Abstract
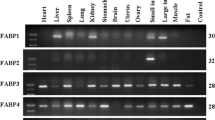
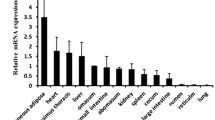
Fatty acid binding protein 3 (FABP3) is a member of the FABP family which bind fatty acids and have an important role in fatty acid metabolism. A large number of studies have shown that the genetic polymorphisms of FABP3 are positively correlated with intramuscular fat (IMF) content in domestic animals, however, the function and transcriptional characteristics of FABP3 in cattle remain unclear. Real-time PCR analysis revealed that bovine FABP3 was highly expressed in cardiac tissue. The 5′-regulatory region of bovine FABP3 was cloned and its transcription initiation sites were identified. Sequence analysis showed that many transcriptional factor binding sites including TATA-box and CCAAT-box were present on the 5′-flanking region of bovine FABP3, and four CpG islands were found on nucleotides from −891 to +118. Seven serial deletion constructs of the 5′-regulatory region evaluated in dual-luciferase reporter assay indicated that its core promoter was 384 base pairs upstream from the transcription initiation site. The transcriptional factor binding sites RXRα, KLF15, CREB and Sp1 were conserved in the core promoter of cattle, sheep, pigs and dogs. These results provide further understanding of the function and regulation mechanism of bovine FABP3.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chmurzynska A (2006) The multigene family of fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs): function, structure and polymorphism. J Appl Genet 47(1):39–48. doi:10.1007/BF03194597
Kusudo T, Hashida Y, Ando F, Shimokata H, Yamashita H (2015) Asp3Gly polymorphism affects fatty acid-binding protein 3 intracellular stability and subcellular localization. FEBS Lett. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2015.07.007
Furuhashi M, Hotamisligil GS (2008) Fatty acid-binding proteins: role in metabolic diseases and potential as drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7(6):489–503. doi:10.1038/nrd2589
Ishimura S, Furuhashi M, Watanabe Y, Hoshina K, Fuseya T, Mita T, Okazaki Y, Koyama M, Tanaka M, Akasaka H, Ohnishi H, Yoshida H, Saitoh S, Miura T (2013) Circulating levels of fatty acid-binding protein family and metabolic phenotype in the general population. PLoS One 8(11):e81318. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0081318
Binas B, Danneberg H, McWhir J, Mullins L, Clark AJ (1999) Requirement for the heart-type fatty acid binding protein in cardiac fatty acid utilization. FASEB J 13(8):805–812
Zhang J, Rickers-Haunerland J, Dawe I, Haunerland NH (1999) Structure and chromosomal location of the rat gene encoding the heart fatty acid-binding protein. Eur J Biochem 266(2):347–351
Vergnes L, Chin R, Young SG, Reue K (2011) Heart-type fatty acid-binding protein is essential for efficient brown adipose tissue fatty acid oxidation and cold tolerance. J Biol Chem 286(1):380–390. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.184754
Yi B, Wang J, Wang S, Yuan D, Sun J, Li Z, Mao Y, Hou Q, Liu W (2014) Overexpression of Banna mini-pig inbred line fatty acid binding protein 3 promotes adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Cell Biol Int 38(8):918–923. doi:10.1002/cbin.10285
Gerbens F, van Erp AJ, Harders FL, Verburg FJ, Meuwissen TH, Veerkamp JH, te Pas MF (1999) Effect of genetic variants of the heart fatty acid-binding protein gene on intramuscular fat and performance traits in pigs. J Anim Sci 77(4):846–852
Gerbens F, Verburg FJ, Van Moerkerk HT, Engel B, Buist W, Veerkamp JH, te Pas MF (2001) Associations of heart and adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein gene expression with intramuscular fat content in pigs. J Anim Sci 79(2):347–354
Li X, Kim SW, Choi JS, Lee YM, Lee CK, Choi BH, Kim TH, Choi YI, Kim JJ, Kim KS (2010) Investigation of porcine FABP3 and LEPR gene polymorphisms and mRNA expression for variation in intramuscular fat content. Mol Biol Rep 37(8):3931–3939. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-0050-1
Serao NV, Veroneze R, Ribeiro AM, Verardo LL, Neto JB, Gasparino E, Campos CF, Lopes PS, Guimaraes SE (2011) Candidate gene expression and intramuscular fat content in pigs. J Anim Breed Genet 128(1):28–34. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0388.2010.00887.x
Cho KH, Kim MJ, Jeon GJ, Chung HY (2011) Association of genetic variants for FABP3 gene with back fat thickness and intramuscular fat content in pig. Mol Biol Rep 38(3):2161–2166. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-0344-3
Tyra M, Ropka-Molik K, Terman A, Piorkowska K, Oczkowicz M, Bereta A (2013) Association between subcutaneous and intramuscular fat content in porcine ham and loin depending on age, breed and FABP3 and LEPR genes transcript abundance. Mol Biol Rep 40(3):2301–2308. doi:10.1007/s11033-012-2311-7
Hong J, Kim D, Cho K, Sa S, Choi S, Kim Y, Park J, Schmidt GS, Davis ME, Chung H (2015) Effects of genetic variants for the swine FABP3, HMGA1, MC4R, IGF2, and FABP4 genes on fatty acid composition. Meat Sci 110:46–51. doi:10.1016/j.meatsci.2015.06.011
Sweeney T, O’Halloran AM, Hamill RM, Davey GC, Gil M, Southwood OI, Ryan MT (2015) Novel variation in the FABP3 promoter and its association with fatness traits in pigs. Meat Sci 100:32–40. doi:10.1016/j.meatsci.2014.09.014
Wang L, Li L, Jiang J, Wang Y, Zhong T, Chen Y, Wang Y, Zhang H (2015) Molecular characterization and different expression patterns of the FABP gene family during goat skeletal muscle development. Mol Biol Rep 42(1):201–207. doi:10.1007/s11033-014-3759-4
Lim D, Chai HH, Lee SH, Cho YM, Choi JW, Kim NK (2015) Gene expression patterns associated with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) Signaling in the longissimus dorsi of hanwoo (Korean Cattle). Asian-Aust J Anim Sci 28(8):1075–1083. doi:10.5713/ajas.14.0811
Gerbens F, Rettenberger G, Lenstra JA, Veerkamp JH, te Pas MF (1997) Characterization, chromosomal localization, and genetic variation of the porcine heart fatty acid-binding protein gene. Mamm genome 8(5):328–332
Kawabe K, Saegusa H, Seto K, Urabe H, Motojima K (2005) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha and its response element are required but not sufficient for transcriptional activation of the mouse heart-type fatty acid binding protein gene. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37(7):1534–1546. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2005.02.011
Shan TZ, Ren Y, Wu T, Liu CX, Wang YZ (2009) Regulatory role of Sirt1 on the gene expression of fatty acid-binding protein 3 in cultured porcine adipocytes. J Cell Biochem 107(5):984–991. doi:10.1002/jcb.22203
Holst D, Luquet S, Nogueira V, Kristiansen K, Leverve X, Grimaldi PA (2003) Nutritional regulation and role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta in fatty acid catabolism in skeletal muscle. Biochim et Biophys Acta 1633(1):43–50
Mullenbach R, Lagoda PJ, Welter C (1989) An efficient salt-chloroform extraction of DNA from blood and tissues. Trends Genet 5(12):391
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23(21):2947–2948. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Li A, Chen Y, Zhao X, Niu Y, Cong P, Zhang Z, Chen W, Jiang W, Mo D (2010) Characterization and transcriptional regulation analysis of the porcine TNFAIP8L2 gene. Mol Genet Genom 284(3):185–195. doi:10.1007/s00438-010-0558-z
Li A, Zhao Z, Zhang Y, Fu C, Wang M, Zan L (2015) Tissue expression analysis, cloning, and characterization of the 5′-regulatory region of the bovine fatty acid binding protein 4 gene. J Anim Sci 93(11):5144–5152. doi:10.2527/jas.2015-9378
Wang H, Cheng G, Fu C, Wang H, Yang W, Wang H, Zan L (2014) Sequence analysis of bovine C/EBPdelta gene and its adipogenic effects on fibroblasts. Mol Biol Rep 41(1):251–257
Heuckeroth RO, Birkenmeier EH, Levin, Gordon JI (1987) Analysis of the tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and linkage relationships of a rodent gene encoding heart fatty acid binding protein. J Biol Chem 262(20):9709–9717
Hochheimer A, Tjian R (2003) Diversified transcription initiation complexes expand promoter selectivity and tissue-specific gene expression. Genes Dev 17(11):1309–1320. doi:10.1101/gad.1099903
Zhang Y, Kent JW 2nd, Lee A, Cerjak D, Ali O, Diasio R, Olivier M, Blangero J, Carless MA, Kissebah AH (2013) Fatty acid binding protein 3 (fabp3) is associated with insulin, lipids and cardiovascular phenotypes of the metabolic syndrome through epigenetic modifications in a Northern European family population. BMC Med Genom 6:9. doi:10.1186/1755-8794-6-9
Frith MC, Valen E, Krogh A, Hayashizaki Y, Carninci P, Sandelin A (2008) A code for transcription initiation in mammalian genomes. Genome Res 18(1):1–12. doi:10.1101/gr.6831208
Megraw M, Pereira F, Jensen ST, Ohler U, Hatzigeorgiou AG (2009) A transcription factor affinity-based code for mammalian transcription initiation. Genome Res 19(4):644–656. doi:10.1101/gr.085449.108
Lemkul JA, Lewis SN, Bassaganya-Riera J, Bevan DR (2015) Phosphorylation of PPARgamma affects the collective motions of the PPARgamma-RXRalpha-DNA complex. PLos One 10(5):e0123984. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0123984
Prosdocimo DA, Sabeh MK, Jain MK (2015) Kruppel-like factors in muscle health and disease. Trends Cardiovasc Med 25(4):278–287. doi:10.1016/j.tcm.2014.11.006
Prosdocimo DA, John JE, Zhang L, Efraim ES, Zhang R, Liao X, Jain MK (2015) KLF15 and PPARalpha cooperate to regulate cardiomyocyte lipid gene expression and oxidation. PPAR Res 2015:201625. doi:10.1155/2015/201625
Mori T, Sakaue H, Iguchi H, Gomi H, Okada Y, Takashima Y, Nakamura K, Nakamura T, Yamauchi T, Kubota N, Kadowaki T, Matsuki Y, Ogawa W, Hiramatsu R, Kasuga M (2005) Role of Kruppel-like factor 15 (KLF15) in transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis. J Biol Chem 280(13):12867–12875. doi:10.1074/jbc.M410515200
Huong PT, Soung NK, Jang JH, Cha-Molstad HJ, Sakchaisri K, Kim SO, Jang JM, Kim KE, Lee KS, Kwon YT, Erikson RL, Ahn JS, Kim BY (2013) Regulation of CEP131 gene expression by SP1. Gene 513(1):75–81. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2012.10.074
Deniaud E, Baguet J, Mathieu AL, Pages G, Marvel J, Leverrier Y (2006) Overexpression of Sp1 transcription factor induces apoptosis. Oncogene 25(53):7096–7105. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209696
Reusch JE, Colton LA, Klemm DJ (2000) CREB activation induces adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. Mol cell biol 20(3):1008–1020
Kim HB, Kim WH, Han KL, Park JH, Lee J, Yeo J, Jung MH (2010) cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB) positively regulates mouse adiponectin gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391(1):634–639. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.11.111
Ling F, Li J, Chen Y, Du H, Mei Y, Mo D, Wang C (2009) Cloning and characterization of the 5′-flanking region of the pig adiponectin gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 381(2):236–240. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.02.031
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31402042), the Technical Innovation Engineering Project of Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 2016KTCL02-15) and the Northwest A&F University Special Funds of Central Colleges Basic Scientific Research Operating Expenses (Grant Nos. 2014YB009 and 2452015296).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Anning Li and Lijuan Wu have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, A., Wu, L., Wang, X. et al. Tissue expression analysis, cloning and characterization of the 5′-regulatory region of the bovine FABP3 gene. Mol Biol Rep 43, 991–998 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-4026-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-4026-7