Abstract
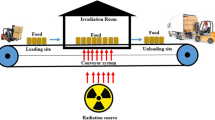
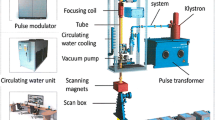
The demand for raw and fresh dairy products with the desired organoleptic characteristics and health benefits led to research in non-thermal processing technologies aiming to retain all the product qualities and nutrients. Irradiation is an emerging non-thermal technology used in destroying micro- and macroorganisms that might exist in food by exposure to either gamma (γ) rays from radioactive isotopes (cobalt60 or caesium137) or an electron accelerator (electron beam or X-radiation) under a controlled environment. With the endorsement of many international food and health organisations such as the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and World Health Organization (WHO), irradiation is becoming more widely researched as a process to maintain quality, improve safety and reduce quarantine and post-harvest loss. Irradiation has the potential for allergenicity reduction and the provision of a sterile diet for immunocompromised patients. Unlike other food categories, the use of irradiation as a preservative technique on dairy products has received little attention due to the complexity of the product varieties. Whilst being accepted in some countries, the adoption of irradiation as an alternative measure of treating and preventing potential problems in the food chain faces strict opposition in many countries. In this review, the focus is on the radiation processing as an emerging technology and its specific application on dairy products.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El Baky, A. A., Farahat, S. M., Rabie, A. M., & Mobasher, S. A. (1986). The manufacture of Ras cheese from gamma irradiated milk. Food Chemistry, 20, 201–212.
ACINF. (1986). The safety and wholesomeness of irradiated foods. London: Advisory Committee on Irradiated and Novel Foods, HMSO.
Adeil Pietranera, M. S., Narvais, P., Horak, C., & Kairiyama, E. (2003). Irradiated ice creams for immunosuppressed patients. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 66, 357–365.
Alothman, M., Rajeev, B., & Karim, A. A. (2009). Effects of radiation processing on phytochemicals and antioxidants in plant produce. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 20, 201–212.
Aquino, K. A.S. (2012). Sterilization by gamma irradiation, gamma radiation. In Adrovic, F. (Ed.), Gamma radiation (pp 171–206).
Arvanitoyannis, I. S., & Tserkezou, P. (2010). Application of irradiation on milk and dairy products. Irradiation of food commodities: techniques, applications, detection, legislation, safety and consumer opinion. London: Elsevier.
Arvanitoyannis, I. S., Stratakos, A., & Mente, E. (2009). Impacts of irradiation on fish and seafood shelf life: a comprehensive review of applications and irradiation detection. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 49, 68–112.
Asselin, J., Hebert, J., & Amiot, J. (1989). Effects of in-vitro proteolysis on the allergenicity of major whey proteins. Journal of Food Science, 54(4), 1037–1039.
Bandekar, J., Kamat, A., & Thomas, P. (1998). Microbiological quality of the dairy product pedha and its improvement using gamma irradiation. Journal of Food Safety, 18(3), 221–230.
Barbano, D. M., MA, Y., & Santos, M. V. (2006). Influence of raw milk quality on fluid milk shelf life. Journal of Dairy Science, 89(E. suppl), E15–E19.
Barros-Velazquez, J. (2011). Innovations in food technology special issue. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 4(6), 831–832.
Berejka, A. J., & Larsen, S. (2014). Enhanced wood durability from radiation-cured penetrants. Radiation Technology Report, 2, 15–21.
Berrocal, D., Arias, M. L., Henderson, M., & Wong, E. (2002). Evaluation of the effect of probiotic cultures over Listeria monocytogenes during the production and storage of yogurt. Archivos Latinoamericanos de Nutrición, 52(4), 375–380.
Blank, G., Shamsuzzaman, K., & Sohal, S. (1992). Use of electron-beam irradiation for mold decontamination on cheddar cheese. Journal of Dairy Science, 75(1), 13–18.
Bougle, D. L., & Stahl, V. (1994). Survival of Listeria monocytogenes after irradiation treatment of camembert cheeses made from raw milk. Journal of Food Protection, 57(9), 811–813.
Brault, D., D’Aprano, G., & Lacroix, M. (1997). Formation of free-standing sterilized edible films from irradiated caseinates. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 45, 2964–2969.
Brewer, M. S. (2009). Irradiation effects on meat flavour: a review. Meat Science, 81, 1–14.
Buchin, S., Delague, V., Duboz, G., Berdague, J. L., Beuvier, E., Pochet, S., & Grappin, R. (1998). Influence of pasteurization and fat composition of milk on the volatile compounds and flavor characteristics of a semi-hard cheese. Journal of Dairy Science, 81(12), 3097–3108.
Byun, M. W., Lee, J. W., Yook, H. S., Jo, C. R., & Kim, H. Y. (2002). Application of gamma irradiation for inhibition of food allergy. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 63(3–6), 369–370.
Camillo, A., & Sabato, S. F. (2004). Effect of combined treatments on viscosity of whey dispersions. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 71(1), 105–108.
Cathalin, J., & McNulty, P. (1996). Textural gain and subsequent loss in irradiated apples, carrots and potatoes with increase in dose from 0.03 to 1.0 kGy. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 20, 403–415.
Chen, H. (1995). Functional properties and application of edible films made of milk proteins. Journal of Dairy Science, 78, 2563–2583.
Cieśla, K., Salmieri, S., Lacroix, M., & Le Tien, C. (2004). Gamma irradiation influence on physical properties of milk proteins. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 71, 93–97.
Cousin, M. A. (1982). Presence and activity of psychrotrophic microorganisms in milk and dairy products: a review. Journal of Food Protection, 45, 172–207.
Crawford, L. M., & Ruff, E. H. (1996). A review of the safety of cold pasteurization through irradiation. Food Control, 7(2), 87–97.
Delincee, H., & Ehlermann, D. A. E. (1989). Recent advances in the identification of irradiated food. International Journal of Radiation Applications and Instrumentation. Part C. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 34(6), 877–890.
Diehl, J. F. (1985). The role of WHO in the field of food irradiation. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 25(1–3), 73–74.
Diehl, J. F. (2002). Food irradiation—past, present and future. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 63, 211–215.
Diehl, J. F., Hasselmann, C., & Kilcast, D. (1991). Regulation of food irradiation in the European community: is nutrition an issue? Food Control, 2, 212–219.
Dionísio, A. P., Gomes, R. T., & Oetterer, M. (2009). Ionizing radiation effects on food vitamins—a review. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology, 52(5), 1267–1278.
Docena, G. H., Fernandez, R., Chirdo, F. G., & Fossati, C. A. (1996). Identification of casein as the major allergenic and antigenic protein of cow’s milk. Allergy, 51(6), 412–416.
Dong, F. M., Lee, C. J., Rasco, B. A., & Hungate, F. P. (1989). Effects of gamma-irradiation on the contents of thiamin, riboflavin, and vitamin-B12 in dairy-products for low microbial diets. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 13(3), 233–244.
EFSA. (2011). Statement summarising the conclusion and recommendations from the opinions on the safety of irradiation of food by the BIOHAZ and CEF panels. EFSA Journal, 9(4), 2107. 1–155.
EFSA & ECDC. (2014). The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2012. EFSA Journal, 12(2), 3547. 312 pp.
Ehlerman, D. A. E. (2014). Safety of food and beverages: safety of irradiated foods. In M. Yasmine (Ed.), Encyclopedia of food safety (Vol. 3, pp. 447–452). Waltham: Academic.
Elias, P. S., & Cohen, A. J. (1977). Radiation chemistry of major food components. Its relevance to the assessment of the wholesomeness of irradiated foods. Elsevier.
Ennahar, S., Kuntz, F., Strasser, A., Bergaentzle, M., Hasselmann, C., & Stahl, V. (1994). Elimination of Listeria monocytogenes in soft and red smear cheese by irradiation with low energy electrons. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 29(4), 395–403.
Fan, X., & Sommers, C. H. (Eds.). (2013). Food irradiation research and technology (2nd ed.). Ames: Wiley-Blackwell.
Farag, K. W., Lyng, J. G., Morgan, D. J., & Cronin, D. A. (2008). A comparison of conventionally and radio frequency tempering of beef meats: effects on product temperature distribution. Meat Science, 80(2), 488–495.
Farag, K. W., Lyng, J. G., Morgan, D. J., & Cronin, D. A. (2011). A comparison of conventionally and radio frequency thawing of beef meats: effects on product temperature distribution. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 4(7), 1128–1136.
Farber, J. M., & Peterkin, P. I. (1991). Listeria monocytogenes, a food-borne pathogen. Microbiological Reviews, 55(3), 476–511.
Farkas, J. (1998). Irradiation as a method for decontaminating food: a review. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 44, 189–204.
Farkas, J., & Mohacsi-Farkas, C. (2011). History and future of food irradiation. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 22, 121–126.
Farkas, J., Ehlermann, D. A. E., & Mohácsi-Farkas, C. (2014). Food technologies: food irradiation. In M. Yasmine (Ed.), Encyclopedia of food safety (Vol. 3, pp. 178–186). Waltham: Academic.
FDA (2005). Irradiation in the production, processing, and handling of food. Federal Register. Final Rule. August 16, 2005, 70(157), 48057–48073.
Ford, J. E., Gregory, M. E., & Thompson, S. Y. (1962). The effect of gamma irradiation on the vitamins and proteins of liquid milk. International Dairy Congress. Abstrac., 917, 917–923.
Gekko, K., & Timasheff, S. (1981). Mechanism of protein stabilization by glycerol: preferential hydration in glycerol-water mixtures. Biochemistry, 20, 4667–4676.
Grandison, A. S. (2012). Irradiation. Food processing handbook, second edition, 153–177.
Guilbert, S., Gontard, N., & Gorris, L. G. M. (1996). Prolongation of the shelf-life of perishable food products using biodegradable films and coatings. LWT--Food Science and Technology, 29(1), 10–17.
Hallman, G. J. (2011). Phytosanitary applications of irradiation. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 10, 143–151.
Ham, J. S., Jeong, S. G., Lee, S. G., Han, G. S., Jang, A., Yoo, Y. M., Chae, H. S., Kim, D. H., Kim, H. J., Lee, W. K., & Jo, C. (2009). Quality of irradiated plain yogurt during storage at different temperatures. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 22(2), 289–295.
Harrison, R. (1962). A method of preparing service of sterilized meals. Nutrition, 16, 105–111.
Hashisaka, A. E., Weagant, S. D., & Dong, F. M. (1989). Survival of Listeria-monocytogenes in mozzarella cheese and ice-cream exposed to gamma irradiation. Journal of Food Protection, 52(7), 490–492.
Hashisaka, A. E., Einstein, M. A., Rasco, B. A., Hungate, F. P., & Dong, F. M. (1990a). Sensory analysis of dairy products irradiated with Cobalt 60 at −78°C. Journal of Food Science, 55(2), 404–408.
Hashisaka, A. E., Matches, J. R., Batters, Y., Hungate, F. P., & Dong, F. M. (1990b). Effects of gamma irradiation at −78°C on microbial populations in dairy products. Journal of Food Science, 55(5), 1284–1289.
Hates, D. J., Murano, E. A., Murano, P. S., Olson, D. G., & Sapp, S. G. (1995). Food irradiation (pp. 71–73). Ames: Iowa State University Press.
Huo, J. X., Bai, C. Y., Guo, L. H., & Zhao, Z. (2013). Effect of electron beam irradiation on the shelf life of mozzarella cheese. International Journal of Dairy Technology, 66(3), 352–358.
IAEA. (2012). Irradiated food authorization database. Available from: http://nucleus.iaea.org/ifa/FoodAuthorisationDisplay.aspx. Accessed 05 Sep 2014.
International Consultative Group on Food Irradiation (ICGFI). (1999). In facts about food irradiation. United Kingdom: Buckinghamshire. http://moreira.tamu.edu/BAEN625/TOC_files/foodirradiation.pdf.
JECFI (1981). Wholesomeness of irradiated food. WHO technical report, Series 659, Geneva, Switzerland.
Jeon, G. R., Lee, J. W., Byun, M. W., & Lee, S. Y. (2002). Reduced allergenicities of irradiated egg white ovalbumin determined by skin prick test and ELISA inhibition test. Journal of Asthma, Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 22, 711–719.
Kaferstein, F. K. (1990). Food irradiation and its role in improving the safety and security of food. Food Control, 1, 211–214.
Kamat, A., Warke, R., Kamat, M., & Thomas, P. (2000). Low-dose irradiation as a measure to improve microbial quality of ice cream. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 62(1–2), 27–35.
Khwaldia, K., Perez, C., Banon, S., Desobry, S., & Hardy, J. (2004). Milk proteins for edible films and coatings. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 44(4), 239–251.
Kilcast, D. (1994). Effect of irradiation on vitamins. Food Chemistry, 49(2), 157–164.
Kilcast, D. (1995). Food irradiation: current problems and future potential. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 36(3–4), 279–296.
Kim, H. J., Jo, C., Lee, N. Y., Ham, J. S., Lee, W. K., & Byun, M. W. (2005). Irradiation of food-borne pathogens inoculated into chocolate ice cream. International symposium “New Frontier of Irradiated Food and Non-Food Products”. Bangkok: KMUTT.
Knorr, D. (1999). Novel approaches in food-processing technology: new technologies for preserving foods and modifying function. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 10(5), 485–491.
Knorr, D., Froehling, A., Jaeger, H., Reineke, K., Schlueter, O., & Schoessler, K. (2011). Emerging technologies in food processing. Annual Review of Food Science and Technology, 2, 203–235.
Kume, T., & Todoriki, S. (2013). Food irradiation in Asia, the European Union and the United States: a status update. Radioisotopes, 62(5), 291–299.
Kume, T., Furuta, M., Todoriki, S., Uenoyama, N., & Kobayashi, Y. (2009). Status of food irradiation in the world. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 78(3), 222–226.
Lacroix, M., Le, T. C., Quattra, B., Yu, H., Letendre, M., Sabato, S. F., Mateescu, M. A., & Patterson, G. (2002). Use of gamma irradiation to produce films from whey, casein and soya proteins: structure and functional characteristics. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 63, 827–832.
Le Tien, C. L., Vachon, C., Mateescu, M. A., & Lacroix, M. (2001). Milk protein coatings prevent oxidative browning of apples and potatoes. Journal of Food Science, 66, 512–516.
Lee, S. (2004). Irradiation as a method for decontaminating food. Internet Journal of Food Safety, 3, 32–35.
Lee, J. W., Kim, J. H., Yook, H. S., Kang, K. O., Lee, S. Y., Hwang, H. J., & Byun, M. W. (2001). Effects of gamma radiation on the allergenic and antigenic properties of milk proteins. Journal of Food Protection, 64(2), 272–276.
Lee, J. W., Lee, K. Y., Lee, S. Y., Jo, C., Yook, H. S., Kim, H. Y., & Byun, M. W. (2002a). Allergenicity of hen’s egg ovomucoid gamma irradiated and heated under different pH condition. Journal of Food Protection, 65, 1196–1199.
Lee, S. Y., Trezza, T. A., Guinard, J. X., & Krochta, J. M. (2002b). Whey protein-coated peanuts assessed by sensory evaluation and static headspace gas chromatography. Journal of Food Science, 67, 1212–1218.
Mahapatra, A. K., Muthukumarappan, K., & Julson, J. L. (2005). Applications of ozone, bacteriocins and irradiation in food processing: a review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 45(6), 447–462.
Matloubi, H., Aflaki, F., & Hadjiezadegan, M. (2004). Effect of γ-irradiation on amino acids content of baby food proteins. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 17(2), 133–139.
McNulty, P. (1988). Food and health—modern techniques used in the production, preparation and presentation of food which may have a detrimental effect on human health. Paper presented at the December 8th, 1988 meeting of the Midland Regional Clinical Veterinary Society in the Bloomfield House Hotel, Mullingar.
Mezgheni, E., D’Aprano, G., & Lacroix, M. (1998). Formation of sterilized edible films based on caseinates: effects of calcium and plasticizers. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 46, 318–324.
Molins, R. A. (Ed.). (2001). Food irradiation: principles and applications (p. 488). New York: Wiley.
Norton, T., & Sun, D. W. (2008). Recent advances in the use of high pressure as an effective processing technique in the food industry. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1, 2–34.
O’Bryan, C. A., Crandall, P. G., Ricke, S. C., & Olson, D. G. (2008). Impact of irradiation on the safety and quality of poultry and meat products: a review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 48, 442–457.
Official Journal of the European Union. (2009). List of member states’ authorisations of food and food ingredients which may be treated with ionizing radiation.
Perko, B. (2011). Effects of prolonged storage on microbiological quality of raw milk. Mljekarstvo, 61(2), 114–124.
Prejean, J. E. (2001). Food irradiation: why aren’t we using it? Report of LEDA at Harvard Law School, available at: http://leda.law.harvard.edu/leda/data/403/Prejanpap.html.
Pryke, D. C., & Taylor, R. R. (1995). The use of irradiated food for immunosuppressed hospital patients in the United Kingdom. Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics, 8, 411–416.
Roberts, P. B. (2014). Food irradiation is safe: half a century of studies. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 105, 78–82.
Sabato, S. F., & Lacroix, M. (2002). Radiation effects on viscosimetry of protein based solutions. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 63, 357–359.
Sadoun, D., Couvercelle, C., Strasser, A., Egler, A., & Hasselmann, C. (1991). Low dose irradiation of liquid milk. Michwissenschaft, 46, 295–299.
Savilahti, E., & Kuitunen, M. (1992). Allergenicity of cow milk-proteins. Journal of Paediatrics, 121(5), S12–S20.
SCF (Scientific Committee on Food). (1992). Food science and techniques. Reports of the Scientific Committee for Food (thirty-second series). Available at: http://aei.pitt.edu/40841/1/32nd_food.pdf
SCF (Scientific Committee on Food). (2002). Statement of the Scientific Committee on Food on a Report on 2-alkylcyclobutanones. Available at: http://ec.europa.eu/food/fs/sc/scf/out135_en.pdf
Schmidl, M. K., Taylor, S. L., & Nordlee, J. A. (1994). Use of hydrolysate based products in special medical diets. Food Technology, 48(10), 77–85.
Seisa, D., Osthoff, G., Hugo, C., Hugo, A., Bothma, C., & Van der Merwe, J. (2004). The effect of low-dose gamma irradiation and temperature on the microbiological and chemical changes during ripening of cheddar cheese. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 69(5), 419–431.
Skala, J. H., McGown, E. L., & Waring, P. P. (1987). Wholesomeness of irradiated foods. Journal of Food Protection, 50, 150–160.
Song, H. P., Byun, M. W., Jo, C., Lee, C. H., Kim, K. S., & Kim, D. H. (2007). Effects of gamma irradiation on the microbiological, nutritional and sensory properties of fresh vegetable juice. Food Control, 18, 5–10.
Steele, J. H. (2001). Food irradiation: a public health challenge for the 21st century. Journal of Food Safety, 33, 376–377.
Stevenson, M. H., Stewart, E. M., & McAteer, N. J. (1995). A consumer trial to assess the acceptability of an irradiated chilled ready meal. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 46, 785–788.
Taylor, S. (1980). Food allergy: the enigma and some potential solutions. Journal of Food Protection, 43, 300–306.
Temur, C., & Tiryaki, O. (2013). Irradiation alone or combined with other alternative treatments to control postharvest diseases. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 8(5), 421–434.
Teuber, M. (2000). Fermented milk products. In The microbiological safety and quality of food (Vol. 1, pp. 535–585). Gaitherburg: Aspen.
Tsiotsias, A., Savvaidis, I., Vassila, A., Kontominas, M., & Kotzekidou, R. (2002). Control of Listeria monocytogenes by low-dose irradiation in combination with refrigeration in the soft whey cheese ‘Anthotyros’. Food Microbiology, 19(2–3), 117–126.
USEPA, US Environmental Protection Agency (2014). Food irradiation: food labeling. 〈http://www.epa.gov/radiation/sources/food_labeling.html〉. Accessed 03 July 2014.
USFDA. (2008). U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Irradiation: a safe measure for safer iceberg lettuce and spinach. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/ForConsumers/ConsumerUpdates/ucm093651.htm.
Vachon, C., Yu, H. L., Yesah, R., Alain, R., St-Gelais, D., & Lacroix, M. (2000). Mechanical and structural properties of milk protein edible films cross-linked by heating and gamma irradiation. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 48, 3202–3209.
Varga, L. (2006). Effect of acacia (Robinia pseudo-acacia L.) honey on the characteristic microflora of yogurt during refrigerated storage. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 108(2), 272–275.
Walker, S. J., Archer, P., & Banks, J. G. (1990). Growth of Listeria-monocytogenes at refrigeration temperatures. Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 68(2), 157–162.
World Health Organization. (1994). Safety and nutritional adequacy of irradiated food. Geneva: World Health Organization.
World Health Organization. (1999). High-dose irradiation: wholesomeness of food irradiated with doses above 10 kGy. Report of a Joint FAO/IAEA/WHO Expert Committee. Technical Report Series No. 890: i–iv, 1–197.
Yagoub, S. O., Awadalla, N. E., & El Zubeir, I. E. M. (2005). Incidence of some potential pathogens in raw milk in Khartoun North Sudan and their susceptibility to antimicrobial agents. International Journal of Animal and Veterinary Advances, 4, 341–344.
Ziporin, Z. Z., Kraybill, H. F., & Thach, H. J. (1957). Vitamin content of foods exposed to ionizing radiations. The Journal of Nutrition, 63(2), 201–209.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the great support received from all the team at Synergy Health Swindon in the UK, now part of STERIS for giving us access and for allowing us to conduct the experiments during a busy time schedule.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Odueke, O.B., Farag, K.W., Baines, R.N. et al. Irradiation Applications in Dairy Products: a Review. Food Bioprocess Technol 9, 751–767 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1709-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1709-y