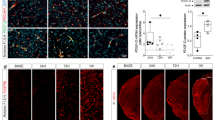
Abstract
Krüppel-like factors (KLFs) belong to the zinc finger family of transcription factors, and their function in the CNS is largely unexplored. KLF11 is a member of the KLF family, and we have previously demonstrated that peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-mediated cerebral protection during ischemic insults needs recruitment of KLF11 as its critical coactivator. Here, we sought to determine the role of KLF11 itself in cerebrovascular function and the pathogenesis of ischemic stroke. Transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) was performed in KLF11 knockout and wild-type control mice, and brain infarction was analyzed by TTC staining. BBB integrity was assessed by using Evans Blue and TMR-Dextran extravasation assays. KLF11 KO mice exhibited significantly larger brain infarction and poorer neurological outcomes in response to ischemic insults. Genetic deficiency of KLF11 in mice also significantly aggravated ischemia-induced BBB disruption by increasing cerebrovascular permeability and edema. Mechanistically, KLF11 was found to directly regulate IL-6 in the brains of ischemic mice. These findings suggest that KLF11 acts as a novel protective factor in ischemic stroke. Elucidating the functional importance of KLF11 in ischemia may lead us to discover novel pharmacological targets for the development of effective therapies against ischemic stroke.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldstein LB, Adams R, Becker K, Furberg CD, Gorelick PB, Hademenos G, Hill M, Howard G et al (2001) Primary prevention of ischemic stroke: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Stroke Council of the American Heart Association. Stroke 32(1):280–299
Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M, Davis SM (2008) Stroke. Lancet 371(9624):1612–1623
Schellinger PD, Kaste M, Hacke W (2004) An update on thrombolytic therapy for acute stroke. Curr Opin Neurol 17(1):69–77
Stapf C, Mohr JP (2002) Ischemic stroke therapy. Annu Rev Med 53:453–475
Love S (2003) Apoptosis and brain ischaemia. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27(2):267–282. doi:10.1016/S0278-5846(03)00022-8
Yuan J (2009) Neuroprotective strategies targeting apoptotic and necrotic cell death for stroke. Apoptosis 14(4):469–477. doi:10.1007/s10495-008-0304-8
Chang YC, Huang CC (2006) Perinatal brain injury and regulation of transcription. Curr Opin Neurol 19(2):141–147. doi:10.1097/01.wco.0000218229.73678.a8
Scholzke MN, Schwaninger M (2007) Transcriptional regulation of neurogenesis: Potential mechanisms in cerebral ischemia. J Mol Med 85(6):577–588. doi:10.1007/s00109-007-0196-z
Yi JH, Park SW, Kapadia R, Vemuganti R (2007) Role of transcription factors in mediating post-ischemic cerebral inflammation and brain damage. Neurochem Int 50(7–8):1014–1027. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2007.04.019
Black AR, Black JD, Azizkhan-Clifford J (2001) Sp1 and Kruppel-like factor family of transcription factors in cell growth regulation and cancer. J Cell Physiol 188(2):143–160
Kaczynski J, Cook T, Urrutia R (2003) Sp1- and Kruppel-like transcription factors. Genome Biol 4(2):206
McConnell BB, Yang VW (2010) Mammalian Kruppel-like factors in health and diseases. Physiol Rev 90(4):1337–1381. doi:10.1152/physrev.00058.2009
Yin KJ, Hamblin M, Fan Y, Zhang J, Chen YE (2013) Krupple-like factors in the central nervous system: novel mediators in stroke. Metab Brain Dis. doi:10.1007/s11011-013-9468-1
Moore DL, Blackmore MG, Hu Y, Kaestner KH, Bixby JL, Lemmon VP, Goldberg JL (2009) KLF family members regulate intrinsic axon regeneration ability. Science (New York, NY) 326(5950):298–301. doi:10.1126/science.1175737
Shi H, Sheng B, Zhang F, Wu C, Zhang R, Zhu J, Xu K, Kuang Y et al (2013) Kruppel-like factor 2 protects against ischemic stroke by regulating endothelial blood brain barrier function. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 304(6):H796–H805. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00712.2012
Yin KJ, Fan Y, Hamblin M, Zhang J, Zhu T, Li S, Hawse JR, Subramaniam M et al (2013) KLF11 mediates PPARgamma cerebrovascular protection in ischaemic stroke. Brain 136(Pt 4):1274–1287. doi:10.1093/brain/awt002
Fernandez-Zapico ME, van Velkinburgh JC, Gutierrez-Aguilar R, Neve B, Froguel P, Urrutia R, Stein R (2009) MODY7 gene, KLF11, is a novel p300-dependent regulator of Pdx-1 (MODY4) transcription in pancreatic islet beta cells. J Biol Chem 284(52):36482–36490
Neve B, Fernandez-Zapico ME, Ashkenazi-Katalan V, Dina C, Hamid YH, Joly E, Vaillant E, Benmezroua Y et al (2005) Role of transcription factor KLF11 and its diabetes-associated gene variants in pancreatic beta cell function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(13):4807–4812
Fan Y, Guo Y, Zhang J, Subramaniam M, Song CZ, Urrutia R, Chen YE (2012) Kruppel-like factor-11, a transcription factor involved in diabetes mellitus, suppresses endothelial cell activation via the nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32(12):2981–2988. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300349
Allen CL, Bayraktutan U (2008) Risk factors for ischaemic stroke. Int J Stroke 3(2):105–116
Ringelstein EB, Nabavi D (2000) Long-term prevention of ischaemic stroke and stroke recurrence. Thromb Res 98(3):83–96
Yin KJ, Deng Z, Hamblin M, Xiang Y, Huang H, Zhang J, Jiang X, Wang Y et al (2010) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta regulation of miR-15a in ischemia-induced cerebral vascular endothelial injury. J Neurosci 30(18):6398–6408
Yin KJ, Deng Z, Hamblin M, Zhang J, Chen YE (2011) Vascular PPAR{delta} protects against stroke-induced brain injury. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31(3):574–581
Swanson RA, Morton MT, Tsao-Wu G, Savalos RA, Davidson C, Sharp FR (1990) A semiautomated method for measuring brain infarct volume. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 10(2):290–293. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.1990.47
Wang J, Shi Y, Zhang L, Zhang F, Hu X, Zhang W, Leak RK, Gao Y et al (2014) Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids enhance cerebral angiogenesis and provide long-term protection after stroke. Neurobiol Dis 68:91–103. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2014.04.014
Zhang W, Wang H, Zhang H, Leak RK, Shi Y, Hu X, Gao Y, Chen J (2015) Dietary supplementation with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids robustly promotes neurovascular restorative dynamics and improves neurological functions after stroke. Exp Neurol 272:170–180. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.03.005
Leak RK, Zhang L, Stetler RA, Weng Z, Li P, Atkins GB, Gao Y, Chen J (2013) HSP27 protects the blood-brain barrier against ischemia-induced loss of integrity. CNS & neurological disorders drug targets 12(3):325–337
Bell RD, Winkler EA, Sagare AP, Singh I, LaRue B, Deane R, Zlokovic BV (2010) Pericytes control key neurovascular functions and neuronal phenotype in the adult brain and during brain aging. Neuron 68(3):409–427. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.09.043
Shi Y, Zhang L, Pu H, Mao L, Hu X, Jiang X, Xu N, Stetler RA et al (2016) Rapid endothelial cytoskeletal reorganization enables early blood-brain barrier disruption and long-term ischaemic reperfusion brain injury. Nat Commun 7:10523. doi:10.1038/ncomms10523
Zhang J, Yuan L, Zhang X, Hamblin MH, Zhu T, Meng F, Li Y, Chen YE et al (2016) Altered long non-coding RNA transcriptomic profiles in brain microvascular endothelium after cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol 277:162–170. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.12.014
Hara H, Huang PL, Panahian N, Fishman MC, Moskowitz MA (1996) Reduced brain edema and infarction volume in mice lacking the neuronal isoform of nitric oxide synthase after transient MCA occlusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16(4):605–611. doi:10.1097/00004647-199607000-00010
Ren TJ, Qiang R, Jiang ZL, Wang GH, Sun L, Jiang R, Zhao GW, Han LY (2013) Improvement in regional CBF by L-serine contributes to its neuroprotective effect in rats after focal cerebral ischemia. PLoS One 8(6):e67044. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0067044
Guo Q, Wang G, Namura S (2010) Fenofibrate improves cerebral blood flow after middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30(1):70–78. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2009.185
DeVries AC, Nelson RJ, Traystman RJ, Hurn PD (2001) Cognitive and behavioral assessment in experimental stroke research: will it prove useful? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 25(4):325–342
Balkaya M, Krober JM, Rex A, Endres M (2013) Assessing post-stroke behavior in mouse models of focal ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33(3):330–338. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2012.185
Rosenberg GA (1999) Ischemic brain edema. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 42(3):209–216
Hoiland RL, Bain AR, Rieger MG, Bailey DM, Ainslie PN (2016) Hypoxemia, oxygen content, and the regulation of cerebral blood flow. American journal of physiology Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology 310(5):R398–R413. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00270.2015
Dziedzic T (2015) Systemic inflammation as a therapeutic target in acute ischemic stroke. Expert Rev Neurother 15(5):523–531. doi:10.1586/14737175.2015.1035712
Kim JS, Gautam SC, Chopp M, Zaloga C, Jones ML, Ward PA, Welch KM (1995) Expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and macrophage inflammatory protein-1 after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. J Neuroimmunol 56(2):127–134
Liu T, Clark RK, McDonnell PC, Young PR, White RF, Barone FC, Feuerstein GZ (1994) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression in ischemic neurons. Stroke 25(7):1481–1488
Stanimirovic DB, Wong J, Shapiro A, Durkin JP (1997) Increase in surface expression of ICAM-1, VCAM-1 and E-selectin in human cerebromicrovascular endothelial cells subjected to ischemia-like insults. Acta Neurochir Suppl 70:12–16
Barone FC, Feuerstein GZ (1999) Inflammatory mediators and stroke: new opportunities for novel therapeutics. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 19(8):819–834
Becker KJ (1998) Inflammation and acute stroke. Curr Opin Neurol 11(1):45–49
Feuerstein GZ, Liu T, Barone FC (1994) Cytokines, inflammation, and brain injury: role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev 6(4):341–360
Castillo J, Rodriguez I (2004) Biochemical changes and inflammatory response as markers for brain ischaemia: molecular markers of diagnostic utility and prognosis in human clinical practice. Cerebrovasc Dis 17(Suppl 1):7–18. doi:10.1159/000074791
Fassbender K, Rossol S, Kammer T, Daffertshofer M, Wirth S, Dollman M, Hennerici M (1994) Proinflammatory cytokines in serum of patients with acute cerebral ischemia: kinetics of secretion and relation to the extent of brain damage and outcome of disease. J Neurol Sci 122(2):135–139
Zamanian JL, Xu L, Foo LC, Nouri N, Zhou L, Giffard RG, Barres BA (2012) Genomic analysis of reactive astrogliosis. J Neurosci 32(18):6391–6410. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6221-11.2012
Enenstein J, Milbauer L, Domingo E, Wells A, Roney M, Kiley J, Wei P, Hebbel RP (2010) Proinflammatory phenotype with imbalance of KLF2 and RelA: risk of childhood stroke with sickle cell anemia. Am J Hematol 85(1):18–23. doi:10.1002/ajh.21558
del Zoppo GJ, Hallenbeck JM (2000) Advances in the vascular pathophysiology of ischemic stroke. Thromb Res 98(3):73–81
Ishikawa M, Zhang JH, Nanda A, Granger DN (2004) Inflammatory responses to ischemia and reperfusion in the cerebral microcirculation. Front Biosci 9:1339–1347
Sandoval KE, Witt KA (2008) Blood-brain barrier tight junction permeability and ischemic stroke. Neurobiol Dis 32(2):200–219
Wang X, Lo EH (2003) Triggers and mediators of hemorrhagic transformation in cerebral ischemia. Mol Neurobiol 28(3):229–244
Yang Y, Rosenberg GA (2011) Blood-brain barrier breakdown in acute and chronic cerebrovascular disease. Stroke 42(11):3323–3328. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.608257
Jackman K, Kahles T, Lane D, Garcia-Bonilla L, Abe T, Capone C, Hochrainer K, Voss H et al (2013) Progranulin deficiency promotes post-ischemic blood-brain barrier disruption. J Neurosci 33(50):19579–19589. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4318-13.2013
Fagan SC, Hess DC, Hohnadel EJ, Pollock DM, Ergul A (2004) Targets for vascular protection after acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 35(9):2220–2225. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000138023.60272.9e
Fisher M (2008) Injuries to the vascular endothelium: vascular wall and endothelial dysfunction. Rev Neurol Dis 5(Suppl 1):S4–11
Rodriguez-Yanez M, Castellanos M, Blanco M, Mosquera E, Castillo J (2006) Vascular protection in brain ischemia. Cerebrovasc Dis 21(Suppl 2):21–29
Atkins GB, Jain MK (2007) Role of Kruppel-like transcription factors in endothelial biology. Circ Res 100(12):1686–1695
Suzuki T, Aizawa K, Matsumura T, Nagai R (2005) Vascular implications of the Kruppel-like family of transcription factors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25(6):1135–1141
SenBanerjee S, Lin Z, Atkins GB, Greif DM, Rao RM, Kumar A, Feinberg MW, Chen Z et al (2004) KLF2 is a novel transcriptional regulator of endothelial proinflammatory activation. J Exp Med 199(10):1305–1315. doi:10.1084/jem.20031132
Atkins GB, Wang Y, Mahabeleshwar GH, Shi H, Gao H, Kawanami D, Natesan V, Lin Z et al (2008) Hemizygous deficiency of Kruppel-like factor 2 augments experimental atherosclerosis. Circ Res 103(7):690–693. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.184663
Lin Z, Natesan V, Shi H, Dong F, Kawanami D, Mahabeleshwar GH, Atkins GB, Nayak L et al (2010) Kruppel-like factor 2 regulates endothelial barrier function. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30(10):1952–1959. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.211474
Hamik A, Lin Z, Kumar A, Balcells M, Sinha S, Katz J, Feinberg MW, Gerzsten RE et al (2007) Kruppel-like factor 4 regulates endothelial inflammation. J Biol Chem 282(18):13769–13779
McCormick SM, Eskin SG, McIntire LV, Teng CL, Lu CM, Russell CG, Chittur KK (2001) DNA microarray reveals changes in gene expression of shear stressed human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(16):8955–8960. doi:10.1073/pnas.171259298
Zhou G, Hamik A, Nayak L, Tian H, Shi H, Lu Y, Sharma N, Liao X et al (2012) Endothelial Kruppel-like factor 4 protects against atherothrombosis in mice. J Clin Invest 122(12):4727–4731. doi:10.1172/JCI66056
Cowan CE, Kohler EE, Dugan TA, Mirza MK, Malik AB, Wary KK (2010) Kruppel-like factor-4 transcriptionally regulates VE-cadherin expression and endothelial barrier function. Circ Res 107(8):959–966. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.219592
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health Grants (NS094930, NS091175, and NS086820 to K.J. Yin).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure/Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 153 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, X., Liu, K., Hamblin, M.H. et al. Genetic Deletion of Krüppel-Like Factor 11 Aggravates Ischemic Brain Injury. Mol Neurobiol 55, 2911–2921 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0556-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0556-9