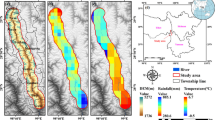
Abstract
The advanced interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) provides an effective tool to detect landslides over a large area. However, it is greatly affected by atmospheric delays and phase unwrapping errors in a complex environment and requires massive calculations and analysis. These factors hinder InSAR from reliably and rapidly identifying landslides. In this study, we propose an improved phase gradient stacking (IPGS) method, which effectively suppresses atmospheric delay disturbance, topographic residuals, and noise while enhancing local deformation signals. The temporally stacked phase gradients with a preset step along four directions are merged to form a phase gradient map. It avoids complicated unwrapping and massive time series analysis. The simulation experiment demonstrates the improvement to traditional methods by combining four directions and a specific step. The IPGS method achieves a comparative landslide detection as the classical SBAS method in terms of Sentinel-1 datasets covering Danba County. Even for some small-scale landslides that are difficult for SBAS to detect, the phase gradients are distinct. A field investigation validates the reliability of IPGS-detected landslides. It provides an effective tool for large-scale, rapid, and reliable detection of geological disasters.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The MATLAB code of the IPGS algorithm is available on demand (please contact: dongjie@whu.edu.cn).
References
Berardino P, Fornaro G, Lanari R, Sansosti E (2002) A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 40:2375–2383. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2002.803792
Ciampalini A, Raspini F, Lagomarsino D, Catani F, Casagli N (2016) Landslide susceptibility map refinement using PSInSAR data. Remote Sens Environ 184:302–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2016.07.018
Dai FC, Lee CF, Ngai YY (2002) Landslide risk assessment and management: an overview. Eng Geol 64:65–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0013-7952(01)00093-x
Dai KR, Li ZH, Xu Q, Burgmann R, Milledge DG, Tomas R, Fan XM, Zhao CY, Liu XJ, Peng JB, Zhang Q, Wang Z, Qu TT, He CY, Li DR, Liu JN (2020) Entering the era of earth observation-based landslide warning systems: a novel and exciting framework. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Mag 8:136–153. https://doi.org/10.1109/MGRS.2019.2954395
Deng H, Wu LZ, Huang RQ, Guo XG, He Q (2016) Formation of the Siwanli ancient landslide in the Dadu River, China. Landslides 14:385–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0756-9
Dong J, Zhang L, Tang M, Liao M, Xu Q, Gong J, Ao M (2018) Mapping landslide surface displacements with time series SAR interferometry by combining persistent and distributed scatterers: a case study of Jiaju landslide in Danba, China. Remote Sens Environ 205:180–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2017.11.022
Ferretti A, Prati C, Rocca F (2001) Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 39:8–20. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.898661
Ferretti A, Fumagalli A, Novali F, Prati C, Rocca F, Rucci A (2011) A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 49:3460–3470. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2011.2124465
Ferretti A, Monti-Guarnieri A, Prati C, Rocca F, Massonet D (2007) InSAR principles - guidelines for SAR interferometry processing and interpretation. ESA, Noordwijk, The Netherlands
Festa D, Bonano M, Casagli N, Confuorto P, De Luca C, Del Soldato M, Lanari R, Lu P, Manunta M, Manzo M, Onorato G, Raspini F, Zinno I, Casu F (2022) Nation-wide mapping and classification of ground deformation phenomena through the spatial clustering of P-SBAS InSAR measurements: Italy case study. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 189:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2022.04.022
Froude MJ, Petley DN (2018) Global fatal landslide occurrence from 2004 to 2016. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 18:2161–2181. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-18-2161-2018
Fu L, Zhang Q, Wang T, Li W, Xu Q, Ge D (2022) Detecting slow-moving landslides usingInSAR phase-gradient stacking and deep-learning network. Front Environ Sci 10:963322. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.963322
Gariano SL, Guzzetti F (2016) Landslides in a changing climate. Earth Sci Rev 162:227–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.08.011
Goldstein RM, Engelhardt H, Kamb B, Frolich RM (1993) Satellite radar interferometry for monitoring ice sheet motion application to an Antarctic ice. Science 262:1525–1530. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.262.5139.1525
Hanssen, Ramon F (2001) Radar interferometry : data interpretation and error analysis. Springer, Netherlands
Hooper A, Zebker H, Segall P, Kampes B (2004) A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers. Geophys Res Lett 31:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004gl021737
Hooper A (2008) A multi-temporal InSAR method incorporating both persistent scatterer and small baseline approaches. Geophys Res Lett 35:L16302. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008gl034654
Hu X, Bürgmann R, Fielding EJ, Lee H (2020) Internal kinematics of the Slumgullion landslide (USA) from high-resolution UAVSAR InSAR data. Remote Sens Environ 251:112057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2020.112057
Huang B, Yin Y, Tan J (2019) Risk assessment for landslide-induced impulse waves in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 16:585–596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-1115-9
Liang CR, Agram P, Simons M, Fielding EJ (2019) Ionospheric correction of InSAR time series analysis of C-band Sentinel-1 TOPS data. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 57:6755–6773. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2019.2908494
Lin Q, Wang Y (2018) Spatial and temporal analysis of a fatal landslide inventory in China from 1950 to 2016. Landslides 15:2357–2372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-1037-6
Lu Z, Fielding E, Patrick MR, Trautwein CM (2003) Estimating lava volume by precision combination of multiple baseline spaceborne and airborne interferometric synthetic aperture radar: the 1997 eruption of Okmok Volcano, Alaska. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 41:1428–1436. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2003.811553
Massonnet D, Holzer T, Vadon H (1997) Land subsidence caused by the East Mesa geothermal field, California, observed using SAR interferometry. Geophys Res Lett 24:901–904. https://doi.org/10.1029/97GL00817
Piciullo L, Calvello M, Cepeda JM (2018) Territorial early warning systems for rainfall-induced landslides. Earth Sci Rev 179:228–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.02.013
Price EJ, Sandwell DT (1998) Small-scale deformations associated with the 1992 Landers, California, earthquake mapped by synthetic aperture radar interferometry phase gradients. J Geophysi Res Solid Earth 103:27001–27016. https://doi.org/10.1029/98JB01821
Rotaru A, Oajdea D, Răileanu P (2007) Analysis of the landslide movements. Int J Geol 1:70–79
Samiei Esfahany S (2017) Exploitation of distributed scatterers in synthetic aperture radar interferometry. [Dissertation (TU Delft), Delft University of Technology]. https://doi.org/10.4233/uuid:22d46f1e-9061-46b0-9726-760c41404b6f
Sandwell DT, Price EJ (1998) Phase gradient approach to stacking interferograms. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 103:30183–30204. https://doi.org/10.1029/1998jb900008
Sharov AI, Gutjahr K, Pellikka PE (2004) Phase gradient approach to the evaluation and mapping of glacier rheology from multi-pass SAR interferograms. In Analysis of multi-temporal remote sensing images. 154–165. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789812702630_0017
Terzaghi K, Paige S (1950) Mechanism of landslides. In: Paige S (ed) Application of geology to engineering practice. Geol Soc Am, pp 83–123. https://doi.org/10.1130/Berkey.1950.83
Wang YA, Liu DL, Dong J, Zhang L, Guo JC, Liao MS, Gong JY (2021) On the applicability of satellite SAR interferometry to landslide hazards detection in hilly areas: a case study of Shuicheng, Guizhou in Southwest China. Landslides 18:2609–2619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01648-y
Wang Y, Dong J, Zhang L, Deng SH, Zhang GK, Liao MS, Gong JY (2023) Automatic detection and update of landslide inventory before and after impoundments at the Lianghekou reservoir using Sentinel-1 InSAR. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 118:14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2023.103224
Wang Y, Dong J, Zhang L, Zhang L, Deng SH, Zhang GK, Liao MS, Gong JY (2022) Refined InSAR tropospheric delay correction for wide-area landslide identification and monitoring. Remote Sens Environ 275:113013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2022.113013
Wasowski J, Bovenga F (2014) Investigating landslides and unstable slopes with satellite multi temporal interferometry: current issues and future perspectives. Eng Geol 174:103–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.03.003
Xu Q, Guo C, Dong X, Li W, Lu H, Fu H, Liu X (2021) Mapping and characterizing displacements of landslides with InSAR and airborne LiDAR technologies: a case study of Danba county, southwest China. Remote Sens 13:4234
Yin YP, Li TQ, Tang J (2008) Landslide reactivation and emergency stabilization on Danba county town in Sichuan province. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 27:971–978. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.05.013
Zebker HA, Villasenor J (1992) Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 30:950–959. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.175330
Zebker HA, Rosen PA, Goldstein RM, Gabriel A, Werner CL (1994) On the derivation of coseismic displacement fields using differential radar interferometry: the Landers earthquake. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 99:19617–19634. https://doi.org/10.1029/94JB01179
Zebker HA, Rosen PA, Hensley S (1997) Atmospheric effects in interferometric synthetic aperture radar surface deformation and topographic maps. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 102:7547–7563. https://doi.org/10.1029/96jb03804
Zhang C, Li Z, Yu C, Chen B, Ding M, Zhu W, Yang J, Liu Z, Peng J (2022a) An integrated framework for wide-area active landslide detection with InSAR observations and SAR pixel offsets. Landslides. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-022-01954-z
Zhang Z, Zeng Q, Jiao J (2022b) Deformations monitoring in complicated-surface areas by adaptive distributed scatterer InSAR combined with land cover: taking the Jiaju landslide in Danba, China as an example. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 186:102–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2022.02.004
Acknowledgements
We thank Paul Wessel for sharing Generic Mapping Tools (GMT). We thank the European Space Agency (ESA) for providing the Sentinel-1 datasets under the framework of the Sino-EU Dragon Project (ID 59332) and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) for providing the SRTM DEM.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2021YFC3000400), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42374013), the Sichuan Province Science and Technology Support Program (Grant No. 2020JDR0394), and the LIESMARS Special Research Funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Zhang, L., Dong, J. et al. Improved phase gradient stacking for landslide detection. Landslides (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-024-02263-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-024-02263-3