Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to elucidate the impact of plant on the activity, abundance, and the community composition of the ammonia oxidizers, including both ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and bacteria (AOB). Moreover, the relationship between AOA and AOB in mangrove sediment was also analyzed.
Materials and methods
Sediment used for microcosm experiments was collected in the mangrove wetland. The native plant species Kandelia obovata and invasive species Spartina alterniflora were selected. Nitrifying activity was determined by assaying the potential nitrification rate (PNR). Abundances of gene and transcript were measured via real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR). Terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP) was used to analyze the nitrifier community structures. Clone libraries were constructed for further phylogenetic analysis.
Results and discussion
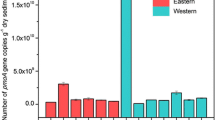
PNR and abundances of both AOA and AOB were greatly enhanced in the vegetated sediments. S. alterniflora showed a greater promoting effect on nitrification activity, indicating the potential of exotic invasion on perturbing the nitrogen balance. Abundance of AOB transcript was hundreds of times higher than that of AOA. Moreover, ammonia-oxidizing communities were distinctly grouped responding to vegetation with two plant species. Along with direct impact of plants, these variations are as well related to the different sediment properties. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that both AOA and AOB communities formed apparent clusters. The latter contained two Nitrosomonas and Nitrosospira clusters. The Nitrosomonas genus is predominant over Nitrosospira genus, which might be due to the better adaption of Nitrosomonas to the flooded habitats in sediments.
Conclusions
Wetland plants were found to influence the activity, abundance, and community structure of ammonia oxidizers. Moreover, AOB is suggested to be more significant than AOA in nitrogen cycling in mangrove wetlands.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves RJE, Wanek W, Zappe A, Richter A, Svenning MM, Schleper C, Urich T (2013) Nitrification rates in Arctic soils are associated with functionally distinct populations of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. ISME J 7:1620–1631
An S, Gu B, Zhou C, Wang Z, Deng Z, Zhi Y, Li H, Chen L, Yu D, Liu Y (2007) Spartina invasion in China: implications for invasive species management and future research. Weed Res 47:183–191
Angeloni NL, Jankowski KJ, Tuchman NC, Kelly JJ (2006) Effects of an invasive cattail species (Typha × glauca) on sediment nitrogen and microbial community composition in a freshwater wetland. FEMS Microbiol Lett 263:86–92
Berg G, Smalla K (2009) Plant species and soil type cooperatively shape the structure and function of microbial communities in the rhizosphere. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 68:1–13
Boyle-Yarwood SA, Bottomley PJ, Myrold DD (2008) Community composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in soils under stands of red alder and Douglas fir in Oregon. Environ Microbiol 10:2956–2965
Briones AM, Okabe S, Umemiya Y, Ramsing N-B, Reichardt W, Okuyama H (2002) Influence of different cultivars on populations of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in the root environment of rice. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3067–3075
Cao H, Li M, Hong Y, Gu J-D (2011) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in polluted mangrove sediment. Syst Appl Microbiol 34:513–523
Colmer T (2003) Long-distance transport of gases in plants: a perspective on internal aeration and radial oxygen loss from roots. Plant Cell Environ 26:17–36
Colmer TD, Flowers TJ (2008) Flooding tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol 179:964–974
Di H, Cameron K, Shen JP, Winefield C, O’Callaghan M, Bowatte S, He J (2009) Nitrification driven by bacteria and not archaea in nitrogen-rich grassland soils. Nat Geosci 2:621–624
Erguder TH, Boon N, Wittebolle L, Marzorati M, Verstraete W (2009) Environmental factors shaping the ecological niches of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33:855–869
Francis CA, Roberts KJ, Beman JM, Santoro AE, Oakley BB (2005) Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:14683–14688
Gao J-F, Luo X, Wu G-X, Li T, Peng Y-Z (2013) Quantitative analyses of the composition and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in eight full-scale biological wastewater treatment plants. Bioresour Technol 138:285–296
Gubry-Rangin C, Nicol GW, Prosser JI (2010) Archaea rather than bacteria control nitrification in two agricultural acidic soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 74:566–574
Hart SC, Stark JM, Davidson EA, Firestone MK (1994). Nitrogen mineralization, immobilization, and nitrification. In: Weaver RW, Angle S, Bottomley P, Bezdicek D, Smith S, Tabatabi A, Wollum A (eds) Methods of soil analysis: microbiological and biochemical properties. Soil Sci Soc Am, Madison, pp 985–1018.
Head IM, Hiorns WD, Embley TM, McCarthy AJ, Saunders JR (1993) The phylogeny of autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria as determined by analysis of 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. J Gen Microbiol 139:1147–1153
Herman D, Johnson K, Jaeger C, Schwartz E, Firestone M (2006) Root influence on nitrogen mineralization and nitrification in rhizosphere soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:1504–1511
Holguin G, Vazquez P, Bashan Y (2001) The role of sediment microorganisms in the productivity, conservation, and rehabilitation of mangrove ecosystems: an overview. Biol Fertil Soils 33:265–278
Jia Z, Conrad R (2009) Bacteria rather than Archaea dominate microbial ammonia oxidation in an agricultural soil. Environ Microbiol 11:1658–1671
Jin T, Zhang T, Yan Q (2010) Characterization and quantification of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and bacteria (AOB) in a nitrogen-removing reactor using T-RFLP and qPCR. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:1167–1176
Könneke M, Bernhard AE, José R, Walker CB, Waterbury JB, Stahl DA (2005) Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 437:543–546
Laanbroek HJ, Speksnijder AG (2008) Niche separation of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria across a tidal freshwater marsh. Environ Microbiol 10:3017–3025
Laanbroek HJ, Keijzer RM, Verhoeven JT, Whigham DF (2012) The distribution of ammonia-oxidizing betaproteobacteria in stands of black mangroves (Avicennia germinans). Front Microbiol 3:153
Leininger S, Urich T, Schloter M, Schwark L, Qi J, Nicol G, Prosser J, Schuster S, Schleper C (2006) Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils. Nature 442:806–809
Lensi R, Domenach A, Abbadie L (1992) Field study of nitrification and denitrification in a wet savanna of West Africa (Lamto, Côte d'Ivoire). Plant Soil 147:107–113
Li M, Gu J-D (2013) Community structure and transcript responses of anammox bacteria, AOA, and AOB in mangrove sediment microcosms amended with ammonium and nitrite. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:9859–9874
Li M, Cao H, Hong Y, Gu J-D (2011) Spatial distribution and abundances of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) in mangrove sediments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:1243–1254
Martens-Habbena W, Berube PM, Urakawa H, de La Torre JR, Stahl DA (2009) Ammonia oxidation kinetics determine niche separation of nitrifying Archaea and Bacteria. Nature 461:976–979
Moin NS, Nelson KA, Bush A, Bernhard AE (2009) Distribution and diversity of archaeal and bacterial ammonia oxidizers in salt marsh sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7461–7468
Nicol GW, Leininger S, Schleper C, Prosser JI (2008) The influence of soil pH on the diversity, abundance and transcriptional activity of ammonia oxidizing archaea and bacteria. Environ Microbiol 10:2966–2978
Norton JM, Firestone MK (1996) N dynamics in the rhizosphere of Pinus ponderosa seedlings. Soil Biol Biochem 28:351–362
Patra AK, Abbadie L, Clays-Josserand A, Degrange V, Grayston SJ, Guillaumaud N, Loiseau P, Louault F, Mahmood S, Nazaret S (2006) Effects of management regime and plant species on the enzyme activity and genetic structure of N-fixing, denitrifying and nitrifying bacterial communities in grassland soils. Environ Microbiol 8:1005–1016
Philippot L, Hallin S, Börjesson G, Baggs E (2009) Biochemical cycling in the rhizosphere having an impact on global change. Plant Soil 321:61–81
Philippot L, Raaijmakers JM, Lemanceau P, van der Putten WH (2013a) Going back to the roots: the microbial ecology of the rhizosphere. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:789–799
Philippot L, Spor A, Henault C, Bru D, Bizouard F, Jones CM, Sarr A, Maron PA (2013b) Loss in microbial diversity affects nitrogen cycling in soil. ISME J 7:1609–1619
Pi N, Tam N, Wu Y, Wong M (2009) Root anatomy and spatial pattern of radial oxygen loss of eight true mangrove species. Aquat Bot 90:222–230
Priha O, Grayston SJ, Pennanen T, Smolander A (1999) Microbial activities related to C and N cycling and microbial community structure in the rhizospheres of Pinus sylvestris, Picea abies and Betula pendula seedlings in an organic and mineral soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 30:187–199
Purkhold U, Wagner M, Timmermann G, Pommerening-Röser A, Koops H-P (2003) 16S rRNA and amoA-based phylogeny of 12 novel betaproteobacterial ammonia-oxidizing isolates: extension of the dataset and proposal of a new lineage within the nitrosomonads. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1485–1494
Purvaja R, Ramesh R, Ray A, Rixen T (2008) Nitrogen cycling: a review of the processes, transformations and fluxes in coastal ecosystems. Curr Sci India 94:1419–1438
Reddy K, Patrick W, Lindau C (1989) Nitrification-denitrification at the plant root-sediment interface in wetlands. Limnol Oceanogr 34:1004–1013
Rotthauwe JH, Witzel KP, Liesack W (1997) The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4704–4712
Ruiz-Rueda O, Hallin S, Bañeras L (2009) Structure and function of denitrifying and nitrifying bacterial communities in relation to the plant species in a constructed wetland. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 67:308–319
Schleper C, Jurgens G, Jonuscheit M (2005) Genomic studies of uncultivated archaea. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:479–488
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Skiba M, George T, Baggs E, Daniell T (2011) Plant influence on nitrification. Biochem Soc Trans 39:275–278
Steltzer H, Bowman WD (1998) Original articles: differential influence of plant species on soil nitrogen transformations within moist meadow alpine tundra. Ecosystems 1:464–474
Tsiknia M, Tzanakakis VA, Paranychianakis NV (2013) Insights on the role of vegetation on nitrogen cycling in effluent irrigated lands. Appl Soil Ecol 64:104–111
Wang Q, An S, Ma Z, Zhao B, Chen J, Li B (2006) Invasive spartina alterniflora: biology, ecology and management. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica 44:559–588
Wang H-T, Su J-Q, Zheng T-L, Yang X-R (2014) Impacts of vegetation, tidal process, and depth on the activities, abundances, and community compositions of denitrifiers in mangrove sediment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:9375–9387
Ward BB, O'Mullan GD (2002) Worldwide distribution of Nitrosococcus oceani, a marine ammonia-oxidizing γ-proteobacterium, detected by PCR and sequencing of 16S rRNA and amoA genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4153–4157
Wedin DA, Tilman D (1990) Species effects on nitrogen cycling: a test with perennial grasses. Oecologia 84:433–441
Wheatley R, Ritz K, Griffiths B (1990) Microbial biomass and mineral N transformations in soil planted with barley, ryegrass, pea or turnip. Plant Soil 127:157–167
Yang W, Zhao H, Chen X, Yin S, Cheng X, An S (2013) Consequences of short-term C4 plant Spartina alterniflora invasions for soil organic carbon dynamics in a coastal wetland of Eastern China. Ecol Eng 61:50–57
Yao H, Gao Y, Nicol GW, Campbell CD, Prosser JI, Zhang L, Han W, Singh BK (2011) Links between ammonia oxidizer community structure, abundance, and nitrification potential in acidic soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:4618–4625
Yu X, Yang J, Liu L, Tian Y, Yu Z (2014) Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion on biogenic elements in a subtropical coastal mangrove wetland. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3568-2
Zhang Q-F, Peng J-J, Chen Q, Li X-F, Xu C-Y, Yin H-B, Yu S (2011) Impacts of Spartina alterniflora invasion on abundance and composition of ammonia oxidizers in estuarine sediment. J Soils Sediments 11:1020–1031
Zhang L-M, Hu H-W, Shen J-P, He J-Z (2012) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea have more important role than ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in ammonia oxidation of strongly acidic soils. ISME J 6:1032–1045
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB15020302, XDB15020402), the Natural Science Foundation of China (31270153, 41376119), and the International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of China (2011DFB91710). We would like to thank Prof. Yong-guan Zhu from the Institute of Urban Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences for valuable suggestions on the earlier version of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Jizheng He
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Su, J., Zheng, T. et al. Insights into the role of plant on ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in the mangrove ecosystem. J Soils Sediments 15, 1212–1223 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1074-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1074-x