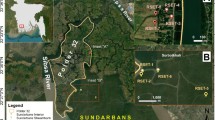
This paper attempts to estimate the possible rate of land subsidence of Kolkata City including Salt Lake City and the adjoining East Kolkata Wetlands located at the lower part of the deltaic alluvial plain of South Bengal basin. Demand of groundwater for drinking, agricultural and industrial purposes has increased due to rapid urbanization. The subsurface geology consists of Quaternary sediments comprising a succession of clay, silty clay and sand of various grades. Groundwater occurs mostly under confined condition except in those places where the top aquitard has been obliterated due to the scouring action of past channels. Currently, the piezometric head shows a falling trend and it may be accelerated due to further over-withdrawal of groundwater resulting in land subsidence. The estimated mean land subsidence rate is 13.53 mm/year and for 1 m drop in the piezometric head, the mean subsidence is 3.28 cm. The surface expression of the estimated land subsidence is however, cryptic because of a time lag between the settlement of the thick low-permeable aquitard at the top and its surface expression. Therefore, groundwater of the cities and wetland areas should be developed cautiously based on the groundwater potential to minimize the threat of land subsidence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal C S 2002 Geomorphological study for land subsidence in a part of District Farrukhabad; Hydrol. J. 25(1) 61–68.
Bhattacharyya A K and Patra M N 2007 Land subsidence in Salt Lake City and adjoining areas of Kolkata; ICFAI J. Earth Sci. 1(2) 75–86.
Bhattacharyya A K, Basak S and Patra M N 2004 Land subsidence in Calcutta under the effect of hydrogeological conditions and over-extraction of groundwater; EJGE 9 1–16.
Biswas A B 1990 Geology and groundwater resources of Calcutta Metropolitan District; Geogr. Rev. India 52(3) 10–24.
Biswas A B and Saha A K 1985 Environmental hazards of the recession of piezometric surface of the groundwater under Calcutta; Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 51A(3) 610–621.
Biswas A B and Saha A K 1986 Groundwater condition of Calcutta Metropolitan Area; Unpublished Project Report, C.S.M.E.
Biswas A B and Saha A K 1992 Water supply problems of the Calcutta Metropolitan Districts; Proceedings of Seminar on Calcutta Water Supply – Techno Economic Options.
Bouwer H 1977 Land subsidence and cracking due to groundwater depletion; Groundwater 15(5) 358–364.
Carminati E and Martinelli G 2002 Subsidence rates in the Po Plain, northern Italy: The relative impact of natural and anthropogenic causation; Eng. Geol. 66 241–255.
Chai J C, Shen S L, Zhu H H and Zhang X L 2004 Land subsidence due to groundwater drawdown in Shanghai; Geotechnique 54 143–147.
Chang H C, Ge L and Rizos C 2005 Radar interferometry for monitoring land subsidence due to underground water extraction; Spatial Sciences Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 736–743, CD-ROM procs, 12–16 September 2005.
Chaterji G C, Biswas A B, Basu S and Niyogi B N 1964 Geology and groundwater resources of the Greater Calcutta Metropolitan Area, West Bengal; Bull. Geol. Surv. India Sr. B21 1–150.
Chatterjee R S, Roy P S, Dadhwal V K, Lakhera R C, Quang T X and Saha R 2007 Assessment of land subsidence phenomenon in Kolkata City, India using satellite-based D-InSAR technique; Curr. Sci. 93(1) 85–90.
Cooper D J, MacDonald L H, Wenger S K and Woods S W 1998 Hydrologic restoration of a fen in Rocky Mountain National Park, Colorado, USA; Wetlands 18 335–345.
Dastidar A G and Ghosh P K 1967 A study of subsoil conditions of Calcutta; J. Inst. Eng. (India) 48(3) 692–714.
Dominico P A 1972 Concepts and Models in Groundwater Hydrology (New York: McGraw Hill Book Co.).
Don N C, Hang N T M, Araki H, Yamanishi H and Koga K 2006 Groundwater resources management under environmental constraints in Shiroishi of Saga plain, Japan; Environ. Geol. 49 601–609.
Drexler J Z, Bedford B L, DeGaetano A T and Seigal D I 1999 Quantification of water budget and nutrient loading in a small peatland; J. Amer. Water Resour. Assoc. 35 753–769.
Gambolati G and Freeze R A 1973 Mathematical simulation of the subsidence of Venice; Water Resour. Res. 9(3) 721–733.
Gloe C S, James J P and McKenzie R J 1973 Earth movements resulting from brown coal open cut mining – Latrobe Valley, Victoria. Subsidence in Mines; 4th Annual Symposium, Illawarra Branch, Australian Institute of Mineral and Metallurgy, 8 1–9.
Hirose K, Maruyama Y, Murdohardono D, Effendi A and Abidin H Z 2001 Land subsidence detection using JERS-1 SAR Interferometry, Paper presented at the 22nd Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, 5–9 November 2001, Singapore.
Leaky P P and Martin M 1993 Geohydrology and simulation of groundwater flow in the Northern Atlantic Coastal Plain aquifer system, USGS Professional Paper, 1404-K, pp. 1–81.
Lofgren B E 1969 Field measurement of aquifer-system compaction, San Joaquin Valley, California, USA, & Land subsidence; Proceedings of the First International Symposium, International Association of Hydrological Sciences, Tokyo, Japan, pp. 272–284.
Mayuga M N and Allen D R 1969 Subsidence in the Wilmington Oil Field, Long Beach, California, USA; IAHS–AISH Publication, 88p.
Motagh M, Djamour Y, Walter T R, Wetzel H U, Zschau J and Arabi S 2007 Land subsidence in Mashhad Valley, northest Iran: Results from InSAR, levelling and GPS; Geophys. J. Int. 168 518–526.
Mukherjee A, Fryar A E and Howell P D 2007 Regional hydrostratigraphy and groundwater flow modeling in the arsenic-affected areas of the western Bengal basin, West Bengal, India; Hydrogeol. J. 15 1397–1418.
Nguyen T Q and Helm D C 1995 Land subsidence due to groundwater withdrawal in Hanoi, Vietnam; Fifth International Symposium on Land Subsidence, The Hague, 1AHS Publ. No. 234, 55–60.
Owen C R 1995 Water budget and flow pattern in an urban wetland; J. Hydrol. 169 171–187.
Poland J F 1969 Land subsidence and aquifer-system compaction, Santa Clara Valley, California, USA; In: Land Subsidence (ed.) Tison L J, vol. 2, International Association of Science Hydrology Publication 88 285–292.
Poland J F and Davis G H 1969 Land subsidence due to withdrawal of fluids; In: Reviews in Engineering Geology, (eds) Varnes D J and Kiersch G A, Geol. Soc. Am. 2 187–269.
Sahu P and Sikdar P K 2009 Groundwater potential zoning of a peri-urban wetland of south Bengal Basin, India; Environ. Monit. Assess. 174 119–134, doi: 10.1007/ s10661-010-1443-2.
Schumann H H and Poland J F 1969 Land subsidence, earth fissures and groundwater withdrawal in South Central Arizona, U.S.A.; International Symposium on Subsidence, Tokyo, 295–302.
Sikdar P K 2000 Geology of the Quaternary aquifers of the twin City of Calcutta–Howrah; J. Geol. Soc. India 56(8) 169–186.
Sikdar P K, Biswas A B and Saha A K 1996 A study on the possible land subsidence in Calcutta and Howrah cities due to groundwater overdraft; Indian J. Geol. 68(3) 193–200.
Sikdar P K and Sahu P 2009 Understanding wetland sub-surface hydrology using geologic and isotopic signatures; Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 13 1313–1323.
Sneed M, Marti E, Galloway Ikehara D L and Amelung F 2001 Detection and measurement of land subsidence using global positioning system and interferometric synthetic aperture radar, Coachella Valley, California; 1996–98.
Ustun A, Tusat E and Yalvac S 2010 Preliminary results of land subsidence monitoring project in Konya Closed Basin between 2006–2009 by means of GNSS observations; Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 10 1151– 1157.
Zhang Y, Xue Y Q, Wu J C, Shi X Q and Yu J 2010 Excessive groundwater withdrawal and resultant land subsidence in the Su-Xi-Chang area, China; Environ. Earth Sci. 61 1135–1143.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SAHU, P., SIKDAR, P.K. Threat of land subsidence in and around Kolkata City and East Kolkata Wetlands, West Bengal, India. J Earth Syst Sci 120, 435–446 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-011-0077-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-011-0077-2