Abstract
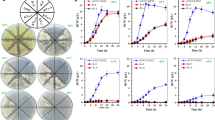
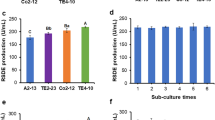
Intergeneric hybridization between S.albulus and B. subtilis to produce ε-poly-L-lysine (ε-PL) from corn starch residues (CSR) was investigated in this study. One hybrid, designated S. albulus LS-84, which incorporated the protease gene from B. subtilis, could effectively utilize the protein in CSR as a nitrogen source. In fed-batch fermentation, LS-84 produced 32.6 g/L ε-PL in the presence of 20 g/L CSR. This was an increase of 256.1% compared to that of the parent strain S. albulus LS-01. The rapid hydrolysis of CSR by protease caused rapid growth for LS-84, which allowed higher respiratory activity. As a result, activities of several key enzymes in LS-84 were higher than those in LS-01; additionally, the content of several intracellular amino acids, such as Asp, Glu, and Arg, was also much higher in LS-84. Therefore, intergeneric hybridization between S. albulus and B. subtilis to produce ε-PL from CSR is an economical method for effective utilization of waste resources.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shima, S. and H. Sakai (1977) Polylysine produced by Streptomyces. Agric. Biol. Chem. 41: 1807–1809.
Hiraki, J., T. Ichikawa, and S. Ninomiya (2003) Use of ADME studies to confirm the safety of polylysine as a preservative in food. Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 37: 328–340.
Kahar, P., T. Iwata, J. Hiraki, E. Y. Park, and M. Okabe (2001) Enhancement of e-polylysine production by Streptomyces albulus strain 410 using pH control. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 91: 190–194.
Hirohara, H., M. Takehara, M. Saimura, A. Ikezaki, and M. Miyamoto (2006) Biosynthesis of poly(e-L-lysine)s in two newly isolated strains of Streptomyces sp. Appl. Microbiol Biotechnol. 73: 321–331.
Chen, X. S., L. Tang, S. Li, L. J. Liao, J. H. Zhang, and Z. G. Mao (2011) Optimization of medium for enhancement of e-poly-Llysine production by Streptomyces sp. M-Z18 with glycerol as carbon source. Bioresour. Technol. 102: 1148–1159.
Xia, J., Z. X. Xu, H. Xu, J. F. Liang, S. Li, and X. H. Feng (2014) Economical production of poly(e-L-lysine) and poly(Ldiaminopropionic acid) using cane molasses and hydrolysate of streptomyces cells by Streptomyces albulus PD-1. Bioresour. Technol. 164: 241–247.
Shima, S. and H. Sakai (1981) Poly-L-lysine produced by Streptomyces. Part II. Taxonomy and fermentation studies. Agric. Biol. Chem. 45: 2497–2502.
Wang, L., X. S. Chen, G. Y. Wu, X. Zeng, X. D. Ren, S. Li, and Z. G. Mao (2017) Enhanced e-poly-L-lysine production by inducing double antibiotic-resistant mutations in Streptomyces albulus. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 40: 271–283.
Li, S., L. Tang, X. S. Chen, L. J. Liao, F. Li, and Z. G. Mao (2011) Isolation and characterization of a novel e-poly-L-lysine producing strain: Streptomyces griseofuscus. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 38: 557–563.
Li, S., X. S. Chen, C. D. Dong, F. L. Zhao, and Z. G. Mao (2013) Combining genome shuffling and interspecific hybridization among Streptomyces improved e-poly-L-lysine production. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 169: 338–350.
Hamano, Y. and I. Nicchu (2007) e-Poly-L-lysine producer, Streptomyces albulus, has feedback inhibition resistant aspartokinase. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 76: 873–882.
Murmu, J. and C. William (2007) Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase protein kinase from developing castor oil seeds: partial purification, characterization, and reversible control by photosynthate supply. Planta 226: 1299–1310.
Kiyohara, H., W. Toshiro, and I. Junko (1990) Intergeneric hybridization between Monascus anka and Asperyillus oryzae by protoplast fusion. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 33: 671–676.
Rojan, P., D. Gangadharan, and K. Madhavan (2008) Genome shuffling of Lactobacillus delbrueckii mutant and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens through protoplasmic fusion for L-lactic acid production from starchy wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 8008–8015.
John, F. and E. Hendrik (1977) Interspecific hybridization between Penicillium chlysogenum and Penicillium cyaneofulvum following protoplast fusion. Mol. Gen. Genet. 157: 281–284.
Takehara, M, and H. Hirohara (2010) in Amino-Acid Homopolymers Occurring in Nature. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany, pp. 1–22.
Driouch, H., B. Sommer, and C. Wittmann (2010) Morphology engineering of Aspergillus niger for improved enzyme production. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 105: 1058–1068.
Driouch, H., R. Hänsch, T. Wucherpfennig, R. Krull, and C. Wittmann (2012) Improved enzyme production by bio-pellets of Aspergillus niger: targeted morphology engineering using titanate microparticles. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 109: 462–471.
Ren, X. D., Y. J. Xu, X. Zeng, X. S. Chen, L. Tang, and Z. G. Mao (2015) Microparticle enhanced production of e-poly- L-lysine in fed-batch fermentation. RSC Adv. 5: 82138–82143.
Helena, B. and G. Hugh (1993) Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): purification of the enzyme, cloning of the ppc gene and over-expression of the protein in a streptomycete. Biochem. J. 293: 131–136.
Vrancken, G., T. Rimaux, and S. Weckx (2009) Environmental pH determines citrulline and ornithine release through the arginine deiminase pathway in Lactobacillus fermentum IMDO 13010. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 135: 216–222.
Zhang, Y., J. Xu, and Z. Yuan (2010) Artificial neural networkgenetic algorithm based optimization for the immobilization of cellulase on the smart polymer eudragit L-100. Bioresour. Technol. 101: 3153–3158.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Wang, N., Du, ZJ. et al. Intergeneric Hybridization between Streptomyces albulus and Bacillus subtilis Facilitates Production of ε-Poly-L-lysine from Corn Starch Residues. Biotechnol Bioproc E 23, 580–587 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-018-0253-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-018-0253-1