Abstract
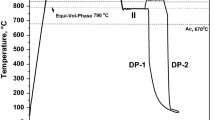
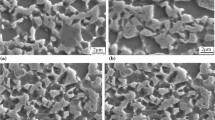
This study concerns influence of martensite morphology on the work-hardening behavior of high-strength ferrite–martensite dual-phase (DP) steel. A low-carbon microalloyed steel was subjected to intermediate quenching (IQ), step quenching (SQ), and intercritical annealing (IA) to develop different martensite morphologies, i.e., fine and fibrous, blocky and banded, and island types, respectively. Analyses of work-hardening behavior of the DP microstructures by differential Crussard–Jaoul technique have demonstrated three stages of work-hardening for IQ and IA samples, whereas the SQ sample revealed only two stages. Similar analyses by modified Crussard–Jaoul technique showed only two stages of work-hardening for all the samples. Among different treatments, IQ route has yielded the best combination of strength and ductility due to its superior work-hardening behavior. The influence of martensite morphology on nucleation and growth of microvoids/microcracks has been correlated with the observed tensile ductility.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Piplani RK, Raghavan V (1981) Steel India 4:1
Speich GR (1981) In: Kot RA, Bramfitt BL (eds) Fundamentals of dual phase steels. AIME, New York, p 1
Jiang Z, Lian J, Guan Z (1995) Mater Sci Eng A190:55
Davies RG (1979) Metall Trans A 10:113
Bag A, Ray KK, Dwarakadasa ES (1999) Metall Trans A 30:1193
Byun TS, Kim IS (1993) J Mater Sci 28:2923. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00354695
Koo JY, Young MJ, Thomos G (1980) Metall Trans A 11:852
Tomita Y (1990) J Mater Sci 25:5179. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00580148
Sankar S, Sangal S, Padmanabhan KA (2005) Mater Sci Technol 21:1152
Erdogan M (2002) J Mater Sci 37:3623. doi:https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016548922555
Hollomon JH (1945) Trans AIME 162:268
Crussard C (1953) Rev Metall 10:697
Jaoul B (1957) J Mech Phys Solids 5:95
Monteiro SN, Reed-Hill RE (1971) Met Trans 2:2947
Mamos LF, Matlock DK, Krauss G (1979) Metall Trans A 10:259
Samuel FH (1987) Mater Sci Eng 92:L1
Jha BK, Avtar R, Dwivedi VS, Ramaswamy V (1987) J Mater Sci Lett 6:891
Jiang Z, Jian L, Chen J (1992) Mater Sci Tech 8:1075
Ludwik P (1909) Element der Technolnischen Mechanick. Springer, Berlin, p 32
Swift HW (1952) J Mech Phys Solids 1:1
Kang S, Kwon H (1987) Metall Trans A 18:1587
Das P, Chattopadhyay PP, Bandyopadhyay NR (2003) J Met Mater Eng 84:84
Gural A, Tekeli S, Ando T (2006) J Mater Sci 41:7894. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0871-4
Chunling Z, Dayong C, Bo L, Tianchen Z, Yunchang F (2004) J Mater Sci 39:4393. doi:https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000033436.06575.aa
Soto R, Saikaly W, Bano X, Issartel C, Rigaut G, Charai A (1999) Acta Mater 47:3475
Wang ZG, Al SH (1999) ISIJ Int 39:747
Kim NJ, Thomas G (1981) Metall Trans A 12:483
Bayram A, Uguz A, Murat U (1999) Mater Charact 43:259
Umemoto M, Tsuchiya K, Liu ZG, Sugimoto S (2000) Metall Trans A 31:1785
Tomita Y, Okabayashi K (1985) Metall Trans A 16:73
Sarwar M, Priestner R (1996) J Mater Sci 31:2091. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00356631
Nam WJ, Bae CM (1999) J Mater Sci 34:5661. doi:https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004705705208
Ahmad E, Sarwar M, Manzoor T, Hussain N (2006) J Mater Sci 41:5417. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0266-6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, D., Chattopadhyay, P.P. Influence of martensite morphology on the work-hardening behavior of high strength ferrite–martensite dual-phase steel. J Mater Sci 44, 2957–2965 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3392-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3392-0