Abstract
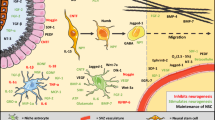
Recent data provides evidence that new neurons are born in cerebral ischemia. Although ultimate evidence for their functional importance is lacking, correlational data suggest that they contribute to recovery. Therefore, the underlying mechanisms of neurogenesis are interesting as a basis for pharmacological enhancement of the phenomenon. Neurogenesis is a multistep process that includes proliferation of precursor cells, migration of the newborn cells to the site of lesion, differentiation, integration into neuronal circuits, and survival. All these steps rely on gene transcription. However, only preliminary data about the specific transcriptional control of neurogenesis in cerebral ischemia have been obtained so far. To promote this investigation, we review currently available information on six pathways (Notch, Wnt/β-catenin, NF-κB, signal transducers and activators of transcription (STA) 3, HIF-1, and cyclic AMP response element-binding protein [CREB]) that have been shown to regulate transcription in neurogenesis and that have been implicated in cerebral ischemia. With the exception of CREB, direct involvement in postischemic neurogenesis is quite conjectural and much more must be learned to draw practical conclusions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krams M, Lees KR, Hacke W, Grieve AP, Orgogozo J-M, Ford GA (2003) Acute stroke therapy by inhibition of neutrophils (ASTIN): an adaptive dose–response study of UK-279,276 in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 34:2543–2548
Enlimomab Acute Stroke Trial Investigators (2001) Use of anti-ICAM-1 therapy in ischemic stroke: results of the Enlimomab Acute Stroke Trial. Neurology 57:1428–1434
Kuan CY, Schloemer AJ, Lu A, Burns KA, Weng WL, Williams MT, Strauss KI, Vorhees CV, Flavell RA, Davis RJ, Sharp FR, Rakic P (2004) Hypoxia-ischemia induces DNA synthesis without cell proliferation in dying neurons in adult rodent brain. J Neurosci 24:10763–10772
Lichtenwalner RJ, Parent JM (2006) Adult neurogenesis and the ischemic forebrain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:1–20
Liu J, Solway K, Messing RO, Sharp FR (1998) Increased neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus after transient global ischemia in gerbils. J Neurosci 18:7768–7778
Tonchev AB, Yamashima T, Zhao L, Okano HJ, Okano H (2003) Proliferation of neural and neuronal progenitors after global brain ischemia in young adult macaque monkeys. Mol Cell Neurosci 23:292–301
Hoehn BD, Palmer TD, Steinberg GK (2005) Neurogenesis in rats after focal cerebral ischemia is enhanced by indomethacin. Stroke 36:2718–2724
Kronenberg G, Wang LP, Synowitz M, Gertz K, Katchanov J, Glass R, Harms C, Kempermann G, Kettenmann H, Endres M (2005) Nestin-expressing cells divide and adopt a complex electrophysiologic phenotype after transient brain ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:1613–1624
Buffo A, Vosko MR, Erturk D, Hamann GF, Jucker M, Rowitch D, Gotz M (2005) Expression pattern of the transcription factor Olig2 in response to brain injuries: implications for neuronal repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:18183–18188
Zhang R, Zhang Z, Zhang C, Zhang L, Robin A, Wang Y, Lu M, Chopp M (2004) Stroke transiently increases subventricular zone cell division from asymmetric to symmetric and increases neuronal differentiation in the adult rat. J Neurosci 24:5810–5815
Jin K, Wang X, Xie L, Mao XO, Zhu W, Wang Y, Shen J, Mao Y, Banwait S, Greenberg DA (2006) Evidence for stroke-induced neurogenesis in the human brain. PNAS 103:13198–13202
Arvidsson A, Collin T, Kirik D, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2002) Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in the adult brain after stroke. Nat Med 8:963–970
Parent JM, Vexler ZS, Gong C, Derugin N, Ferriero DM (2002) Rat forebrain neurogenesis and striatal neuron replacement after focal stroke. Ann Neurol 52:802–813
Jin K, Sun Y, Xie L, Peel A, Mao XO, Batteur S, Greenberg DA (2003) Directed migration of neuronal precursors into the ischemic cerebral cortex and striatum. Mol Cell Neurosci 24:171–189
Nakatomi H, Kuriu T, Okabe S, Yamamoto S, Hatano O, Kawahara N, Tamura A, Kirino T, Nakafuku M (2002) Regeneration of hippocampal pyramidal neurons after ischemic brain injury by recruitment of endogenous neural progenitors. Cell 110:429–441
Levine M, Tjian R (2003) Transcription regulation and animal diversity. Nature 424:147–151
Alvarez-Buylla A, Lim DA (2004) For the long run: maintaining germinal niches in the adult brain. Neuron 41:683–686
Kageyama R, Ohtsuka T, Hatakeyama J, Ohsawa R (2005) Roles of bHLH genes in neural stem cell differentiation. Exp Cell Res 306:343–348
Ohtsuka T, Ishibashi M, Gradwohl G, Nakanishi S, Guillemot F, Kageyama R (1999) Hes1 and Hes5 as notch effectors in mammalian neuronal differentiation. Embo J 18:2196–2207
Nishimura M, Isaka F, Ishibashi M, Tomita K, Tsuda H, Nakanishi S, Kageyama R (1998) Structure, chromosomal locus, and promoter of mouse Hes2 gene, a homologue of Drosophila hairy and enhancer of split. Genomics 49:69–75
Androutsellis-Theotokis A, Leker RR, Soldner F, Hoeppner DJ, Ravin R, Poser SW, Rueger MA, Bae SK, Kittappa R, McKay RD (2006) Notch signalling regulates stem cell numbers in vitro and in vivo. Nature 442:823–826
Ishibashi M, Moriyoshi K, Sasai Y, Shiota K, Nakanishi S, Kageyama R (1994) Persistent expression of helix-loop-helix factor HES-1 prevents mammalian neural differentiation in the central nervous system. Embo J 13:1799–1805
Ohtsuka T, Sakamoto M, Guillemot F, Kageyama R (2001) Roles of the basic helix-loop-helix genes Hes1 and Hes5 in expansion of neural stem cells of the developing brain. J Biol Chem 276:30467–30474
Ross SE, Greenberg ME, Stiles CD (2003) Basic helix-loop-helix factors in cortical development. Neuron 39:13–25
Sriuranpong V, Borges MW, Strock CL, Nakakura EK, Watkins DN, Blaumueller CM, Nelkin BD, Ball DW (2002) Notch signaling induces rapid degradation of achaete-scute homolog 1. Mol Cell Biol 22:3129–3139
Sun Y, Nadal-Vicens M, Misono S, Lin MZ, Zubiaga A, Hua X, Fan G, Greenberg ME (2001) Neurogenin promotes neurogenesis and inhibits glial differentiation by independent mechanisms. Cell 104:365–376
Beatus P, Lendahl U (1998) Notch and neurogenesis. J Neurosci Res 54:125–136
Louvi A, Artavanis-Tsakonas S (2006) Notch signalling in vertebrate neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:93–102
Ge W, Martinowich K, Wu X, He F, Miyamoto A, Fan G, Weinmaster G, Sun YE (2002) Notch signaling promotes astrogliogenesis via direct CSL-mediated glial gene activation. J Neurosci Res 69:848–860
Sestan N, Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rakic P (1999) Contact-dependent inhibition of cortical neurite growth mediated by notch signaling. Science 286:741–746
Arumugam TV, Chan SL, Jo DG, Yilmaz G, Tang SC, Cheng A, Gleichmann M, Okun E, Dixit VD, Chigurupati S, Mughal MR, Ouyang X, Miele L, Magnus T, Poosala S, Granger DN, Mattson MP (2006) Gamma secretase-mediated Notch signaling worsens brain damage and functional outcome in ischemic stroke. Nat Med 12:621–623
Kawai T, Takagi N, Nakahara M, Takeo S (2005) Changes in the expression of Hes5 and Mash1 mRNA in the adult rat dentate gyrus after transient forebrain ischemia. Neurosci Lett 380:17–20
Gustafsson MV, Zheng X, Pereira T, Gradin K, Jin S, Lundkvist J, Ruas JL, Poellinger L, Lendahl U, Bondesson M (2005) Hypoxia requires notch signaling to maintain the undifferentiated cell state. Dev Cell 9:617–628
Kleber M, Sommer L (2004) Wnt signaling and the regulation of stem cell function. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16:681–687
Nelson WJ, Nusse R (2004) Convergence of Wnt, beta-catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science 303:1483–1487
Haegele L, Ingold B, Naumann H, Tabatabai G, Ledermann B, Brandner S (2003) Wnt signalling inhibits neural differentiation of embryonic stem cells by controlling bone morphogenetic protein expression. Mol Cell Neurosci 24:696–708
Sato N, Meijer L, Skaltsounis L, Greengard P, Brivanlou AH (2004) Maintenance of pluripotency in human and mouse embryonic stem cells through activation of Wnt signaling by a pharmacological GSK-3-specific inhibitor. Nat Med 10:55–63
Chenn A, Walsh CA (2002) Regulation of cerebral cortical size by control of cell cycle exit in neural precursors. Science 297:365–369
Lee SM, Tole S, Grove E, McMahon AP (2000) A local Wnt-3a signal is required for development of the mammalian hippocampus. Development 127:457–467
McMahon AP, Bradley A (1990) The Wnt-1 (int-1) proto-oncogene is required for development of a large region of the mouse brain. Cell 62:1073–1085
Ikeya M, Lee SM, Johnson JE, McMahon AP, Takada S (1997) Wnt signalling required for expansion of neural crest and CNS progenitors. Nature 389:966–970
Lie DC, Colamarino SA, Song HJ, Desire L, Mira H, Consiglio A, Lein ES, Jessberger S, Lansford H, Dearie AR, Gage FH (2005) Wnt signalling regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Nature 437:1370–1375
Hari L, Brault V, Kleber M, Lee HY, Ille F, Leimeroth R, Paratore C, Suter U, Kemler R, Sommer L (2002) Lineage-specific requirements of beta-catenin in neural crest development. J Cell Biol 159:867–880
Lee HY, Kleber M, Hari L, Brault V, Suter U, Taketo MM, Kemler R, Sommer L (2004) Instructive role of Wnt/beta-catenin in sensory fate specification in neural crest stem cells. Science 303:1020–1023
Hirabayashi Y, Itoh Y, Tabata H, Nakajima K, Akiyama T, Masuyama N, Gotoh Y (2004) The Wnt/beta-catenin pathway directs neuronal differentiation of cortical neural precursor cells. Development 131:2791–2801
Kleber M, Lee HY, Wurdak H, Buchstaller J, Riccomagno MM, Ittner LM, Suter U, Epstein DJ, Sommer L (2005) Neural crest stem cell maintenance by combinatorial Wnt and BMP signaling. J Cell Biol 169:309–320
Kasai M, Satoh K, Akiyama T (2005) Wnt signaling regulates the sequential onset of neurogenesis and gliogenesis via induction of BMPs. Genes Cells 10:777–783
Castelo-Branco G, Wagner J, Rodriguez FJ, Kele J, Sousa K, Rawal N, Pasolli HA, Fuchs E, Kitajewski J, Arenas E (2003) Differential regulation of midbrain dopaminergic neuron development by Wnt-1, Wnt-3a, and Wnt-5a. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:12747–12752
Cappuccio I, Calderone A, Busceti CL, Biagioni F, Pontarelli F, Bruno V, Storto M, Terstappen GT, Gaviraghi G, Fornai F, Battaglia G, Melchiorri D, Zukin S, Nicoletti F, Caricasole A (2005) Induction of Dickkopf-1, a negative modulator of the Wnt pathway, is required for the development of ischemic neuronal death. J Neurosci 25:2647–2657
Sen R, Baltimore D (1986) Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell 46:705–716
Widera D, Mikenberg I, Kaltschmidt B, Kaltschmidt C (2006) Potential role of NF-kappaB in adult neural stem cells: the underrated steersman? Int J Dev Neurosci 24:91–102
Karin M, Lin A (2002) NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol 3:221–227
Li Q, Verma IM (2002) NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2:725–734
Schmidt-Ullrich R, Memet S, Lilienbaum A, Feuillard J, Raphael M, Israel A (1996) NF-kB activity in transgenic mice: developmental regulation and tissue specificity. Development 122:2117–2128
Bhakar AL, Tannis L-L, Zeindler C, Russo MP, Jobin C, Park DS, MacPherson S, Barker PA (2002) Constitutive nuclear factor-kappa B activity is required for central neuron survival. J Neurosci 22:8466–8475
Li Q, Estepa G, Memet S, Israel A, Verma IM (2000) Complete lack of NF-kappaB activity in IKK1 and IKK2 double-deficient mice: additional defect in neurulation. Genes Dev 14:1729–1733
Denis-Donini S, Caprini A, Frassoni C, Grilli M (2005) Members of the NF-kappaB family expressed in zones of active neurogenesis in the postnatal and adult mouse brain. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 154:81–89
Shingo T, Sorokan ST, Shimazaki T, Weiss S (2001) Erythropoietin regulates the in vitro and in vivo production of neuronal progenitors by mammalian forebrain neural stem cells. J Neurosci 21:9733–9743
Iosif RE, Ekdahl CT, Ahlenius H, Pronk CJH, Bonde S, Kokaia Z, Jacobsen S-EW, Lindvall O (2006) Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 is a negative regulator of progenitor proliferation in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. J Neurosci 26:9703–9712
Widera D, Holtkamp W, Entschladen F, Niggemann B, Zanker K, Kaltschmidt B, Kaltschmidt C (2004) MCP-1 induces migration of adult neural stem cells. Eur J Cell Biol 83:381–387
Sironi L, Banfi C, Brioschi M, Gelosa P, Guerrini U, Nobili E, Gianella A, Paoletti R, Tremoli E, Cimino M (2006) Activation of NF-kB and ERK1/2 after permanent focal ischemia is abolished by simvastatin treatment. Neurobiol Dis 22:445–451
Feng Z, Porter AG (1999) NF-kappaB/Rel proteins are required for neuronal differentiation of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 274:30341–30344
Gutierrez H, Hale VA, Dolcet X, Davies A (2005) NF-kappaB signalling regulates the growth of neural processes in the developing PNS and CNS. Development 132:1713–1726
Schneider A, Martin-Villalba A, Weih F, Vogel J, Wirth T, Schwaninger M (1999) NF-kB is activated and promotes cell death in focal cerebral ischemia. Nat Med 5:554–559
Stephenson D, Yin T, Smalstig EB, Hsu MA, Panetta J, Little S, Clemens J (2000) Transcription factor nuclear factor-kappa B is activated in neurons after focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:592–603
Gabriel C, Justicia C, Camins A, Planas AM (1999) Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in the rat brain after transient focal ischemia. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 65:61–69
Nadjar A, Tridon V, May MJ, Ghosh S, Dantzer R, Amédée T, Parnet P (2005) NFkB activates in vivo the synthesis of inducible Cox-2 in the brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:1047–1059
Herrmann O, Baumann B, De Lorenzi R, Muhammad S, Zhang W, Kleesiek J, Malfertheiner M, Köhrmann M, Potrovita I, Maegele I, Beyer C, Burke JR, Hasan MT, Bujard H, Wirth T, Pasparakis M, Schwaninger M (2005) IKK mediates ischemia-induced neuronal cell death. Nat Med 11:1322–1329
Zhang X, Winkles JA, Gongora MC, Polavarapu R, Michaelson JS, Hahm K, Burkly L, Friedman M, Li XJ, Yepes M (2006) TWEAK-Fn14 pathway inhibition protects the integrity of the neurovascular unit during cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab
Crack PJ, Taylor JM, Ali U, Mansell A, Hertzog PJ (2006) Potential contribution of NF-kappaB in neuronal cell death in the glutathione peroxidase-1 knockout mouse in response to ischemia–reperfusion injury. Stroke 37:1533–1538
Karin M (2006) Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer development and progression. Nature 441:431–436
Aaronson DS, Horvath CM (2002) A road map for those who don’t know JAK-STAT. Science 296:1653–1655
Burdon T, Smith A, Savatier P (2002) Signalling, cell cycle and pluripotency in embryonic stem cells. Trends Cell Biol 12:432–438
Bonni A, Sun Y, Nadal-Vicens M, Bhatt A, Frank DA, Rozovsky I, Stahl N, Yancopoulos GD, Greenberg ME (1997) Regulation of gliogenesis in the central nervous system by the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Science 278:477–483
Rajan P, McKay RD (1998) Multiple routes to astrocytic differentiation in the CNS. J Neurosci 18:3620–3629
Molne M, Studer L, Tabar V, Ting YT, Eiden MV, McKay RD (2000) Early cortical precursors do not undergo LIF-mediated astrocytic differentiation. J Neurosci Res 59:301–311
Takizawa T, Nakashima K, Namihira M, Ochiai W, Uemura A, Yanagisawa M, Fujita N, Nakao M, Taga T (2001) DNA methylation is a critical cell-intrinsic determinant of astrocyte differentiation in the fetal brain. Dev Cell 1:749–758
Gu F, Hata R, Ma YJ, Tanaka J, Mitsuda N, Kumon Y, Hanakawa Y, Hashimoto K, Nakajima K, Sakanaka M (2005) Suppression of Stat3 promotes neurogenesis in cultured neural stem cells. J Neurosci Res 81:163–171
Schneider A, Kruger C, Steigleder T, Weber D, Pitzer C, Laage R, Aronowski J, Maurer MH, Gassler N, Mier W, Hasselblatt M, Kollmar R, Schwab S, Sommer C, Bach A, Kuhn HG, Schabitz WR (2005) The hematopoietic factor G-CSF is a neuronal ligand that counteracts programmed cell death and drives neurogenesis. J Clin Invest 115:2083–2098
Nakashima K, Yanagisawa M, Arakawa H, Kimura N, Hisatsune T, Kawabata M, Miyazono K, Taga T (1999) Synergistic signaling in fetal brain by STAT3-Smad1 complex bridged by p300. Science 284:479–482
Fukuda S, Kondo T, Takebayashi H, Taga T (2004) Negative regulatory effect of an oligodendrocytic bHLH factor OLIG2 on the astrocytic differentiation pathway. Cell Death Differ 11:196–202
Zhang SS, Liu MG, Kano A, Zhang C, Fu XY, Barnstable CJ (2005) STAT3 activation in response to growth factors or cytokines participates in retina precursor proliferation. Exp Eye Res 81:103–115
Herrmann O, Tarabin V, Suzuki S, Attigah N, Prinz S, Schneider A, Coserea I, Monyer H, Brombacher F, Schwaninger M (2003) Regulation of body temperature and neuroprotection by endogenous interleukin-6 in focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:406–415
Suzuki S, Tanaka K, Nogawa S, Ito D, Dembo T, Kosakai A, Fukuuchi Y (2000) Immunohistochemical detection of leukemia inhibitory factor after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:661–668
Justicia C, Gabriel C, Planas AM (2000) Activation of the JAK/STAT pathway following transient focal cerebral ischemia: signaling through Jak1 and Stat3 in astrocytes. Glia 30:253–270
Choi JS, Kim SY, Cha JH, Choi YS, Sung KW, Oh ST, Kim ON, Chung JW, Chun MH, Lee SB, Lee MY (2003) Upregulation of gp130 and STAT3 activation in the rat hippocampus following transient forebrain ischemia. Glia 41:237–246
Suzuki S, Tanaka K, Nogawa S, Dembo T, Kosakai A, Fukuuchi Y (2001) Phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (Stat3) after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Exp Neurol 170:63–71
Schweizer U, Gunnersen J, Karch C, Wiese S, Holtmann B, Takeda K, Akira S, Sendtner M (2002) Conditional gene ablation of Stat3 reveals differential signaling requirements for survival of motoneurons during development and after nerve injury in the adult. J Cell Biol 156:287–297
Studer L, Csete M, Lee SH, Kabbani N, Walikonis J, Wold B, McKay R (2000) Enhanced proliferation, survival, and dopaminergic differentiation of CNS precursors in lowered oxygen. J Neurosci 20:7377–7383
Semenza GL (2006) Regulation of physiological responses to continuous and intermittent hypoxia by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Exp Physiol 91:803–806
Tomita S, Ueno M, Sakamoto M, Kitahama Y, Ueki M, Maekawa N, Sakamoto H, Gassmann M, Kageyama R, Ueda N, Gonzalez FJ, Takahama Y (2003) Defective brain development in mice lacking the Hif-1{alpha} gene in neural cells. Mol Cell Biol 23:6739–6749
Milosevic J, Maisel M, Wegner F, Leuchtenberger J, Wenger RH, Gerlach M, Storch A, Schwarz J (2007) Lack of hypoxia-inducible factor-1{alpha} impairs midbrain neural precursor cells involving vascular endothelial growth factor signaling. J Neurosci 27:412–421
Bergeron M, Yu AY, Solway KE, Semenza GL, Sharp FR (1999) Induction of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) and its target genes following focal ischaemia in rat brain. Eur J Neurosci 11:4159–4170
Mu D, Jiang X, Sheldon RA, Fox CK, Hamrick SE, Vexler ZS, Ferriero DM (2003) Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and induction of vascular endothelial growth factor in a rat neonatal stroke model. Neurobiol Dis 14:524–534
Zhao BQ, Wang S, Kim HY, Storrie H, Rosen BR, Mooney DJ, Wang X, Lo EH (2006) Role of matrix metalloproteinases in delayed cortical responses after stroke. Nat Med 12:441–445
Abumiya T, Lucero J, Heo JH, Tagaya M, Koziol JA, Copeland BR, del Zoppo GJ (1999) Activated microvessels express vascular endothelial growth factor and integrin alpha(v)beta3 during focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 19:1038–1050
Jin K, Zhu Y, Sun Y, Mao XO, Xie L, Greenberg DA (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) stimulates neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo. PNAS 99:11946–11950
Fabel K, Fabel K, Tam B, Kaufer D, Baiker A, Simmons N, Kuo CJ, Palmer TD (2003) VEGF is necessary for exercise-induced adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci 18:2803–2812
Kawai T, Takagi N, Mochizuki N, Besshoh S, Sakanishi K, Nakahara M, Takeo S (2006) Inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase attenuates cellular proliferation and differentiation to mature neurons in the hippocampal dentate gyrus after transient forebrain ischemia in the adult rat. Neuroscience 141:1209–1216
Wang Y, Jin K, Mao XO, Xie L, Banwait S, Marti HH, Greenberg DA (2007) VEGF-overexpressing transgenic mice show enhanced post-ischemic neurogenesis and neuromigration. J Neurosci Res 85:740–747
Sun Y, Jin K, Xie L, Childs J, Mao XO, Logvinova A, Greenberg DA (2003) VEGF-induced neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J Clin Invest 111:1843–1851
Chen J, Zacharek A, Li A, Zhang C, Ding J, Roberts C, Lu M, Kapke A, Chopp M (2006) Vascular endothelial growth factor mediates atorvastatin-induced mammalian achaete-scute homologue-1 gene expression and neuronal differentiation after stroke in retired breeder rats. Neuroscience 141:737–744
Zhang H, Vutskits L, Pepper MS, Kiss JZ (2003) VEGF is a chemoattractant for FGF-2-stimulated neural progenitors. J Cell Biol 163:1375–1384
Tsai PT, Ohab JJ, Kertesz N, Groszer M, Matter C, Gao J, Liu X, Wu H, Carmichael ST (2006) A critical role of erythropoietin receptor in neurogenesis and post-stroke recovery. J Neurosci 26:1269–1274
Wang L, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Zhang R, Chopp M (2004) Treatment of stroke with erythropoietin enhances neurogenesis and angiogenesis and improves neurological function in rats. Stroke 35:1732–1737
Wang L, Zhang ZG, Zhang RL, Jiao ZX, Wang Y, Pourabdollah-Nejad DS, LeTourneau Y, Gregg SR, Chopp M (2006) Neurogenin 1 mediates erythropoietin enhanced differentiation of adult neural progenitor cells. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:556–564
Mayr B, Montminy M (2001) Transcriptional regulation by the phosphorylation-dependent factor CREB. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:599–609
Gonzalez GA, Montminy MR (1989) Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell 59:675–680
Nakagawa S, Kim JE, Lee R, Malberg JE, Chen J, Steffen C, Zhang YJ, Nestler EJ, Duman RS (2002) Regulation of neurogenesis in adult mouse hippocampus by cAMP and the cAMP response element-binding protein. J Neurosci 22:3673–3682
Nakagawa S, Kim JE, Lee R, Chen J, Fujioka T, Malberg J, Tsuji S, Duman RS (2002) Localization of phosphorylated cAMP response element-binding protein in immature neurons of adult hippocampus. J Neurosci 22:9868–9876
Palmer TD, Takahashi J, Gage FH (1997) The adult rat hippocampus contains primordial neural stem cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 8:389–404
Giachino C, De Marchis S, Giampietro C, Parlato R, Perroteau I, Schutz G, Fasolo A, Peretto P (2005) cAMP response element-binding protein regulates differentiation and survival of newborn neurons in the olfactory bulb. J Neurosci 25:10105–10118
Siesjo BK (1992) Pathophysiology and treatment of focal cerebral ischemia. Part I: pathophysiology. J Neurosurg 77:169–184
Walton MR, Dragunow M (2000) Is CREB a key to neuronal survival? Trends Neurosci 23:48–53
Hara T, Hamada JI, Yano S, Morioka M, Kai Y, Ushio Y (2003) CREB is required for acquisition of ischemic tolerance in gerbil hippocampal CA1 region. J Neurochem 86:805–814
Meller R, Minami M, Cameron JA, Impey S, Chen D, Lan JQ, Henshall DC, Simon R (2005) CREB-mediated Bcl-2 protein expression after ischemic preconditioning. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:234–246
Barnabe-Heider F, Miller FD (2003) Endogenously produced neurotrophins regulate survival and differentiation of cortical progenitors via distinct signaling pathways. J Neurosci 23:5149–5160
Sairanen M, Lucas G, Ernfors P, Castren M, Castren E (2005) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and antidepressant drugs have different but coordinated effects on neuronal turnover, proliferation, and survival in the adult dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 25:1089–1094
Zhu DY, Lau L, Liu SH, Wei JS, Lu YM (2004) Activation of cAMP-response-element-binding protein (CREB) after focal cerebral ischemia stimulates neurogenesis in the adult dentate gyrus. PNAS 101:9453–9457
Tonchev AB, Yamashima T, Sawamoto K, Okano H (2006) Transcription factor protein expression patterns by neural or neuronal progenitor cells of adult monkey subventricular zone. Neuroscience 139:1355–1367
Ding S, Wu TY, Brinker A, Peters EC, Hur W, Gray NS, Schultz PG (2003) Synthetic small molecules that control stem cell fate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:7632–7637
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the BMBF/NGFN2. MN Schölzke is a member of the postdoc program of the Medical Faculty Heidelberg.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schölzke, M.N., Schwaninger, M. Transcriptional regulation of neurogenesis: potential mechanisms in cerebral ischemia. J Mol Med 85, 577–588 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-007-0196-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-007-0196-z