Abstract
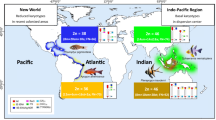
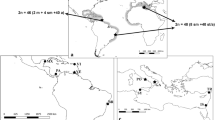
The order Gobiiformes is made up of more than 2200 species, representing one of the most diverse groups among teleost fishes. The biological causes for the tachytelic karyotype evolution of the gobies have not yet been fully studied. Here we expanded cytogenetic data for the Eleotridae family, analyzing the neotropical species Dormitator maculatus, Eleotris pisonis, Erotelis smaragdus, and Guavina guavina. In addition, a meta-analytical approach was followed for elucidating the karyotype diversification versus biological aspects (habitat and egg type) of the Gobiiformes. The species E. smaragdus and E. pisonis present 2n = 46 acrocentric chromosomes (NF = 46), D. maculatus 2n = 46 (36sm + 4st + 6a; NF = 86), and G. guavina, the most divergent karyotype, with 2n = 52 acrocentric chromosomes (NF = 52). Besides numeric and structural diversification in the karyotypes, the mapping of rDNAs and microsatellites also showed noticeable numerical and positional variation, supporting the high chromosomal evolutionary dynamism of these species. In Gobiiformes, karyotype patterns which are more divergent from the basal karyotype (2n = 46a) are associated with characteristics less effective to dispersion, such as the benthic habit. These adaptive characteristics, connected with the organization of the repetitive DNA content in the chromosomes, likely play a synergistic role in the remarkable karyotype diversification of this group.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amores A, Giles V, Thode G (1990) Adaptive character of a Robertsonian fusion in chromosomes of the fish Gobius paganellus (Pisces, Perciformes). Heredity 65:151–155
Arai R (2011) Fish karyotypes: a check list. Springer, Japan
Arai R, Sawada Y (1974) Chromosomes of Japanese gobioid fishes. Bull Natl Sci Mus [Tokyo] 17:97–102
Araújo WC, Martínez PA, Molina WF (2010) Mapping of ribosomal DNA by FISH, EcoRI digestion and replication bands in the cardinalfish Apogon americanus (Perciformes). Cytologia 75:109–117
Ayala D, Acevedo P, Pombi M, Dia I, Boccolini D, Costantini C, Simard F, Fontenille D (2017) Chromosome inversions and ecological plasticity in the main African malaria mosquitoes. Evolution 71:686–701
Baensch HA, Riehl R (1991) Aquarien Atlas. Band. 3. Melle: Mergus, Verlag für Natur-und Heimtierkunde, Germany, p 992
Berg P, Star B, Pampoulie C, Sodeland M, Barth JMI, Knutsen H, Jakobsen KS, Jentoft S (2016) Three chromosomal rearrangements promote genomic divergence between migratory and stationary ecotypes of Atlantic cod. Sci Rep 6:23246
Berg P, Star B, Pampoulie C, Bradbury IR, Bentzen P, Hutchings JA, Jentoft S, Jakobsen KS (2017) Trans-oceanic genomic divergence of Atlantic cod ecotypes is associated with large inversions. Heredity 119:418–428
Betancur-R R, Broughton RE, Wiley EO, Carpenter K, Lopez JA, Li C, Holcroft NI, Arcila D, Sanciangco M, Cureton JC II, Zhang F, Buser T, Campbell MA, Ballesteros JA, Roa-Varon A, Willis S, Borden WC, Rowley T, Reneau PC, Hough DJ et al (2013) The tree of life and a new classification of bony fishes. PLoS Curr 5:ecurrents.tol.53ba26640df0ccaee75bb165c8c26288
Betancur-R R, Wiley EO, Arratia G, Acero A, Bailly N, Miya M, Lecointre G, Orti G (2017) Phylogenetic classification of bony fishes. BMC Evol Biol 17:162
Caputo V, Marchegiani F, Sorice M, Olmo E (1997) Heterochromatin heterogeneity and chromosome variability in four species of gobiid fishes (Perciformes: Gobiidae). Cytogenet Cell Genet 79:266–271
Caputo V, Caniglia ML, Machella N (1999) The chromosomal complement of Aphia minuta, a paedomorphic goby. J Fish Biol 55:455–458
Ene AC (2003) Chromosomal polymorphism in the goby Neogobius eurycephalus (Perciformes: Gobiidae). Mar Biol 142:583–588
Eschmeyer WN, Fong JD (2020) Species by family/subfamily. http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/SpeciesByFamily.asp. Accessed 30 Jun 2020.
Fanta E (1997) Behaviour and circadian rhythm of the fish Bathygobius soporator Valenciennes (Gobiidae) under the influence of environmental salinity and temperature. Rev Bras Zool 1:221–244
Faria R, Johannesson K, Butlin RK, Westram AM (2019) Evolving inversions. Trends Ecol Evol 34:239–248
Galetti PM Jr, Aguilar CT, Molina WF (2000) An overview of marine fish cytogenetics. Hydrobiologia 420:55–62
Galván-Quesada S, Doadrio I, Alda F, Perdices A, Reina RG, Varela MG, Hernández N, Mendoza AC, Bermingham E, Domínguez-Domínguez O (2016) Molecular phylogeny and biogeography of the amphidromous fish genus Dormitator Gill 1861 (Teleostei: Eleotridae). PLoS ONE 11:e0153538
Giovannotti M, La Mesa M, Caputo V (2009) Life style and genetic variation in teleosts: the case of pelagic (Aphia minuta) and benthic (Gobius niger) gobies (Perciformes: Gobiidae). Mar Biol 156:239–252
Gold JR, Li C, Shipley NS, Powers PK (1990) Improved methods for working with fish chromosomes with a review of metaphase chromosome banding. J Fish Biol 37:563–575
Gornung E (2013) Twenty years of physical mapping of major ribosomal RNA genes across the teleosts: a review of research. Cytogenet Genome Res 141:90–102
Grigoryan KA, Vasiliev VP (1993) Karyotypes of five species of goby (Gobiidae) from the basins of the Black and Caspian seas. J Ichthyol 33:137–143
Howell WM, Black DA (1980) Controlled silver staining of nucleolus organizer region with protective colloidal developer: a 1-step method. Experientia 36:1014–1015
Kess T, Bentzen P, Lehnert SJ, Sylvester EVA, Lien S, Kent MP, Sinclair-Waters M, Morris C, Wringe B, Fairweather R, Bradbury IR (2020) Modular chromosome rearrangements reveal parallel and nonparallel adaptation in a marine fish. Ecol Evol 10:638–653
Kirubakaran TG, Grove H, Kent MP, Sandve SR, Baranski M, Nome T, De Rosa MC, Righino B, Johansen T, Otterå H, Sonesson A, Lien S, Andersen Ø (2016) Two adjacent inversions maintain genomic differentiation between migratory and stationary eco-types of Atlantic cod. Mol Ecol 25:2130–2143
Kottelat M, Freyhof J (2007) Handbook of European freshwater fishes. Publications Kottelat, Cornol and Freyhof, Berlin, p 646
Kubat Z, Hobza R, Vyskot B, Kejnovsky E (2008) Microsatellite accumulation on the Y chromosome in Silene latifolia. Genome 51:350–356
Levan A, Fredga K, Sandeberg AA (1964) Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Heredity 52:201–220
Lima-Filho PA, Cioffi MB, Bertollo LAC, Molina WF (2012) Chromosomal and morphological divergences in Atlantic populations of the frillfin goby Bathygobius soporator (Gobiidae, Perciformes). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 434:63–70
Lima-Filho PA, Bertollo LAC, Cioffi MB, Costa GWWF, Molina WF (2014a) Karyotype divergence and spreading of 5S rDNA sequences between genomes of two species: darter and emerald gobies (Ctenogobius, Gobiidae). Cytogenet Genome Res 3:197–203
Lima-Filho PA, Amorim KDJ, Cioffi MB, Bertollo LAC, Molina WF (2014b) Chromosomal mapping of repetitive DNAs in Gobionellus oceanicus and G. stomatus (Gobiidae; Perciformes): a shared XX/XY system and an unusual distribution of 5S rDNA sites on the Y chromosome. Cytogenet Genome Res 144:333–340
Lima-Filho PA, Rosa RS, Souza AS, Costa GWWF, Oliveira C, Molina WF (2016) Evolutionary diversification of Western Atlantic Bathygobius species based on cytogenetic, morphologic and DNA barcode data. Rev Fish Biol Fisher 26:109–121
Maldonado-Monroy MC, Uribe-Alcocer M, Arreguin-Espinosa J, Castro-Perez A (1985) Karyological studies on Dormitator maculatus Bloch and Gobiomorus dormitor Lacépède (Gobiidae: Perciformes). Cytologia 50:663–669
Molina WF (2005) Intraspecific karyotypical diversity in brackish water fishes of the Eleotridae family (Pisces, Perciformes). Cytologia 70:39–45
Molina WF, Alves DEO, Araújo WC, Martinez PA, Silva MFM, Costa GWWF (2010) Performance of human immunostimulating agents in the improvement of fish cytogenetic preparations. Genet Mol Res 9:1807–1814
Molina WF, Martinez PA, Bertollo LAC, Bidau CJ (2014a) Evidence for meiotic drive as an explanation for karyotype changes in fishes. Mar Genomics 15:29–34
Molina WF, Martinez PA, Bertollo LAC, Bidau CJ (2014b) Preferential accumulation of sex and Bs chromosomes in biarmed karyotypes by meiotic drive and rates of chromosomal changes in fishes. An Acad Bras Ciênc 86:1801–1812
Motta-Neto CC, Cioffi MB, Costa GWWF, Amorim KDJ, Bertollo LAC, Artoni RF, Molina WF (2019) Overview on karyotype stasis in Atlantic grunts (Eupercaria, Haemulidae) and the evolutionary extensions for other marine fish groups. Front Mar Sci 6:628
Muus BJ, Nielsen JG (1999) Sea fish. Scandinavian Fishing Year Book, Hedehusene, p 340
Nakashima Y, Kuwamura T, Yogo Y (1996) Both-ways sex change in monogamous coral gobies, Gobiodon spp. Environ Biol Fishes 3:281–288
Nelson JS, Grande TC, Wilson MVH (2016) Fishes of the world, 5th edn. Wiley, Hoboken, p 752
Nishikawa S, Amaoka K, Nakanishi K (1974) A comparative study of chromosomes of twelve species of gobioid fishes in Japan. Jpn J Ichthyol 21:61–71
Ocalewicz K, Sapota MR (2011) Cytogenetic characteristics of the round goby Neogobius melanostomus (Pallas, 1814) (Teleostei: Gobiidae: Benthophilinae). Mar Biol Res 7:195–201
Oliveira C, Almeida-Toledo LF (2006) Evidence of an XX/XY sex chromosome system in the fish Dormitator maculatus (Teleostei, Eleotrididae). Genet Mol Biol 4:635–655
Oliveira EJ, Pádua JG, Zucchi MI, Vencovsky R, Vieira MLC (2006) Origin, evolution and genome distribution of microsatellites. Genet Mol Biol 29:294–307
Oto Y, Nakamura M, Murakami H, Masuda R (2017) Inconsistency between salinity preference and habitat salinity in euryhaline gobiid fishes in the Isazu River, northern Kyoto Prefecture. J Ethol 35:203–211
Patzner RA, Tassell JLV, Kovacic M, Kapoor BG (2012) The biology of gobies. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, New York
Pearse DE, Miller MR, Abadía-Cardoso A, Garza JC (2014) Rapid parallel evolution of standing variation in a single, complex, genomic region is associated with life history in steelhead/rainbow trout. Proc R Soc B 281:20140012
Pendás AM, Morán P, García-Vázquez E (1994) Organization and chromosomal location of the major histone cluster in brown trout, Atlantic salmon and rainbow trout. Chromosoma 103:147–152
Pezold F (1984) Evidence for multiple sex chromosomes in the freshwater goby, Gobionellus shufeldti (Pisces: Gobiidae). Copeia 1984:235–238
Prazdnikov DV, Vasil’ev VP, Vasil’eva ED (2013) Polymorphism and interpopulation variability of karyotype of Caspian bighead goby Neogobius gorlap (Gobiidae, Perciformes). J Ichthyol 53:425–430
Rocha LA, Robertson DR, Rocha CR, Van-Tassell JL, Craig MT, Bowen BW (2005) Recent invasion of the tropical Atlantic by an Indo-Pacific coral reef fish. Mol Ecol 14:3921–3928
Ruber L, Vantassell JL, Zardoya R (2003) Rapid speciation and ecological divergence in the American seven-spined gobies (Gobiidae, Gobiosomatini) inferred from a molecular phylogeny. Evolution 57:1584–1598
Schweizer D (1976) Reverse fluorescent chromosome banding with chromomycin and DAPI. Chromosome 58:307–224
Skóra K, Olenin S, Gollasch S (1999) Neogobius melanostomus (Pallas, 1811) In: Gollasch S, Michin D, Rosenthal H, Voight M (eds) Exotics across the ocean. Case histories on introduced species: their general biology, distribution, range expansion and impact: prepared by members of the European Union Concerted Action on testing monitoring systems for risk assessment of harmful introductions by ships to European waters (MAS-CT-97-0111), Department of Fishery Biology, Institute for Marine Science, University of Kiel, Germany, pp 69–73
Sumner AT (1972) A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp Cell Res 75:304–306
Suzuki T (1996) Hypseleotris cyprinoides. In: Fisheries Agency of Japan (ed) Basic data on rare Japanese wild aquatic species. (III). Nihonsuisanshigenhogokyokai, Tokyo, pp 215–221.
Suzuki T, Shibukawa K, Senou H, Chen I (2015) Redescription of Rhinogobius similis Gill 1859 (Gobiidae: Gobionellinae), the type species of the genus Rhinogobius Gill 1859, with designation of the neotype. Ichthyol Res 63:227–238
Thacker CE (2003) Molecular phylogeny of the gobioid fishes (Teleostei: Perciformes: Gobioidei). Mol Phylogenet Evol 26:354–368
Thacker CE (2009) Phylogeny of Gobioidei and placement within Acanthomorpha, with a new classification and investigation of diversification and character evolution. Copeia 2009:93–104
Thode G, Martinez G, Ruiz JL, Lopez JR (1988) A complex chromosomal polymorphism in Gobius fallax (Gobiidae, Perciformes). Genetica 76:65–71
Uribe-Alcocer M, Diaz-Jaimes P (1996) Chromosome complements of Gobionellus microdon and Eleotris picta collected in México. J Fish Biol 48:796–798
Uribe-Alcocer M, Ramirez-Escamilla A (1989) Comparacion citogenetica entre las especies del genero Dormitator (Pisces: Gobiidae). An Inst Cienc del Mary Limnol Univ Nal Auton México 16:75–80
Uribe-Alcocer M, Espinosa JA, Padilla AT, Pérez AC (1983) Los cromosomas de Dormitator latifrons (Pisces: Gobiidae). An Inst Cienc del Mary Limnol Univ Nal Auton México 10:23–30
Vasilev VP, Grigoryan KA (1994) Chromosome polymorphism and karyological relationships in the group of gobies Neogobius cephalarges Pallas-Neogobius platyrostris Pallas (Gobiidae). Russ J Genet 30:1251–1259
Webb CJ (1986) Karyology of the Indo-Pacific Parioglossus raoi (Herre) (Teleostei: Gobioidei) from Fiji. Mar Freshwater Res 37:347–351
Wellenreuther M, Bernatchez L (2018) Eco-evolutionary genomics of chromosomal inversions. Trends Ecol Evol 33:427–440
White TJ, Bruns TD, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols, a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 315–322
Xu D, Molina WF, Yano CF, Zhang Y, De OEA, Lou B, Cioffi MB (2017) Comparative cytogenetics in three sciaenid species (Teleostei, Perciformes): evidence of interspecific chromosomal diversification. Mol Cytogenet 10:37
Yu X, Zhou T, Li K, Zhou M (1987) On the karyosystematics of cyprinid fishes and a summary of fish chromosome studies in China. Genetica 72:225–235
Acknowledgements
The authors thank to the ICMBio/SISBIO (#19135-4) for the authorization in collecting specimens. We are also grateful to Dr. José Garcia Júnior for the taxonomic identification of specimens utilized in the study. This work was supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Cient.ico e Tecnol.gico (CNPq) [#442664/2015-0; #442626/2019-3].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SASS: conceptualization, methodology, writing- original draft preparation, data curation. WFM: conceptualization, methodology, writing- original draft preparation, funding acquisition, project administration, writing—reviewing and editing. GWWFC: investigation, validation. PAL-F, CCM-N: supervision, visualization. MBC, LACB: writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Animal and human rights statement
The experimental work fulfilled all ethical guidelines regarding the handling of specimens. The experiments followed ethical and anesthesia conducts in accordance with the Ethics Committee on the Use of Animals (#044/2015) at the Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte (UFRN). The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Edited by Jiamei Li.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva, S.A.S., de Lima-Filho, P.A., da Motta-Neto, C.C. et al. High chromosomal evolutionary dynamics in sleeper gobies (Eleotridae) and notes on disruptive biological factors in Gobiiformes karyotypes (Osteichthyes, Teleostei). Mar Life Sci Technol 3, 293–302 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42995-020-00084-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42995-020-00084-6