Abstract
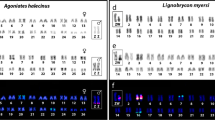
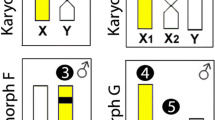
We describe chromosomal and electric signal diversity in three sympatric species of Gymnotus (Gymnotidae) fish from the Central Amazon Floodplain. Gymnotus arapaima presents a karyotype of 2n = 44 (24 m-sm + 20st-a), G. mamiraua 2n = 54 (42 m-sm + 12st-a), and G. jonasi 2n = 52 (12 m-sm + 40st-a). No evidence for a chromosomal sexual system was observed in two species for which both males and females were analyzed (G. mamiraua and G. arapaima). In all three species the constitutive heterochromatin is located primarily in pericentromeric regions, but also at some other sites. G. arapaima and G. mamiraua exhibit simple nucleolar organizing regions (NORs) on short arms of chromosome pairs 19 and 24, respectively. Gymnotus jonasi exhibits a multiple interstitial NOR on the long arm of pairs 9 and 10, and on the short arm of pair 11. G. arapaima and G. mamiraua exhibit several additional similarities in their karyotypic formulas—reflecting the phylogenetic proximity of these species within a G. carapo group clade (based on molecular phylogenetic evidence). The chromosomal differences among these three sympatric species imply complete post-zygotic reproductive isolation. A prominent pattern of partitioning of the peak power frequency of the electric organ discharge of these three species indicates pre-zygotic reproductive isolation of mate attraction signals. We conclude by discussing the evolutionary events that may have promoted signal divergence and reproductive isolation in Gymnotus of the Central Amazon, and the role that chromosomal rearrangements may place in diversification.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert JS, Crampton WGR (2001) Five new species of Gymnotus (Teleostei: Gymnotiformes) from an Upper Amazon floodplain, with descriptions of electric organ discharges and ecology. Ichthyol Explor Freshw 12(3):241–266
Albert JS, Crampton WGR (2003) Seven new species of the Neotropical electric fish Gymnotus (Teleostei, Gymnotiformes) with a redescription of G. carapo (Linnaeus). Zootaxa 28:1–54
Albert JS, Fernandes-Matioli FMC, Almeida-Toledo LF (1999) New species of Gymnotus (Gymnotiformes-Teleostei) from southeastern Brazil: toward the deconstruction of Gymnotus carapo. Copeia 2:410–421
Albert JS, Crampton WGR, Thorsen DH, Lovejoy NR (2005) Phylogenetic systematics and historical biogeography of the Neotropical electric fish Gymnotus (Teleostei: Gymnotidae). Syst Biodivers 4:375–417. doi:10.1017/S1477200004001574
Artoni RF, Bertollo LAC (2001) Trends in the karyotype evolution of Loricariidae fish (Siluriformes). Hereditas 134:201–210
Bertollo LAC, Takashi CS, Moreira-Filho O (1978) Cytotaxonomic considerations on Hoplias lacerdae (Pisces, Erythrinidae). Braz J Genet 2:103–120
Bertollo LAC, Born GG, Dergam JA, Fenocchio AS, Moreira-Filho O (2000) A biodiversity approach in the Neotropical Erythrinidae fish, Hoplias malabaricus. Karyotypic survey, geographic distribution of cytotypes and cytotaxonomic considerations. Chromosome Res 8:603–613
Bullock TH, Hopkins CD, Popper AN, Fay RR (2005) Electroreception. Springer, New York
Cardoso AL, Pieczarka JC, Feldberg E, Milhomem SSR, Moreira-Almeida T, Silva DS, Silva PC, Nagamachi CY (2011) Chromosomal characterization of two species of genus Steatogenys (Gymnotiformes: Rhamphichthyoidea: Steatogenini) from the Amazon basin: sex chromosomes and correlations with Gymnotiformes phylogeny. Rev Fish Biol Fish. doi:10.1007/s11160-010-9196-0
Claro FL (2008) Gymnotus carapo and Gymnotus sylvius (Teleostei: Gymnotidae): a molecular-cytogenetic approach. PhD Dissertation (in Portuguese). Universidade de São Paulo
Coghlan A, Eichler EE, Oliver SG, Paterson AH, Stein L (2005) Chromosome evolution in eukaryotes: a multi-kingdom perspective. Trends Genet 21(12):673–682
Cozzolino S, D’Emerico S, Widmer A (2004) Evidence for reproductive isolate selection in Mediterranean orchids: karyotype differences compensate for the lack of pollinator specificity. Proc R Soc Lond B (271):S259–S262. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2004.0166
Crampton WGR (2006) Evolution of electric signal diversity in gymnotiform fishes. II. Signal design. In: Ladich F, Collin SP, Moller P, Kapoor BG (eds) Communication in fishes. Science Publishers Inc., Enfield, pp 696–731
Crampton WGR (2011) An ecological perspective on diversity and distributions. In: Albert JS, Reis RE (eds) Historical biogeography of Neotropical Freshwater Fishes. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 165–189
Crampton WGR, Albert JS (2003) A redescription of Gymnotus coropinae, an often misidentified species of gymnotid fish, with notes on ecology and electric organ discharge. Zootaxa 348:1–20
Crampton WGR, Albert JS (2004) Redescription of Gymnotus coatesi (Gymnotiformes, Gymnotidae), a rare species of electric fish from the lowland Amazon Basin, with descriptions of osteology, electric signals and ecology. Copeia 3:525–533
Crampton WGR, Albert JS (2006) Evolution of electric signal diversity in gymnotiform fishes. I. Phylogenetic systematics, ecology and biogeography. In: Ladich F et al (eds) Communication in fishes. Science Publishers, Enfield, pp 647–696, 718–731
Crampton WGR, Thorsen DH, Albert JS (2005) Three new species from a diverse, sympatric assemblage of the electric fish Gymnotus (Gymnotiformes: Gymnotidae) in the lowland Amazon Basin, with notes on ecology. Copeia 1:82–99
Crampton WGR, Davis JK, Lovejoy NR, Pensky M (2008) Multivariate classification of animal communication signals: a simulation-based comparison of alternative signal processing procedures using electric fishes. J Physiol Paris 102:304–321. doi:10.1016/j.jphysparis.2008.10.001
Crampton WGR, Lovejoy NR, Waddell JC (2011) Reproductive character displacement and signal ontogeny in a sympatric assemblage of electric fishes. Evolution 65:1650–1666. doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.2011.01245
De Souza ACP, Nagamachi CY, Milhomem SSR, Feldberg E, Pieczarka JC (2009) Cytogenetic analysis in catfish species of the genus Peckoltia Miranda Ribeiro, 1912 (Teleostei: Siluriformes: Loricariidae). Comp Cytogenet 2:103–109. doi:10.3897/compcytogen.v3i2.17
Fernandes FMC, Albert JS, Daniel-Silva MFZ, Lopes CE, Crampton WGR, Almeida-Toledo LF (2005) A new Gymnotus (Teleostei: Gymnotiformes: Gymnotidae) from the Pantanal Matogrossense of Brazil and adjacent drainages: continued documentation of a cryptic fauna. Zootaxa 933:1–14
Fernandes-Matioli FMC, Almeida-Toledo LF (2001) A molecular phylogenetic analysis in Gymnotus species (Pisces: Gymnotiformes) with inferences on chromosome evolution. Caryologia 54:23–30
Fernandes-Matioli FMC, Almeida-Toledo LF, Toledo-Filho SA (1997) Extensive nucleolus organizer region polymorphism in Gymnotus carapo (Gymnotoidei, Gymnotidae). Cytogenet Cell Genet 78:236–239. doi:10.1159/000134665
Fernandes-Matioli FMC, Almeida-Toledo LF, Toledo-Filho SA (1998a) Natural triploidy in the Neotropical species Gymnotus carapo (Pisces: Gymnotiformes). Caryologia 3:319–322
Fernandes-Matioli FMC, Marchetto MCN, Almeida-Toledo LF, Toledo-Filho SA (1998b) High intraspecific karyological conservation in four species of Gymnotus (Pisces: Gymnotiformes) from Southeastern Brazilian basins. Caryologia 3:221–234
Foresti F, Almeida-Toledo LF, de Almeida-Toledo FS (1984) Chromosome studies in Gymnotus carapo and Gymnotus sp. (Pisces, Gymnotidae). Caryologia 37:141–146
Hatanaka T, Galetti PM Jr (2004) Mapping of the 18S and 5S ribosomal RNA genes in the fish Prochilodus argenteus Agassiz, 1829 (Characiformes, Prochilodontidae). Genetica 122:239–244
Henderson PA, Hamilton WD, Crampton WGR (1998) Evolution and diversity in Amazonian floodplain communities. In: Newbery DM, Prins HHT, Brown ND (eds) Dynamics of tropical communities. Blackwell Science, Oxford, pp 385–419
Hopkins CD (1976) Stimulus filtering and electroreception: tuberous electroreceptors in three species of gymnotoid fish. J Comp Physiol 111:171–208. doi:10.1007/BF00605531
Howell WM, Black DA (1980) Controlled silver-staining of nucleolus organizer regions with a protective colloidal developer: a 1-step method. Experientia 36:1014–1015. doi:10.1007/BF01953855
Lacerda MCV, Maistro EL (2007) Cytogenetic analysis of three sympatric Gymnotus species (Teleostei: Gymnotidae) from the Fundo Stream, MG, Brazil. Cytologia 72:89–93
Levan A, Fredga K, Sandberg HA (1964) Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas 52:201–220
Lovejoy NR, Lester K, Crampton WGR, Marques FPL, Albert JS (2010) Phylogeny, biogeography, and electric signal evolution of Neotropical knifefishes of the genus Gymnotus (Osteichthyes: Gymnotidae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 54:278–290. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2009.09.017
Lukhtanov VA, Kandul NP, Plotkin JB, Dantchenko AV, David Haig D, Pierce N (2005) Reinforcement of pre-zygotic isolation and karyotype evolution in Agrodiaetus butterflies. Nature 436:385–389. doi:10.1038/nature03704
Marchetto MC, Fernandes-Matioli FM, Almeida-Toledo LF (1998) Estudos citogenéticos comparativos em populações de Gymnotus pantherinus (Pisces, Gymnotidae). Genet Mol Biol 3:65
Margarido VP, Bellafronte E, Moreira-Filho O (2007) Cytogenetic analysis of three sympatric Gymnotus (Gymnotiformes, Gymnotidae) species verifies invasive species in the Upper Paraná River basin, Brazil. J Fish Biol 70:155–164. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2007.01365.x
McGregor PK, Westby GWM (1992) Discrimination of individually characteristic electric organ discharges by a weakly electric fish. Anim Behav 43:977–986. doi:10.1016/S0003-3472(06)80011-4
Milhomem SSR, Pieczarka JC, Crampton WGR, Souza ACP, Carvalho JR Jr, Nagamachi CY (2007) Differences in karyotype between two sympatric species of Gymnotus (Gymnotiformes: Gymnotidae) from the eastern amazon of Brazil. Zootaxa 1397:55–62
Milhomem SSR, Pieczaka JC, Crampton WGR, Silva DS, Souza ACP, Carvalho JR, Nagamachi CY (2008) Chromosomal evidence for a cryptic species in the Gymnotus carapo species-complex (Gymnotiformes, Gymnotidae). BMC Genet 9:75. doi:10.1186/1471-2156-9-75
Milhomem SSR, Castro RR, Nagamachi CY, Souza ACP, Feldberg E, Pieczarka JC (2010) Different cytotypes in fishes of the genus Hypostomus Lacépède, 1803 (Siluriformes: Loricariidae) from Xingu river (Amazon region, Brazil). Comp Cytogenet 4(1):45–54. doi:10.3897/compcytogen.v4i1.31
Milhomem SSR, Crampton WGR, Pieczarka JC, Shetka GH, Silva DS, Nagamachi CY (2011) Gymnotus capanema, a new species of electric knife fish (Gymnotidae-Gymnotiformes) from eastern Amazonia, with comments on an unusual karyotype. J Fish Biol (in press)
Nagamachi CY, Pieczarka JC, Milhomem SSR, O’Brien PCM, Souza ACP, Ferguson-Smith MA (2010) Multiple rearrangements in cryptic species of electric knifefish, Gymnotus carapo (Gymnotidae, Gymnotiformes) revealed by chromosome painting. BMC Genet 11:28. doi:10.1186/1471-2156-11-28
Navarro A, Barton NH (2003) Accumulating postzygotic isolation genes in parapatry: a new twist on chromosomal speciation. Evolution 57(3):447–459
Pieczarka JC, Nagamachi CY, Souza ACP, Milhomem SSR, Castro RR, Nascimento AL (2006) An adaptation to DAPI-banding to fishes chromosomes. Caryologia 59:43–46
Queiroz HL (2005) The Mamirauá Sustainable development reserve. Advanced studies 19(54). doi:10.1590/S0103-40142005000200011
Rodriguez-Cattaneo A, Pereira AC, Aguilera PA, Crampton WGR, Caputi AA (2008) Species-specific diversity of a fixed motor pattern: the electric organ discharge of Gymnotus. PLoS ONE 3(5):e2038. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002038
Sánchez S, Laudicina A, Jorge LC (2004) A new report of multiple sex chromosome system in the order Gymnotiformes (Pisces). Cytologia 69:155–160. doi:10.1508/cytologia.69.155
Schweizer D (1980) Simultaneous fluorescent staining of R bands and specific heterochromatic regions (DA/DAPI Bands) in human chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 27:190–193. doi:10.1159/000131482
Silva EB, Margarido VP (2005) An X1X1X2X2/X1X2Y multiple sex chromosome system in a new species of the genus Gymnotus (Pisces, Gymnotiformes). Environ Biol Fishes 73:293–297. doi:10.1007/s10641-005-2144-5
Silva DS, Milhomem SSR, Souza ACP, Pieczarka JC, Nagamachi CY (2008) A conserved karyotype of Sternopygus macrurus (Sternopygidae, Gymnotiformes) in the Amazon region: differences from other hydrographic basins suggest cryptic speciation. Micron 39:1251–1254. doi:10.1016/j.micron.2008.04.001
Silva DS, Milhomem SSR, Pieczarka JC, Nagamachi CY (2009) Cytogenetic studies in Eigenmannia virescens (Sternopygidae, Gymnotiformes) and new inferences on the origin of sex chromosomes in the Eigenmannia genus. BMC Genet 10:74. doi:10.1186/1471-2156-10-74
Sumner AT (1972) Simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp Cell Res 75:304–306. doi:10.1016/0014-4827(72)90558-7
Vicari MR, Artoni RF, Bertollo LAC (2005) Comparative cytogenetics of Hoplias malabaricus (Pisces, Erythrinidae): a population analysis in adjacent hydrographic basins. Genet Mol Biol 28(1):103–110
Watson D, Bastian J (1979) Frequency response characteristics of electroreceptors in the weakly electric fish, Gymnotus carapo. A: neuroethology sensory neural and behavioral physiology. J Comp Physiol 134:191–202. doi:10.1007/BF00610394
Wells JK, Crampton WGR (2006) A portable bio-amplifier for electric fish research: design and construction. Neotrop Ichthyol 4(2):295–299
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the IDSM (Instituto de Desenvolvimento Sustentável Mamirauá) for logistic support to collect samples. The Cytogenetic lab was funded by CNPq, FAPESPA, CAPES, and UFPA. Collecting was authorized by IBAMA (Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente) permit 13248-1 (IBAMA Registration 242396). W. Crampton was funded by the US National Science Foundation grant DEB-0614334, and grants from CNPq and MCT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milhomem, S.S.R., Crampton, W.G.R., Pieczarka, J.C. et al. Chromosomal and electric signal diversity in three sympatric electric knifefish species (Gymnotus, Gymnotidae) from the Central Amazon Floodplain. Rev Fish Biol Fisheries 22, 485–497 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11160-011-9239-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11160-011-9239-1