Comput Simul 67(4):351–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2004.06.003
Chatterjee RS, Fruneau B, Rudant JP, Roy PS, Frison PL, Lakhera RC, Dadhwal VK, Saha R (2006) Subsidence of Kolkata City, India during the 1990s as observed from space by Differential Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry (D-InSAR) technique. Remote Sens Environ 102:176–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2006.02.006
Chaussard E, Wdowinski S, Cabral-Cano E, Amelung F (2014) Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time-series. Remote Sens Environ 140:94–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2013.08.038
Galloway DL, Hudnut KW, Ingebritsen SE, Phillips SP, Peltzer G, Rogez F, Rosen PA (1998) Detection of aquifer system compaction and land subsidence using interferometric synthetic aperture radar, Antelope Valley, Mojave Desert, California. Water Resour Res 34(10):2573–2583
Guzzetti F, Manunta M, Ardizzone F, Pepe A, Cardinali M, Zeni G, Reichenbach P, Lanari R (2009) Analysis of ground deformation detected using the SBAS-DInSAR Technique in Umbria, Central Italy. Pure Appl Geophy 166:1425–1459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-009-0491-4
Hasanuddin ZA, Djaja R, Andreas H, Gamal M, Hirose K, Maruyama Y (2004) TS16 – Disaster Management. Capabilities and constraints of geodetic techniques for monitoring land subsidence in the urban areas of Indonesia. 3rd FIG regional conference for Asia and the Pacific, Jakarta, Indonesia 1–15
Hu RL, Yue ZQ, Wang LC, Wang SJ (2004) Review on current status and challenging issues of land subsidence in China. Eng Geol 76:65–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2004.06.006
Kim JS, Kim DJ, Kim SW, Won JS, Moon WM (2007) Monitoring of urban land surface subsidence using PSInSAR. Geosci J 11(1):59–73
KMC(2007) Kolkata Municipal Corporations's Groundwater Information Booklet. http://cgwb.gov.in/District-Profile/WestBangal/KolkataMunicipalCorporation.pdf.
Lanari R, Casu F, Manzo M, Zeni G, Berardino P, Manunta M, Pepe A (2007) An overview of the small baseline subset algorithm: a DInSAR technique for surface deformation analysis. Pure Appl Geophys 164(4):637–661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-007-0192-9
Leake SA (2004) Land subsidence from ground-water pumping. U.S Geological Survey
Mora O, Mallorqui JJ, Broquetas A (2003) Linear and nonlinear terrain deformation maps from a reduced set of interferometric SAR Images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 41(10):2243–2253. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2003.814657
Prati C, Ferretti A, Perissin D (2010) Recent advances on surface ground deformation measurement by means of repeated space-borne SAR observations. J Geodyn 49:161–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2009.10.011
Sahu P, Sikdar PK (2011) Threat of land subsidence in and around Kolkata City and East Kolkata Wetlands, West Bengal, India. J Earth Syst Sci 120(3):435–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-011-0077-2
Sarmap (2009) Synthetic Aperture Radar and SARscape. SAR Guidebook, Sarmap SA: Purasca, Switzerland
Serpolla A, Bonafoni S, Biondi R, Arinò O, Basili EP (2009) Validation of near infrared satellite based algorithms to retrieve atmospheric water vapour content over land. Rivis Ital di Tel 41(1):37–44
Sikdar PK, Biswas AB, Saha AK (1996) A study on the possible land subsidence in Calcutta and Howarh cities due to groundwater overdraft. Indian J Geol 68(3):193–200
Stramondo S, Saroli M, Tolomei C, Moro M, Doumaz F, Pesci A, Loddo F, Baldi P, Boschi E (2007) Surface movement in Bologna (Po plain-Italy) detected by multi temporal DInSAR. Remote Sens Environ 110 (3):304-316
Strozzi T, Wegmuller U (1999) Land subsidence in Mexico City mapped by ERS differential SAR interferometry. In Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposiuml, pp. 1940-1942.
Sikdar PK,, Sarkar S, Palchoudhury S (2001) Geochemical evolution of groundwater in the Quaternary aquifer of Calcutta and Howrah, India. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 19 (5):579-594
Tung H, Hu JC (2012) Assessment of serious anthropogenic land subsidence in Yunlin country of central Taiwan from 1996 to 1999 by Persistent Scatterers InSAR. Tectonophys 578:126–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2012.08.009
Yang C-S, Zhang Q, Zhao C-Y, Qu W, Ji L-Y, Zhang J (2009) Surface subsidence and ground fissures activity monitoring based on D-InSAR: a Case of Datong City. 2009 Urban remote sensing joint event 978-1-4244-3461-IEEE
Yu J, Ng AHM, Jung S, Ge L, Rizos C (2008) Urban Monitoring using persistent scatterer INSAR and Photogrammetry. Int Arch Photogramm Remote Sens Spat Inf Sci XXXVII(B1):257–262
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the European Space Agency for providing ENVISAT-1 ASAR data. The authors are thankful to the State Water Investigation Directorate (SWID), Kolkata for providing groundwater head data of some wells.
Funding
This work was carried with the funding (Grant No: NRSC/HGD/EOAM-AU/2009) from the National Remote Sensing Centre, Department of Space, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suganthi, S., Elango, L. & Subramanian, S. Microwave D-InSAR technique for assessment of land subsidence in Kolkata city, India. Arab J Geosci 10, 458 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3207-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3207-6