Abstract
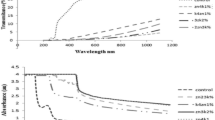
Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) have been explored for controlling food spoilage microorganism. ZnO NPs were prepared by wet chemical synthesis using zinc nitrate as a precursor and sodium hydroxide as reducing agent. Nanorods and hexagonal plate shape ZnO NPs were obtained for different reaction time of 2 h and 24 h, respectively. Effect of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) as capping material on the morphology, size distribution, and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles was studied by FESEM, TEM, DLS, UV-visible spectroscopy, and XRD analyses. Results showed that HPMC as capping material prevent the agglomeration of nanoparticles during synthesis and maintained uniformity in ZnO NPs size. Strong antimicrobial activity of prepared ZnO NPs was observed and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for food application was determined. MIC for Staphylococcus aureus was 0.5 mg/ml. For Penicillium expansum 1 mg/ml showed approximately 80% inhibition and 2 mg/ml concentration showed 95% inhibition at the twelfth day for all ZnO NPs. HPMC-ZnO bio-nanocomposite films, prepared by incorporating capped ZnO NPs in HPMC biopolymer, showed improved mechanical and barrier properties and decreased transparency of film. Results showed that capped ZnO NPs obtained from 24 h reaction time were more effective in improving the barrier properties of HPMC film.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amjadi, S., Emaminia, S., Heyat, S., & Pourmohammad, S. (2019). Preparation and characterization of gelatin-based nanocomposite containing chitosan nano fi ber and ZnO nanoparticles. Carbohydrate Polymers, 216(December 2018), 376–384.
Arefi, M. R., & Rezaei-Zarchi, S. (2012). Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their effect on the compressive strength and setting time of self-compacted concrete paste as cementitious composites. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(4), 4340–4350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13044340.
Arfat, Y. A., Benjakul, S., Prodpran, T., Sumpavapol, P., & Songtipya, P. (2016). Physico-mechanical characterization and antimicrobial properties of fish protein isolate/fish skin gelatin-zinc oxide (ZnO) nanocomposite films. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 9(1), 101–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-015-1602-0.
Bajpai, S. K., Chand, N., & Chaurasia, V. (2012). Nano zinc oxide-loaded calcium alginate films with potential antibacterial properties. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5(5), 1871–1881. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-011-0587-6.
Baltaci, A. K., Mogulkoc, R., & Baltaci, S. B. (2019). The role of zinc in the endocrine system. Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 32(1), 231–239.
Basch, C. Y., Jagus, R. J., & Flores, S. K. (2013). Physical and antimicrobial properties of tapioca starch-HPMC edible films incorporated with nisin and/or potassium sorbate. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6(9), 2419–2428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-0860-3.
Blanco, I. (2016). Lifetime prediction of food and beverage packaging wastes. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 125(2), 809–816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-5169-9.
Blanco, I. (2018). Lifetime prediction of polymers : to bet , or not to bet — is this the question ? Materials, 11(1383), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081383.
Brown, K. H., Hambidge, K. M., & Ranum, P. (2010). Zinc fortification of cereal flours: current recommendations and research needs. Food and Nutrition Bulletin, 31(1 SUPPL), 62–74. https://doi.org/10.1177/15648265100311s106.
Dada, E. O., & Olusola-Makinde, O. O. (2015). Microbial and parasitic contamination on vegetables collected from retailers in main market, Akure. American Journal of Microbiological Research, 3(3), 112–117. https://doi.org/10.12691/ajmr-3-3-3.
De Moura, M. R., Mattoso, L. H. C., & Zucolotto, V. (2012). Development of cellulose-based bactericidal nanocomposites containing silver nanoparticles and their use as active food packaging. Journal of Food Engineering, 109(3), 520–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.10.030.
Debanath, M. K., & Karmakar, S. (2013). Study of blueshift of optical band gap in zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles prepared by low-temperature wet chemical method. Materials Letters, 111, 116–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2013.08.069.
Espitia, P. J. P., Soares, N. d. F. F., Coimbra, J. S. d. R., de Andrade, N. J., Cruz, R. S., & Medeiros, E. A. A. (2012). Zinc oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, antimicrobial activity and food packaging applications. Food and Bioprocess Technology., 5(5), 1447–1464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-0797-6.
Farahmandjou, M., & Jurablu, S. (2014). Co-precipitation synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles by zinc nitrate precursor. International Journal of Bio-Inorganic Hybrid Nanometer, 3(3), 179–184.
Hambidge, M. (2000). Zinc and Health: Current status and future directions. J. Nutr., 130(5), 1344S–1349S.
Han, Y. S., Lee, S. H., Choi, K. H., & Park, I. (2010). Preparation and characterization of chitosan-clay nanocomposites with antimicrobial activity. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 71(4), 464–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2009.12.012.
He, L., Liu, Y., Mustapha, A., & Lin, M. (2011). Antifungal activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Botrytis cinerea and Penicillium expansum. Microbiological Research, 166(3), 207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2010.03.003.
Judith, P., Espitia, P., De Fátima, N., Soares, F., Teófilo, R. F., Sélia, J., et al. (2013). Physical – mechanical and antimicrobial properties of nanocomposite films with pediocin and ZnO nanoparticles. Carbohydrate Polymers, 94, 199–208.
Kanmani, P., & Rhim, J. (2014). Properties and characterization of bionanocomposite films prepared with various biopolymers and ZnO nanoparticles. Carbohydrate Polymers, 106, 190–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.02.007.
Kumar, S., Mitra, A., & Halder, D. (2017). Centella asiatica leaf mediated synthesis of silver nanocolloid and its application as filler in gelatin based antimicrobial nanocomposite film. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 75, 293–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.06.061.
Miedes, E., & Lorences, E. P. (2004). Apple (Malus domestica) and tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum) fruits cell-wall hemicelluloses and xyloglucan degradation during Penicillium expansum infection. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 52(26), 7957–7963. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf048890f.
Möller, H., Grelier, S., Pardon, P., & Coma, V. (2004). Antimicrobial and physicochemical properties of chitosan - HPMC-based films. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 52(21), 6585–6591. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0306690.
Naveed Ul Haq, A., Nadhman, A., Ullah, I., Mustafa, G., Yasinzai, M., & Khan, I. (2017). Synthesis approaches of zinc oxide nanoparticles: the dilemma of ecotoxicity. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2017(Table 1). https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8510342.
Oun, A. A., & Rhim, J. W. (2017). Carrageenan-based hydrogels and films: effect of ZnO and CuO nanoparticles on the physical, mechanical, and antimicrobial properties. Food Hydrocolloids, 67, 45–53.
Premanathan, M., Karthikeyan, K., Jeyasubramanian, K., & Manivannan, G. (2011). Selective toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles toward Gram-positive bacteria and cancer cells by apoptosis through lipid peroxidation. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine, 7(2), 184–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2010.10.001.
Priyadarshi, R., & Negi, Y. S. (2017). Effect of varying filler concentration on zinc oxide nanoparticle embedded chitosan films as potential food packaging material. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 25(4), 1087–1098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-016-0890-4.
Raghupathi, K. R., Koodali, R. T., & Manna, A. C. (2011). Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir, 27(7), 4020–4028. https://doi.org/10.1021/la104825u.
Salleh, E., & Muhamad, I. I. (2010). Starch-based antimicrobial films incorporated with lauric acid and chitosan. In AIP Conference Proceedings (Vol. 1217, pp. 432–436). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3377861
Sebti, I., Chollet, E., Degraeve, P., Noel, C., & Peyrol, E. (2007). Water sensitivity, antimicrobial, and physicochemical analyses of edible films based on HPMC and/or chitosan. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55(3), 693–699. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf062013n.
Shankar, S., Teng, X., Li, G., & Rhim, J. (2015). Preparation, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of gelatin/ZnO nanocomposite films. Food Hydrocolloids, 45, 264–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.12.001.
Siracusa, V., & Blanco, I. (2020). Bio-Polyethylene (Bio-PE), Bio-Polypropylene (Bio-PP) and Bio-Poly (ethylene terephthalate)(Bio-PET): recent developments in bio-based polymers analogous to petroleum-derived ones for packaging and engineering applications. Polymers, 12(8), 1641.
Sirelkhatim, A., Mahmud, S., Seeni, A., Kaus, N. H. M., Ann, L. C., Bakhori, S. K. M., Hasan, H., & Mohamad, D. (2015). Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro Letters, 7(3), 219–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-015-0040-x.
Sun, Y. K., In, S. L., Yun, S. Y., Seung, M. P., & Jae, K. S. (2008). ZnO nanoparticles with hexagonal cone, hexagonal plate, and rod shapes: synthesis and characterization. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 29(10), 1960–1964. https://doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2008.29.10.1960.
Talam, S., Karumuri, S. R., & Gunnam, N. (2012). Synthesis, characterization, and spectroscopic properties of ZnO nanoparticles. ISRN Nanotechnology, 2012, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/372505.
Tang, X. Z., Kumar, P., Alavi, S., & Sandeep, K. P. (2012). Recent advances in biopolymers and biopolymer-based nanocomposites for food packaging materials recent advances in biopolymers and biopolymer-based nanocomposites. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 8398(52), 426–442. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2010.500508.
Vaezi, K., Asadpour, G., & Shari, H. (2019). International Journal of Biological Macromolecules Effect of ZnO nanoparticles on the mechanical , barrier and optical properties of thermoplastic cationic starch / montmorillonite biodegradable films., 124, 519–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.142.
Valencia-Sullca, C., Atarés, L., Vargas, M., & Chiralt, A. (2018). Physical and antimicrobial properties of compression-molded cassava starch-chitosan films for meat preservation. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 11(7), 1339–1349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2094-5.
Wang, H., Gong, X., Miao, Y., Guo, X., Liu, C., Fan, Y., & Zhang, J. (2019). Preparation and characterization of multilayer fi lms composed of chitosan , sodium alginate and carboxymethyl chitosan-ZnO nanoparticles. Food Chemistry, 283(November 2018), 397–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.022.
Wu, Y. L., Tok, A. I. Y., Boey, F. Y. C., Zeng, X. T., & Zhang, X. H. (2007). Surface modification of ZnO nanocrystals. Applied Surface Science, 253(12), 5473–5479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2006.12.091.
Yu, J., Yang, J., Liu, B., & Ma, X. (2009). Preparation and characterization of glycerol plasticized-pea starch/ZnO-carboxymethylcellulose sodium nanocomposites. Bioresource Technology, 100(11), 2832–2841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.12.045.
Acknowledgments
The authors duly acknowledge the support provided by Central Research Facility (CRF) IIT Kharagpur, India.
Funding
The findings reported in the current paper is part of a research project funded by ISIRD grant, Ministry of Human Resource and Development, Govt. of India and the research has been undertaken at Agricultural and Food Engineering Department, IIT Kharagpur.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malik, G.K., Mitra, J. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Synthesis, Characterization, and Their Effect on Mechanical, Barrier, and Optical Properties of HPMC-Based Edible Film. Food Bioprocess Technol 14, 441–456 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02566-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02566-y