Abstract
Introduction
The estimation of the time since death, or post-mortem interval (PMI), still remains a main conundrum in forensic science. Several approaches have been so far proposed from either a qualitative or a quantitative point of view, but they still lack reliability and robustness. Recently, metabolomics has shown to be a potential tool to investigate the time-related post-mortem metabolite modifications in animal models.
Objectives
Here we propose, for the first time, the use of a 1H NMR metabolomic approach for the estimation of PMI from aqueous humour (AH) in an ovine model.
Methods
AH samples were collected at different times after death (from 118 to 1429 min). 1H NMR experiments were performed and spectral data analysed by multivariate statistical tools.
Results
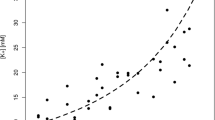
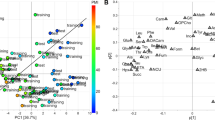
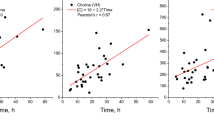
A multivariate calibration model was built to estimate PMI on the basis of the metabolite content of the samples. The model was validated with an independent test set, obtaining a prediction error of 59 min for PMI < 500 min, 104 min for PMI from 500 to 1000 min, and 118 min for PMI > 1000 min. Moreover, the metabolomic approach suggested a picture of the mechanisms underlying the post-mortem biological modifications, highlighting the role played by taurine, choline, and succinate.
Conclusion
The time-related modifications of the 1H NMR AH metabolomic profile seem to be encouraging in addressing the issue of a reproducible and robust model to be employed for the estimation of the time since death.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Barbas-Bernardos, C., Armitage, E. G., García, A., Mérida, S., Navea, A., Bosch-Morell, F., et al. (2016). Looking into aqueous humor through metabolomics spectacles—exploring its metabolic characteristics in relation to myopia. Journal Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 127, 18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2016.03.032.
Bifari, F., & Nisoli, E. (2017). Branched-chain amino acids differently modulate catabolic and anabolic states in mammals: a pharmacological point of view. British Journal of Pharmacology, 174(11), 1366–1377. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13624.
Bocaz-Beneventi, G., Tagliaro, F., Bortolotti, F., Manetto, G., & Havel, J. (2002). Capillary zone electrophoresis and artificial neural networks for estimation of the post-mortem interval (PMI) using electrolyte measurements in human vitreous humor. International Journal of Legal Medicine, 116(1), 5–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004140100239.
Camba, A., Lendoiro, E., Cordeiro, C., Martínez-Silva, I., Rodríguez-Calvo, M. S., & Vieira, D. N. (2014). High variation in hypoxanthine determination after analytical treatment of vitreous humor samples. Forensic Science, Medicine and Pathology, 10(4), 627–633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-014-9590-3.
Castillo-Peinado, L. S., & Luque de Castro, M. D. (2016). Present and foreseeable future of metabolomics in forensic analysis. Anaytica Chimica Acta, 925, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.04.040.
Chandrakanth, H. V., Kanchan, T., Balaraj, B. M., Virupaksha, H. S., & Chandrashekar, T. N. (2013). Postmortem vitreous chemistry—an evaluation of sodium, potassium and chloride levels in estimation of time since death (during the first 36 h after death). Journal of Forensic and Legal Medicine, 20(4), 211–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jflm.2012.09.001.
Chouchani, E. T., Pell, V. R., Gaude, E., Aksentijević, D., Sundier, S. Y., Robb, E. L., et al. (2014). Ischaemic accumulation of succinate controls reperfusion injury through mitochondrial ROS. Nature, 515(7527), 431–435. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13909.
Coe, J. I. (1989). Vitreous potassium as a measure of the postmortem interval: An historical review and critical evaluation. Forensic Science International, 42(3), 201–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/0379-0738(89)90087-X.
Ding, Y., Li, X., Guo, Y., Duan, W., Ling, J., Zha, L., et al. (2017). Estimation of postmortem interval by vitreous potassium evaluation with a novel fluorescence aptasensor. Scientific Reports, 7, 1868. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-02027-1.
Donaldson, A. E., & Lamont, I. L. (2013). Biochemistry changes that occur after death: Potential markers for determining post-mortem interval. PLoS ONE, 8(11), e82011. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0082011.
Donaldson, A. E., & Lamont, I. L. (2014). Metabolomics of postmortem blood: Identifying potential markers of post-mortem interval. Metabolomics, 11(1), 237–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-014-0691-5.
Du, T., Lin, Z., Xie, Y., Ye, X., Tu, C., Jin, K., et al. (2018). Metabolic profiling of femoral muscle from rats at different periods of time after death. PLoS ONE, 13(9), e0203920. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0203920.
Fais, P., Mazzotti, M. C., Teti, G., Boscolo-Berto, R., Pelotti, S., & Falconi, M. (2018). HIF1α protein and mRNA expression as a new marker for post mortem interval estimation in human gingival tissue. Journal of Anatomy, 232(6), 1031–1037. https://doi.org/10.1111/joa.23800.
Ferreira, P. G., Muñoz-Aguirre, M., Reverter, F., Sá Godinho, C. P., Sousa, A., Amadoz, A., et al. (2018). The effects of death and post-mortem cold ischemia on human tissue transcriptomes. Nature Communications, 9(1), 490. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02772-x.
He, X., & Slupsky, M. (2014). Metabolic fingerprint of dymethil sulfone (DMSO2) in microbial-mammalian co-metabolism. Journal of Proteome Research, 13(12), 5281–5292. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr500629t.
Heinämäki, A. A., Muhonen, A. S., & Piha, R. S. (1986). Taurine and other free amino acids in the retina, vitreous, lens, iris-ciliary body, and cornea of the rat eye. Neurochemical Research, 11(4), 535–542.
Henssge, C., & Madea, B. (2004). Estimation of the time since death in the early post-mortem period. Forensic Science International, 144(2–3), 167–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2004.04.051.
Henssge, C., & Madea, B. (2007). Estimation of the time since death. Forensic Science International, 165(2–3), 182–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2006.05.017.
Hirakawa, K., Koike, K., Uekusa, K., Nihira, M., Yuta, K., & Ohno, Y. (2009). Experimental estimation of postmortem interval using multivariate analysis of proton NMR metabolomic data. Legal Medicine, 11(Supplement 1), S282–S285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.legalmed.2009.02.007.
Javan, G. T., & Finley, S. J. (2018). What is the “thanatomicrobiome” and what is the relevance to forensic investigations? In T. K. Ralebitso-Senior (Ed.), Forensic Ecogenomics (pp. 133–143). London: Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809360-3.00006-0.
Ji, Y., Rao, J., Rong, X., Lou, S., Zheng, Z., & Lu, Y. (2017). Metabolic characterization of human aqueous humor in relation to high myopia. Experimental Eye Research, 159, 147–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2017.03.004.
Ji, Y., Rong, X., & Lu, Y. (2018). Metabolic characterization of human aqueous humor in the cataract progression after pars plana vitrectomy. BMC Ophtalmology, 18, 63. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-018-0729-y.
Jong, C. J., Azuma, J., & Schaffer, S. (2012). Mechanism underlying the antioxidant activity of taurine: Prevention of mitochondrial oxidant production. Amino Acids, 42(6), 2223–2232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0962-7.
Kalra, J., Mulla, A., & Kopargaonkar, A. (2016). Diagnostic value of vitreous humor in postmortem analysys. SM Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1(1), 1005.
Kang, Y. R., Park, Y. S., Park, Y. C., Yoon, S. M., JongAhn, H., Kim, G., et al. (2012). UPLC/Q-TOF MS based metabolomics approach to post-mortem-interval discrimination: Mass spectrometry based metabolomics approach. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation, 42(1), 41–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-012-0006-7.
Kaszynski, R. H., Nishiumi, S., Azuma, T., Yoshida, M., Kondo, T., & Takahashi, M. (2016). Postmortem interval estimation: A novel approach utilizing gas chromatography/mass spectrometry-based biochemical profiling. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 408(12), 3103–3112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9355-9.
Kuligowski, J., Solberg, R., Sànchez-Illana, A., Pankratov, L., Parra-Llorca, A., Quintas, G., et al. (2017). Plasma metabolite score correlates with hypoxia time in a newly born piglet model for asphyxia. Redox Biology, 12, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.02.002.
Kunikata, H., Ida, T., Sato, K., Aizawa, N., Sawa, T., Tawarayama, H., et al. (2017). Metabolomic profiling of reactive persulfides and polysulfides in the aqueous and vitreous humors. Scientific Reports, 7, 41984. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41984.
Kvalheim, O. M., Arneberg, R., Bleie, O., Rajalahti, T., Smilde, A. K., & Westerhuis, J. A. (2014). Variable importance in latent variable regression models. Journal of Chemometrics, 28, 615–622. https://doi.org/10.1002/cem.2626.
Lange, N., Swearer, S., & Sturner, W. Q. (1994). Human postmortem interval estimation from vitreous potassium: An analysis of original data from six different studies. Forensic Science International, 66(1994), 159–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/0379-0738(94)90341-7.
Lendoiro, E., Cordeiro, C., Rodríguez-Calvo, M. S., Vieira, D. N., Suárez-Peñaranda, J. M., & López-Rivadulla, M. (2012). Applications of tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MSMS) in estimating the post-mortem interval using the biochemistry of the vitreous humour. Forensic Science International, 223(1–3), 160–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/jdorsciint.2012.08.022.
Li, C., Ma, D., Deng, K., Chen, Y., Huang, P., & Wang, Z. (2017). Application of MALDI-TOF MS for estimating the postmortem interval in rat muscle samples. Journal of Forensic Science, 62(5), 1345–1350. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.13413.
Lloyd, D. K. (2008). Capillary electrophoresis analysis of biofluids with a focus on less commonly analyzed matrices. Journal of Chromatography B, 866(1–2), 154–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chromb.2008.01.058.
Locci, E., Scano, P., Rosa, M. F., Nioi, M., Noto, A., Atzori, L., et al. (2014). A metabolomic approach to animal vitreous humor topographical composition: A pilot study. PLoS ONE, 9(5), e97773. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0097773.
Madea, B. (2005). Is there a recent progress in the estimation of the postmortem interval by means of thanatochemistry? Forensic Science International, 151(2–3), 139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/forsciint.2005.01.013.
Madea, B., Kreuser, C., & Banaschak, S. (2001). Postmortem biochemical examination of synovial fluid—a preliminary study. Forensic Science International, 118(1), 29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0379-0738(00)00372-8.
Madea, B., & Musshof, F. (2007). Postmortem biochemistry. Forensic Science International, 165(2–3), 165–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2006.05.023.
Madea, B., & Rodig, A. (2006). Time of death dependent criteria in vitreous humor: Accuracy of estimating the time since death. Forensic Science International, 164(2–3), 87–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2005.12.002.
Mayordomo-Febrer, A., Lopez-Murcia, M., Morales-Tatay, J. M., Monleon-Salvado, D., & Pinazo-Dur, M. D. (2015). Metabolomics of the aqueous humor in the rat glaucoma model induced by a series of intracamerular sodium hyaluronate injection. Experimental Eye Research, 131, 84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2014.11.012.
Metcalf, J. L., Xu, Z. Z., Bouslimani, A., Dorrestein, P., Carter, D. O., & Knight, R. (2017). Microbiome tools for forensic science. Trends in Biotechnology, 35(9), 814–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2017.03.006.
Muñoz Barús, J. I., Febrero-Bande, M., & Cadarso-Suárez, C. (2008). Flexible regression models for estimating postmortem interval (PMI) in forensic medicine. Statistics in Medicine, 27(24), 5026–5038. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.3319.
Newman, J. C., & Verdin, E. (2014). Ketone bodies as signalling metabolites. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism, 25(1), 42–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2013.09.002.
Nioi, M., Napoli, P. E., Demontis, R., Locci, E., Fossarello, M., & d’Aloja, E. (2018). Morphological analysis of corneal findings modifications after death: A preliminary OCT study on an animal model. Experimental Eye Reseach, 169, 20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2018.01.013.
Ortmann, J., Markwerth, P., & Madea, B. (2016). Precision of estimating the time since death by vitreous potassium—Comparison of 5 different equations. Forensic Science International, 269, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2016.10.005.
Palmiere, C., & Mangin, P. (2015). Urea nitrogen, creatinine, and uric acid levels in postmortem serum, vitreous humor, and pericardial fluid. International Journal of Legal Medicine, 129(2), 301–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-014-1076-z.
Passos, M. L., Santos, A. M., Pereira, A. I., Santos, J. R., Santos, A. J., & Saraiva, M. L. (2009). Estimation of postmortem interval by hypoxanthine and potassium evaluation in vitreous humor with a sequential injection system. Talanta, 79(4), 1094–1099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2009.02.054.
Pietrowska, K., Dmuchowska, D. A., Krasnicki, P., Bujalska, A., Samczuk, P., Parfieniuk, E., et al. (2018). An exploratory LC-MS-based metabolomics study reveals differences in aqueous humor composition between diabetic and non-diabetic patients with cataract. Electrophoresis, 39(9–10), 1233–1240. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201700411.
Pittner, S., Ehrenfellner, B., Monticelli, F. C., Zissler, A., Sänger, A. M., Stoiber, W., et al. (2016). Postmortem muscle protein degradation in humans as a tool for PMI delimitation. International Journal of Legal Medicine, 130(6), 1547–1555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-016-1349-9.
Poulsen, J. P., Rognum, T. O., & Sagustad, O. D. (1990). Changes in oxypurine concentrations in vitreous humor of pigs during hypoxemia and post-mortem. Pediatric Research, 28(5), 482–484.
Rajalahti, T., Arneberg, R., Kroksveen, A. C., Berle, M., Myhr, K. M., & Kvalheim, O. M. (2009). Discriminating variable test and selectivity ratio plot: Quantitative tools for interpretation and variable (biomarker) selection in complex spectral or chromatographic profiles. Analytical Chemistry, 81(7), 2581–2590. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac802514y.
Risa, Ø., Sæther, O., Midelfart, A., Krane, J., & Cejková, J. (2002). Analysis of immediate changes of water-soluble metabolites in alkali-burned rabbit cornea, aqueous humor and lens by high-resolution 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Graefe’s Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology, 240, 49–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-001-0403-5.
Rognum, T. O., Holmen, S., Musse, M. A., Dahlberg, P. S., Stray-Pedersen, A., Saugstad, O. D., et al. (2016). Estimation of time since death by vitreous humor hypoxanthine, potassium, and ambient temperature. Forensic Science International, 262, 160–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2016.03.001.
Rosa, M. F., Scano, P., Noto, A., Nioi, M., Sanna, R., Paribello, F., et al. (2015). Monitoring the modifications of the vitreous humor metabolite profile after death: An animal model. BioMed Research International, 2015, 627201. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/6272201.
Sampaio-Silva, F., Magalhães, T., Carvalho, F., Dinis-Oliveira, R. J., & Silvestre, R. (2013). Profiling of RNA degradation for estimation of post morterm interval. PLoS ONE, 8(2), e56507. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0056507.
Sato, T., Zaitsu, K., Tsuboi, K., Nomura, M., Kusano, M., Shima, N., et al. (2015). A preliminary study on potmortem interval estimation of suffocated rats by GC-MS/MS-based plasma metabolic profiling. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 407(13), 3659–3665. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8584-7.
Snytnikova, O. A., Khlichkina, A. A., Yanshole, L. V., Yanshole, V. V., Iskakov, I. A., & Egorova, E. V. (2017a). Metabolomics of the human aqueous humor. Metabolomics, 13, 5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1144-0.
Snytnikova, O. A., Yanshole, L. V., Iskakov, I. A., Yanshole, V. V., Chernykh, V. V., & Stepakov, D. A. (2017b). Quantitative analysis of the human cornea and aqueous humor. Metabolomics, 13, 152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1281-0.
Song, Z., Gao, H., Liu, H., & Sun, X. (2011a). Metabolomics of rabbit aqueous humor after administration of glucocorticosteroid. Current Eye Research, 36(6), 563–570. https://doi.org/10.3109/02713683.2011.566410.
Song, Z., Gong, Y., Liu, H., Ren, Q., & Sun, X. (2011b). Glycyrrhizin could reduce ocular hypertension induced by triamcinolone acetonide in rabbits. Molecular Vision, 17, 2056–2064.
Stocchero, M., Locci, E., d’Aloja, E., Nioi, M., Baraldi, E., & Giordano, G. (2019). PLS in Metabolomics. Metabolites, 9(3), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9030051.
Stocchero, M., Riccadonna, S., & Franceschi, P. (2018). Projection to latent structures with orthogonal constraints for metabolomics data. Journal of Chemometrics, 32, e2987. https://doi.org/10.1002/cem.2987.
Sumner, L. W., Amberg, A., Barrett, D., Beale, M. H., Beger, R., Daykin, C. A., et al. (2007). Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis—chemical analysis working Group (CAWG) metabolomics standards initiative (MSI). Metabolomics, 3, 211–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-007-0082-2.
Swain, R., Kumar, A., Sahoo, A., Lakshmy, R., Gupta, S. K., Bhardwaj, D. N., et al. (2015). Estimation of post-mortem interval: A comparison between cerebrospinal fluid and vitreous humour chemistry. Journal of Forensic and Legal Medicine, 36, 144–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jflm.2015.09.017.
Tagliaro, F., Bortolotti, F., Manetto, G., Cittadini, F., Pascali, V., & Marigo, M. (2001). Potassium concentration differences in the vitreous humour from the two eyes revisited by microanalysis with capillary electrophoresis. Journal of Chromatography A, 924(1–2), 493–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(01)00713-0.
Tagliaro, F., Manetto, G., Cittadini, F., Marchetti, D., Bortolotti, F., & Marigo, M. (1999). Capillary zone electrophoresis of potassium in human vitreous humour: validation of a new method. Journal of Chromatography B, 733(1–2), 273–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4347(99)00338-2.
Takata, T., Kitao, T., & Miyaishi, S. (2014). Relationship between post-mortem interval and creatine concentration in vitreous humour and cerebrospinal fluid. Australian Journal of Forensic Sciences, 46(2), 160–165. https://doi.org/10.1080/00450618.2013.824027.
Tan, S. Z., Mullard, G., Hollywood, K. A., Dunne, W. B., & Bishop, P. N. (2016). Characterisation of the metabolome of ocular tissues and post-mortem changes in the rat retina. Experimental Eye Research, 149, 8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2016.05.019.
Tessem, M. B., Bathen, T. F., Cejkova, J., & Midelfart, A. (2005). Effect of UV-A and UV-B irradiation on the metabolic profile of aqueous humor in rabbits analyzed by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 46(3), 776–781. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.04-0787.
Tripathi, R. C., Millard, C. B., & Tripathi, B. J. (1989). Protein composition of human aqueous: SDS-PAGE analysis of surgical and post-mortem samples. Experimental Eye Research, 48, 117–130.
Tumram, N. K., Ambade, V. N., & Dongre, A. P. (2014). Thanatochemistry: Study of vitreous humor potassium. Alexandria Journal of Medicine, 50, 365–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajme.2013.12.002.
Tumram, N. K., Bardale, R. V., & Dongre, A. P. (2011). Postmortem analysis of synovial fluid and vitreous humour for determination of death interval: A comparative study. Forensic Science International, 204(1–3), 186–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2010.06.007.
Udawatte, C., Qian, H., Mangini, N. J., Kennedy, B. G., & Ripps, H. (2008). Taurine suppresses the spread of cell death in electrically coupled RPE cells. Molecular Vision, 14, 1940–1950.
Williamson, B. K., Hawkey, N. M., Blake, D. A., Frenkel, J. W., McDaniel, K. P., Davis, J. K., et al. (2018). The effects of glaucoma drainage devices on oxygen tension, glycolytic metabolites, and metabolomics profile of aqueous humor in the rabbit. Translational Vision Science & Technology, 7(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.1167/tvst.7.1.14.
Wishart, D. S., Feunang, Y. D., Marcu, A., Guo, A. C., Liang, K., Vázquez-Fresno, R., et al. (2018). HMDB 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Research, 46(1), 608–617. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1089.
Wood, P. L., & Shirley, N. R. (2013). Lipidomics analysis of postmortem interval: Preliminary evaluation of human skeletal muscle. Metabolomics, 3(3), 127. https://doi.org/10.4172/2153-0769.1000127.
Wu, Z., Lu, X., Chen, F., Dai, X., Ye, Y., Yan, Y., et al. (2018). Estimation of early postmortem interval in rats by GC-MS-based metabolomics. Legal Medicine, 31, 42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.legalmed.2017.12.014.
Xie, G., Zhang, S., Zheng, X., & Jia, W. (2013). Metabolomics approaches for characterizing metabolic interactions between host and its commensal microbes. Electrophoresis, 34(19), 2787–2798. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201300017.
Yang, M., Li, H., Yang, T., Ding, Z., Wu, S., Qiu, X., et al. (2018). A study on the estimation of postmortem interval based on environmental temperature and concentrations of substance in vitreous humor*. Journal of Forensic Sciences, 63(3), 745–751. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.13615.
Zelentsova, E. A., Yanshole, L. V., Snytnikova, O. A., Yanshole, V. Y., Tsentalovich, Y. P., & Sagdeev, R. Z. (2016). Post-mortem changes in the metabolomic compositions of rabbit blood, aqueous and vitreous humors. Metabolomics, 12, 172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1118-2.
Zhu, Y., Wang, L., Yin, Y., & Yang, E. (2017). Systematic analysis of gene expression patterns associated with postmortem interval in human tissues. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 5435. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-05882-0.
Zilg, B., Bernard, S., Alkass, K., Berg, S., & Druid, H. (2015). A new model for the estimation of time of death from vitreous potassium levels corrected for age and temperature. Forensic Science International, 254, 158–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2015.07.020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EdA, EL, MS, FdG conceived and designed research; MN, RC, LN, AC, PEN collected and pre–processed samples; EL and AN performed NMR experiments; EL and MS analysed data; EL, MS, EdA wrote and review the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Research involving animal rights
Sheep heads represent waste material, so there were neither need of an ad hoc animal protocol nor associated costs.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Locci, E., Stocchero, M., Noto, A. et al. A 1H NMR metabolomic approach for the estimation of the time since death using aqueous humour: an animal model. Metabolomics 15, 76 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1533-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1533-2